RMP Navigation
This repository contains related code for the following three papers:
-
Neural Autonomous Navigation with Riemannian Motion Policy.
Xiangyun Meng, Nathan Ratliff, Yu Xiang and Dieter Fox. ICRA 2019
-
Scaling Local Control to Large Scale Topological Navigation.
Xiangyun Meng, Nathan Ratliff, Yu Xiang and Dieter Fox. ICRA 2020
-
Learning Composable Behavior Embeddings for Long-horizon Visual Navigation.
Xiangyun Meng, Yu Xiang and Dieter Fox. Robotics and Automation Letters 2021.
The base code is written for paper 1 and is also used by paper 2 and 3.
- For paper 2, please check out the subdirectory topological_nav.
- For paper 3, please check out the subdirectory cbe.
Neural Autonomous Navigation with Riemannian Motion Policy
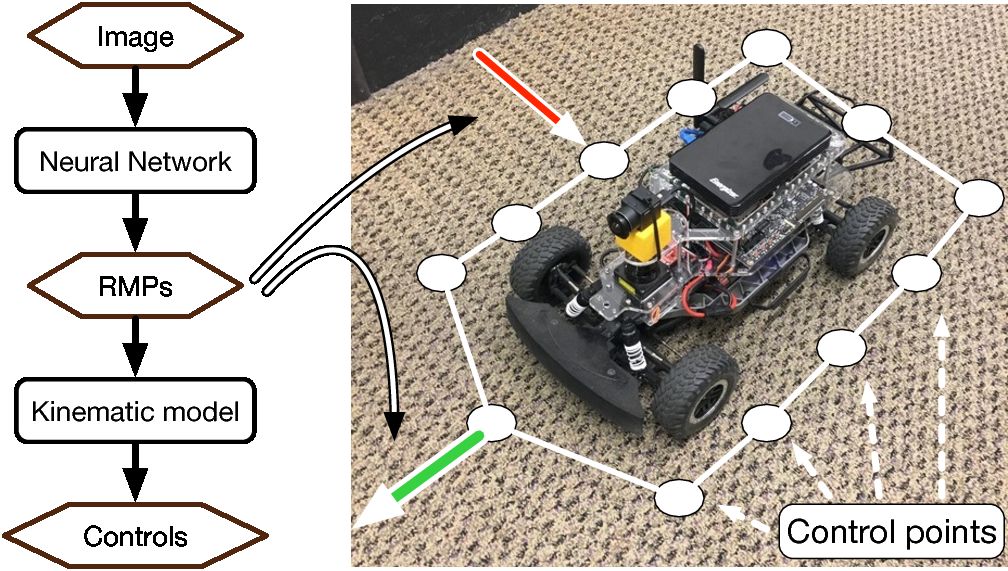
This code implements a local reactive controller using RMP. RMP is a joint representation of environmental geometry and robot dynamics. It produces complex local reactive behaviors that allows a robot to robustly navigate with the presence of obstacles. We also show that an image-based RMP controller can be learned with a neural network.
Click the image to see the video:
Dependencies
This code has been tested under Ubuntu 16.04.
python
python3 is required. This code is developed with python3.6 in an Anaconda environment.
pybind11
To improve efficiency, part of our code is written in C++. pybind11 is a tool to create python bindings of C++ code.
gibson
We use a modified version of gibson (mainly to speed things up). Since the compilation of gibson can be a daunting task, we provide a precompiled version that you can download directly from here.
The archive contains only the license-free environments. If you want to train with more diverse environments you need to contact the gibson authors to obtain additional environments.
range_libc
This library is used for fast raycasting (simulating a laser scanner). A copy is provided
under third_party if you clone with --recursive. Please follow the instructions provided
by the library to install its python binding into your chosen python environment.
Preparation
Clone the repository and cd to the project directory.
git clone --recursive https://github.com/xymeng/rmp_nav.gitSet up environment variables:
source set_envs.shInstall requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txt Additional requirements that you may already have:
-
pytorchandtorchvision. You may install via pip:pip install torch torchvision -
opencvYou may install via pip:pip install opencv-python -
wxPythonYou could install it via pip, but you may get compilation errors. There may exist a prebuilt pip wheel for your system.
Build and install range_libc. You may skip this step if you already have it
installed:
bash tools/build_rangelibc.shBuild python bindings of C++ code:
bash tools/compile_python_cpp_libs.shExtract the provided gibson archive:
tar xf gibson.tar.gz -C "${RMP_NAV_ROOT}/rmp_nav" --strip-components=1 gibson/gibsonExtract the provided models archive:
tar xf models.tar.gz -C "${RMP_NAV_ROOT}"Running the simulator
Set up environment variables:
source set_envs.shRun the simulation GUI:
python tools/run_sim.py --scene_id=space2You should see the simulation window appearing on the screen. As the first test, press the "Start" button on the top right corner. You should see a car running.

Running a neural agent
We provide an example neural agent gibson12v2_240fov_minirccar_z0228_fisheye64_metric. This
agent is able to avoid obstacles reactively with a monocular RGB camera. Since it requires images
as input, we need to launch the corresponding gibson environment first:
cd tools
python launch_sim_server_load_balancer_multi.py gibson_space2_gpu0_128.yaml 5000gibson_space2_gpu0_128.yaml contains configurations of which gibson environments to launch.
Here we launch the space2 environment, which corresponds to --scene_id=space2 when we
launch the GUI.
Tip: launch_sim_server_load_balancer_multi.py can launch multiple environments simultaneously
and load-balance between them. Take a look at gibson_2envs_gpu01_128.yaml and modify from
there.
After the simulator has launched, press the "Start" button. You should see a car running. On the left side it will show the live image stream.
Simulation options
Start and goal location
You may press the "Set start" button and then click on the map to set the start location. The coordinates of the location will be reflected in the text box next to the button. Alternatively you may directly type the coordinate "x, y" in the text box. Same thing applies to setting the goal location.
Initial heading
You may type in the text box to specify the initial heading of an agent (in degrees).
Max steps
If an agent has not reached the goal after this number of steps, simulation will terminate.
Step size
Time granularity for simulation. Usually you don't have to change this.
Agents
The simulator can run multiple agents simultaneously, which is useful for tuning. To enable an
agent, check the corresponding checkbox. Additional parameters of an agent can be specified by
pressing the "..." button on the left side. These parameters are passed into agent's constructors as
kwargs.
Add your own agent
The simulator supports user-defined agents with arbitrary 2D geometry and dynamics. agents.py
contains example agent definitions.
Take a look at rmp_nav/simulation/agent_factory_minirccar.py
and rmp_nav/simulation/agent_factory_rccar.py as examples of how
to register an agent. Registered agents automatically appear in the simulator. To hide an agent,
either comment out the code or name the constructor with "_" as the first character.