Cal.com (formerly Calendso)
The open-source Calendly successor.
Learn more »
Discussions
·
Website
·
Issues
·
Roadmap
About the Project
Scheduling infrastructure for absolutely everyone
The open source Calendly successor. You are in charge of your own data, workflow, and appearance.
Calendly and other scheduling tools are awesome. It made our lives massively easier. We're using it for business meetings, seminars, yoga classes, and even calls with our families. However, most tools are very limited in terms of control and customization.
That's where Cal.com comes in. Self-hosted or hosted by us. White-label by design. API-driven and ready to be deployed on your own domain. Full control of your events and data.
Recognition
Hacker News
<img style="width: 250px; height: 54px;" width="250" height="54" alt="Featured on Hacker News" src="https://hackernews-badge.vercel.app/api?id=34507672" />
<img style="width: 250px; height: 54px;" width="250" height="54" alt="Featured on Hacker News" src="https://hackernews-badge.vercel.app/api?id=26817795" />
Product Hunt
Built With
Contact us
Meet our sales team for any commercial inquiries.
Stay Up-to-Date
Cal.com officially launched as v.1.0 on the 15th of September 2021 and we've come a long way so far. Watch releases of this repository to be notified of future updates:
Getting Started
To get a local copy up and running, please follow these simple steps.
Prerequisites
Here is what you need to be able to run Cal.com.
- Node.js (Version: >=18.x)
- PostgreSQL (Version: >=13.x)
- Yarn (recommended)
If you want to enable any of the available integrations, you may want to obtain additional credentials for each one. More details on this can be found below under the integrations section.
Development
Setup
-
Clone the repo into a public GitHub repository (or fork https://github.com/calcom/cal.com/fork). If you plan to distribute the code, keep the source code public to comply with AGPLv3. To clone in a private repository, acquire a commercial license
git clone https://github.com/calcom/cal.com.gitIf you are on Windows, run the following command on
gitbashwith admin privileges:
>git clone -c core.symlinks=true https://github.com/calcom/cal.com.git
See docs for more details. -
Go to the project folder
cd cal.com -
Install packages with yarn
yarn -
Set up your
.envfile- Duplicate
.env.exampleto.env - Use
openssl rand -base64 32to generate a key and add it underNEXTAUTH_SECRETin the.envfile. - Use
openssl rand -base64 32to generate a key and add it underCALENDSO_ENCRYPTION_KEYin the.envfile.
- Duplicate
-
Setup Node If your Node version does not meet the project's requirements as instructed by the docs, "nvm" (Node Version Manager) allows using Node at the version required by the project:
nvm useYou first might need to install the specific version and then use it:
nvm install && nvm useYou can install nvm from here.
Quick start with yarn dx
- Requires Docker and Docker Compose to be installed
- Will start a local Postgres instance with a few test users - the credentials will be logged in the console
yarn dxDevelopment tip
Add NEXT_PUBLIC_LOGGER_LEVEL={level} to your .env file to control the logging verbosity for all tRPC queries and mutations.\
Where {level} can be one of the following:
0 for silly \
1 for trace \
2 for debug \
3 for info \
4 for warn \
5 for error \
6 for fatal
When you set NEXT_PUBLIC_LOGGER_LEVEL={level} in your .env file, it enables logging at that level and higher. Here's how it works:
The logger will include all logs that are at the specified level or higher. For example: \
- If you set
NEXT_PUBLIC_LOGGER_LEVEL=2, it will log from level 2 (debug) upwards, meaning levels 2 (debug), 3 (info), 4 (warn), 5 (error), and (fatal) will be logged. \ - If you set
NEXT_PUBLIC_LOGGER_LEVEL=3, it will log from level 3 (info) upwards, meaning levels 3 (info), 4 (warn), 5 (error), and 6 (fatal) will be logged, but level 2 (debug) and level 1 (trace) will be ignored. \
echo 'NEXT_PUBLIC_LOGGER_LEVEL=3' >> .envfor Logger level to be set at info, for example.
Gitpod Setup
-
Click the button below to open this project in Gitpod.
-
This will open a fully configured workspace in your browser with all the necessary dependencies already installed.
Manual setup
-
Configure environment variables in the
.envfile. Replace<user>,<pass>,<db-host>, and<db-port>with their applicable valuesDATABASE_URL='postgresql://<user>:<pass>@<db-host>:<db-port>'If you don't know how to configure the DATABASE_URL, then follow the steps here to create a quick local DB
1. [Download](https://www.postgresql.org/download/) and install postgres in your local (if you don't have it already). 2. Create your own local db by executing `createDB` 3. Now open your psql shell with the DB you created: `psql -h localhost -U postgres -d ` 4. Inside the psql shell execute `\conninfo`. And you will get the following info.  5. Now extract all the info and add it to your DATABASE_URL. The url would look something like this `postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5432/Your-DB-Name`. The port is configurable and does not have to be 5432. If you don't want to create a local DB. Then you can also consider using services like railway.app or render.
-
Copy and paste your
DATABASE_URLfrom.envto.env.appStore. -
Set up the database using the Prisma schema (found in
packages/prisma/schema.prisma)In a development environment, run:
yarn workspace @calcom/prisma db-migrateIn a production environment, run:
yarn workspace @calcom/prisma db-deploy -
Run mailhog to view emails sent during development
NOTE: Required when
E2E_TEST_MAILHOG_ENABLEDis "1"docker pull mailhog/mailhog docker run -d -p 8025:8025 -p 1025:1025 mailhog/mailhog -
Run (in development mode)
yarn dev
Setting up your first user
Approach 1
-
Open Prisma Studio to look at or modify the database content:
yarn db-studio -
Click on the
Usermodel to add a new user record. -
Fill out the fields
email,username,password, and setmetadatato empty{}(remembering to encrypt your password with BCrypt) and clickSave 1 Recordto create your first user.New users are set on a
TRIALplan by default. You might want to adjust this behavior to your needs in thepackages/prisma/schema.prismafile. -
Open a browser to http://localhost:3000 and login with your just created, first user.
Approach 2
Seed the local db by running
cd packages/prisma
yarn db-seedThe above command will populate the local db with dummy users.
E2E-Testing
Be sure to set the environment variable NEXTAUTH_URL to the correct value. If you are running locally, as the documentation within .env.example mentions, the value should be http://localhost:3000.
# In a terminal just run:
yarn test-e2e
# To open the last HTML report run:
yarn playwright show-report test-results/reports/playwright-html-reportResolving issues
E2E test browsers not installed
Run npx playwright install to download test browsers and resolve the error below when running yarn test-e2e:
Executable doesn't exist at /Users/alice/Library/Caches/ms-playwright/chromium-1048/chrome-mac/Chromium.app/Contents/MacOS/ChromiumUpgrading from earlier versions
-
Pull the current version:
git pull -
Check if dependencies got added/updated/removed
yarn -
Apply database migrations by running one of the following commands:
In a development environment, run:
yarn workspace @calcom/prisma db-migrate(This can clear your development database in some cases)
In a production environment, run:
yarn workspace @calcom/prisma db-deploy -
Check for
.envvariables changesyarn predev -
Start the server. In a development environment, just do:
yarn devFor a production build, run for example:
yarn build yarn start -
Enjoy the new version.
Deployment
Docker
The Docker configuration for Cal.com is an effort powered by people within the community.
If you want to contribute to the Docker repository, reply here.
The Docker configuration can be found in our docker repository.
Issues with Docker? Find your answer or open a new discussion here to ask the community.
Cal.com, Inc. does not provide official support for Docker, but we will accept fixes and documentation. Use at your own risk.
Railway
You can deploy Cal.com on Railway using the button above. The team at Railway also have a detailed blog post on deploying Cal.com on their platform.
Vercel
Currently Vercel Pro Plan is required to be able to Deploy this application with Vercel, due to limitations on the number of serverless functions on the free plan.
Render
Elestio
Roadmap
See the roadmap project for a list of proposed features (and known issues). You can change the view to see planned tagged releases.
License
Cal.com, Inc. is a commercial open source company, which means some parts of this open source repository require a commercial license. The concept is called "Open Core" where the core technology (99%) is fully open source, licensed under AGPLv3 and the last 1% is covered under a commercial license ("/ee" Enterprise Edition) which we believe is entirely relevant for larger organisations that require enterprise features. Enterprise features are built by the core engineering team of Cal.com, Inc. which is hired in full-time. Find their compensation on https://cal.com/open.
[!NOTE]
Our philosophy is simple, all "Singleplayer APIs" are open-source under AGPLv3. All commercial "Multiplayer APIs" are under a commercial license.
| AGPLv3 | EE | |
|---|---|---|
| Self-host for commercial purposes | ✅ | ✅ |
| Clone privately | ✅ | ✅ |
| Fork publicly | ✅ | ✅ |
| Requires CLA | ✅ | ✅ |
| Official Support | ❌ | ✅ |
| Derivative work privately | ❌ | ✅ |
| SSO | ❌ | ✅ |
| Admin Panel | ❌ | ✅ |
| Impersonation | ❌ | ✅ |
| Managed Event Types | ❌ | ✅ |
| Organizations | ❌ | ✅ |
| Payments | ❌ | ✅ |
| Platform | ❌ | ✅ |
| Teams | ❌ | ✅ |
| Users | ❌ | ✅ |
| Video | ❌ | ✅ |
| Workflows | ❌ | ✅ |
[!TIP] We work closely with the community and always invite feedback about what should be open and what is fine to be commercial. This list is not set and stone and we have moved things from commercial to open in the past. Please open a discussion if you feel like something is wrong.
Repo Activity
Contributing
Please see our contributing guide.
Good First Issues
We have a list of help wanted that contain small features and bugs which have a relatively limited scope. This is a great place to get started, gain experience, and get familiar with our contribution process.
Bounties
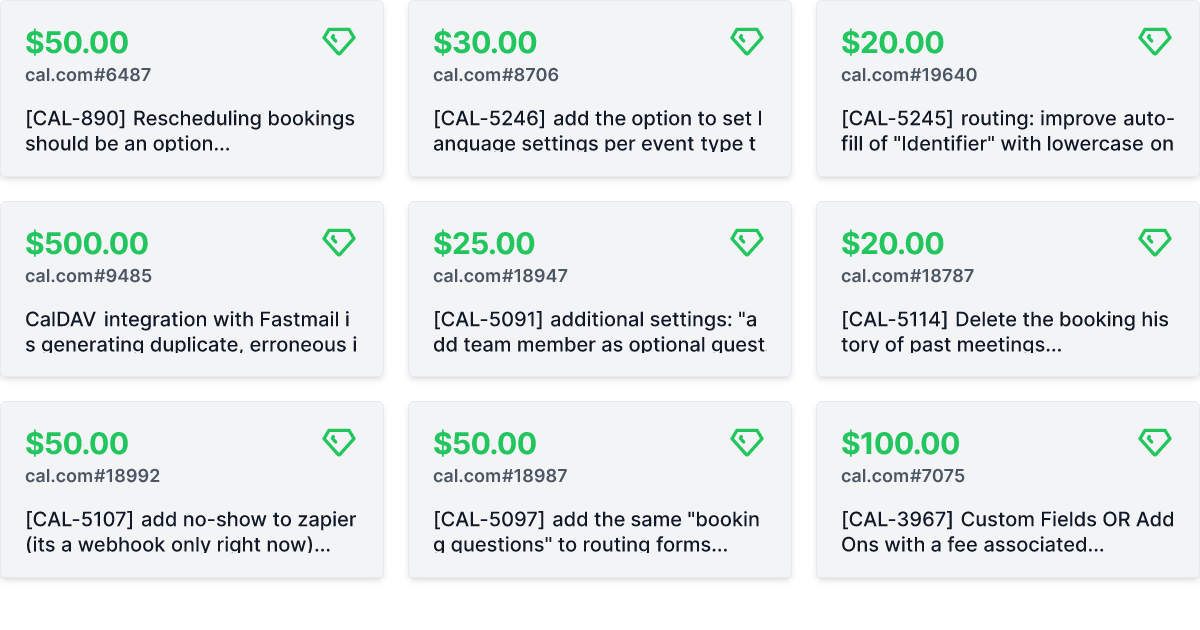
Contributors
Translations
Don't code but still want to contribute? Join our Discussions and join the #Translate channel and let us know what language you want to translate.



























Enabling Content Security Policy
- Set CSP_POLICY="non-strict" env variable, which enables Strict CSP except for unsafe-inline in style-src . If you have some custom changes in your instance, you might have to make some code change to make your instance CSP compatible. Right now it enables strict CSP only on login page and on other SSR pages it is enabled in Report only mode to detect possible issues. On, SSG pages it is still not supported.
Integrations
Obtaining the Google API Credentials
- Open Google API Console. If you don't have a project in your Google Cloud subscription, you'll need to create one before proceeding further. Under Dashboard pane, select Enable APIS and Services.
- In the search box, type calendar and select the Google Calendar API search result.
- Enable the selected API.
- Next, go to the OAuth consent screen from the side pane. Select the app type (Internal or External) and enter the basic app details on the first page.
- In the second page on Scopes, select Add or Remove Scopes. Search for Calendar.event and select the scope with scope value
.../auth/calendar.events,.../auth/calendar.readonlyand select Update. - In the third page (Test Users), add the Google account(s) you'll be using. Make sure the details are correct on the last page of the wizard and your consent screen will be configured.
- Now select Credentials from the side pane and then select Create Credentials. Select the OAuth Client ID option.
- Select Web Application as the Application Type.
- Under Authorized redirect URI's, select Add URI and then add the URI
<Cal.com URL>/api/integrations/googlecalendar/callbackand<Cal.com URL>/api/auth/callback/googlereplacing Cal.com URL with the URI at which your application runs. - The key will be created and you will be redirected back to the Credentials page. Select the newly generated client ID under OAuth 2.0 Client IDs.
- Select Download JSON. Copy the contents of this file and paste the entire JSON string in the
.envfile as the value forGOOGLE_API_CREDENTIALSkey.
Adding google calendar to Cal.com App Store
After adding Google credentials, you can now Google Calendar App to the app store. You can repopulate the App store by running
cd packages/prisma
yarn seed-app-storeYou will need to complete a few more steps to activate Google Calendar App. Make sure to complete section "Obtaining the Google API Credentials". After that do the following
- Add extra redirect URL
<Cal.com URL>/api/auth/callback/google - Under 'OAuth consent screen', click "PUBLISH APP"
Obtaining Microsoft Graph Client ID and Secret
- Open Azure App Registration and select New registration
- Name your application
- Set Who can use this application or access this API? to Accounts in any organizational directory (Any Azure AD directory - Multitenant)
- Set the Web redirect URI to
<Cal.com URL>/api/integrations/office365calendar/callbackreplacing Cal.com URL with the URI at which your application runs. - Use Application (client) ID as the MS_GRAPH_CLIENT_ID attribute value in .env
- Click Certificates & secrets create a new client secret and use the value as the MS_GRAPH_CLIENT_SECRET attribute
Obtaining Zoom Client ID and Secret
- Open Zoom Marketplace and sign in with your Zoom account.
- On the upper right, click "Develop" => "Build App".
- Select "General App" , click "Create".
- Name your App.
- Choose "User-managed app" for "Select how the app is managed".
- De-select the option to publish the app on the Zoom App Marketplace, if asked.
- Now copy the Client ID and Client Secret to your
.envfile into theZOOM_CLIENT_IDandZOOM_CLIENT_SECRETfields. - Set the "OAuth Redirect URL" under "OAuth Information" as
<Cal.com URL>/api/integrations/zoomvideo/callbackreplacing Cal.com URL with the URI at which your application runs. - Also add the redirect URL given above as an allow list URL and enable "Subdomain check". Make sure, it says "saved" below the form.
- You don't need to provide basic information about your app. Instead click on "Scopes" and then on "+ Add Scopes". On the left,
- click the category "Meeting" and check the scope
meeting:write:meeting. - click the category "User" and check the scope
user:read:settings.
- click the category "Meeting" and check the scope
- Click "Done".
- You're good to go. Now you can easily add your Zoom integration in the Cal.com settings.
Obtaining Daily API Credentials
- Visit our Daily.co Partnership Form and enter your information
- From within your dashboard, go to the developers tab.
- Copy your API key.
- Now paste the API key to your
.envfile into theDAILY_API_KEYfield in your.envfile. - If you have the Daily Scale Plan set the
DAILY_SCALE_PLANvariable totruein order to use features like video recording.
Obtaining Basecamp Client ID and Secret
- Visit the 37 Signals Integrations Dashboard and sign in.
- Register a new application by clicking the Register one now link.
- Fill in your company details.
- Select Basecamp 4 as the product to integrate with.
- Set the Redirect URL for OAuth
<Cal.com URL>/api/integrations/basecamp3/callbackreplacing Cal.com URL with the URI at which your application runs. - Click on done and copy the Client ID and secret into the
BASECAMP3_CLIENT_IDandBASECAMP3_CLIENT_SECRETfields. - Set the
BASECAMP3_CLIENT_SECRETenv variable to{your_domain} ({support_email}). For example,Cal.com (support@cal.com).
Obtaining HubSpot Client ID and Secret
- Open HubSpot Developer and sign into your account, or create a new one.
- From within the home of the Developer account page, go to "Manage apps".
- Click "Create app" button top right.
- Fill in any information you want in the "App info" tab
- Go to tab "Auth"
- Now copy the Client ID and Client Secret to your
.envfile into theHUBSPOT_CLIENT_IDandHUBSPOT_CLIENT_SECRETfields. - Set the Redirect URL for OAuth
<Cal.com URL>/api/integrations/hubspot/callbackreplacing Cal.com URL with the URI at which your application runs. - In the "Scopes" section at the bottom of the page, make sure you select "Read" and "Write" for scope called
crm.objects.contacts - Click the "Save" button at the bottom footer.
- You're good to go. Now you can see any booking in Cal.com created as a meeting in HubSpot for your contacts.
Obtaining Webex Client ID and Secret
Obtaining ZohoCRM Client ID and Secret
- Open Zoho API Console and sign into your account, or create a new one.
- From within the API console page, go to "Applications".
- Click "ADD CLIENT" button top right and select "Server-based Applications".
- Fill in any information you want in the "Client Details" tab
- Go to tab "Client Secret" tab.
- Now copy the Client ID and Client Secret to your
.envfile into theZOHOCRM_CLIENT_IDandZOHOCRM_CLIENT_SECRETfields. - Set the Redirect URL for OAuth
<Cal.com URL>/api/integrations/zohocrm/callbackreplacing Cal.com URL with the URI at which your application runs. - In the "Settings" section check the "Multi-DC" option if you wish to use the same OAuth credentials for all data centers.
- Click the "Save"/ "UPDATE" button at the bottom footer.
- You're good to go. Now you can easily add your ZohoCRM integration in the Cal.com settings.
Obtaining Zoho Calendar Client ID and Secret
Obtaining Zoho Bigin Client ID and Secret
Obtaining Pipedrive Client ID and Secret
Workflows
Setting up SendGrid for Email reminders
- Create a SendGrid account (https://signup.sendgrid.com/)
- Go to Settings -> API keys and create an API key
- Copy API key to your
.envfile into theSENDGRID_API_KEYfield - Go to Settings -> Sender Authentication and verify a single sender
- Copy the verified E-Mail to your
.envfile into theSENDGRID_EMAILfield - Add your custom sender name to the
.envfile into theNEXT_PUBLIC_SENDGRID_SENDER_NAMEfield (fallback is Cal.com)
Setting up Twilio for SMS reminders
- Create a Twilio account (https://twilio.com/try-twilio)
- Click ‘Get a Twilio phone number’
- Copy Account SID to your
.envfile into theTWILIO_SIDfield - Copy Auth Token to your
.envfile into theTWILIO_TOKENfield - Copy your Twilio phone number to your
.envfile into theTWILIO_PHONE_NUMBERfield - Add your own sender ID to the
.envfile into theNEXT_PUBLIC_SENDER_IDfield (fallback is Cal.com) - Create a messaging service (Develop -> Messaging -> Services)
- Choose any name for the messaging service
- Click 'Add Senders'
- Choose phone number as sender type
- Add the listed phone number
- Leave all other fields as they are
- Complete setup and click ‘View my new Messaging Service’
- Copy Messaging Service SID to your
.envfile into theTWILIO_MESSAGING_SIDfield - Create a verify service
- Copy Verify Service SID to your
.envfile into theTWILIO_VERIFY_SIDfield
License
Distributed under the AGPLv3 License. See LICENSE for more information.
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to these amazing projects which help power Cal.com:
Cal.com is an open startup and Jitsu (an open-source Segment alternative) helps us to track most of the usage metrics.

















