Domain Driven Design
DDD example focus on Core concept of DDD like
- Entities
- Aggregates
- Repository
- Value Objects
- ACL(Anti Corruption Layer)
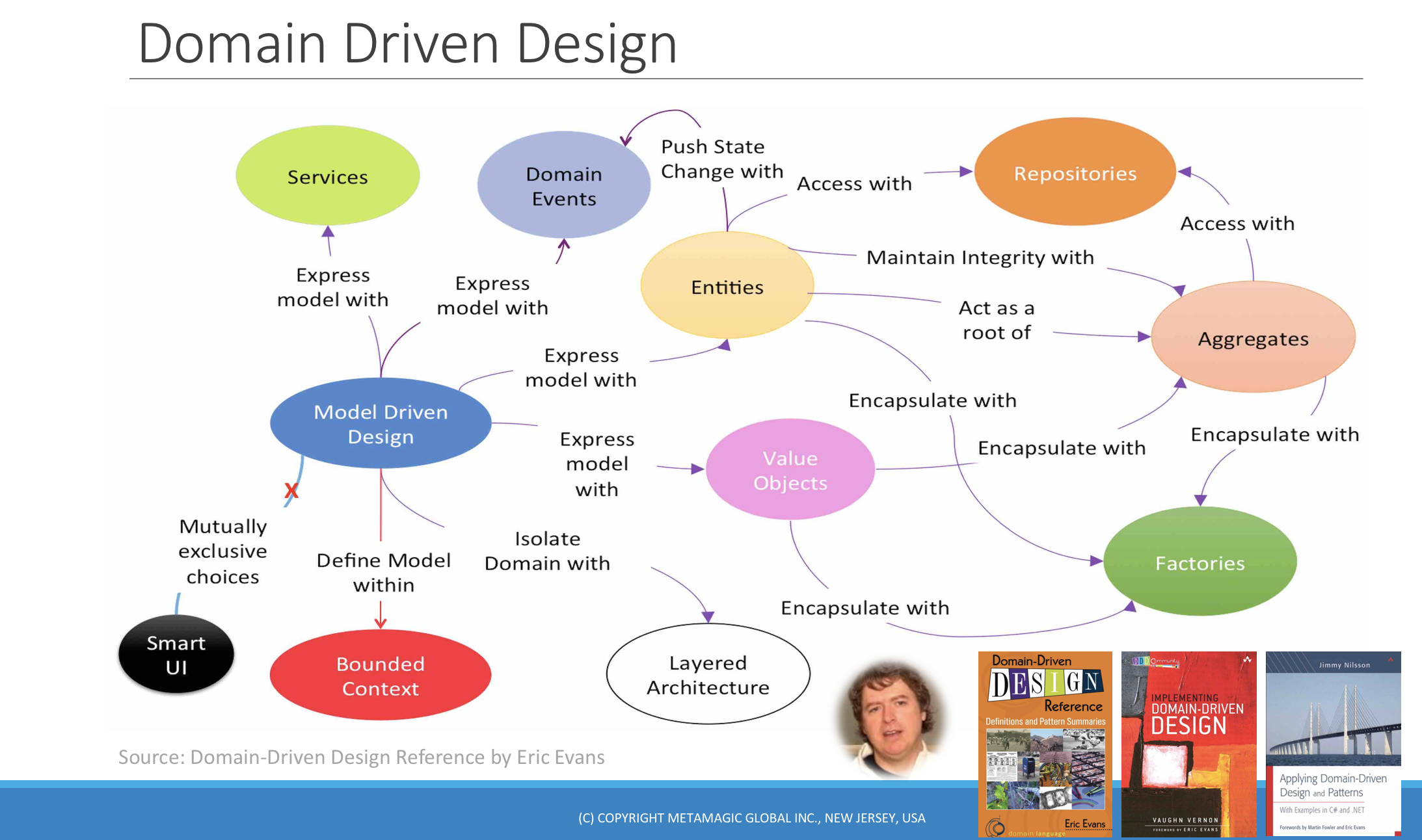
Entities
Entities are objects in the domain model that have a unique identity that does not change throughout the state changes of the software. Entities encapsulate both state and behavior. An example of entity could be a Order object that represents and maintains state about a specific order, and implements different operations (add items, add shipping address, add payment details etc) that can be carried out on that order.
Aggregates
A cluster of associated objects that are treated as a unit for the purpose of data changes. External references are restricted to one member of the AGGREGATE, designated as the root. A set of consistency rules applies within the AGGREGATE’S boundaries.
Repository
Repositories are responsible for retrieving and storing aggregate roots, typically using an Object/Relational Mapping (O/RM) framework.
Value objects
Value objects are objects in the domain model that are used to describe certain aspects of a domain. They do not have a unique identity and are immutable. An example of value object could be a Order Monetory Value.
Properties of value objects:
- Measures, quantity or describe the things in domain.
- Identity is based on composition of values.
- Immutable
- Compared using all values
- No Side affect
ACL(Anti Corruption Layer)
Implement a façade or adapter layer between different subsystems that don't share the same semantics. This layer translates requests that one subsystem makes to the other subsystem. Use this pattern to ensure that an application's design is not limited by dependencies on outside subsystems.
Issues and considerations
- The anti-corruption layer may add latency to calls made between the two systems.
- The anti-corruption layer adds an additional service that must be managed and maintained.
- Consider how your anti-corruption layer will scale.
- Consider whether you need more than one anti-corruption layer. You may want to decompose functionality into multiple services using different technologies or languages, or there may be other reasons to partition the anti-corruption layer.
- Consider how the anti-corruption layer will be managed in relation with your other applications or services. How will it be integrated into your monitoring, release, and configuration processes?
- Make sure transaction and data consistency are maintained and can be monitored.
- Consider whether the anti-corruption layer needs to handle all communication between different subsystems, or just a subset of features.
- If the anti-corruption layer is part of an application migration strategy, consider whether it will be permanent, or will be retired after all legacy functionality has been migrated.
Order Example focus on some of the key aspects of DDD such as. Aggregate, Entities, Value Object, Repository
License
Licensed under the Apache 2.0 License.
Enjoy!