Social Relation Recognition TensorFlow
This repository contains the TensorFlow implementation of CVPR 2017 Paper A Domain Based Approach to Social Relation Recognition by Qianru Sun, Mario Fritz, and Bernt Schiele.
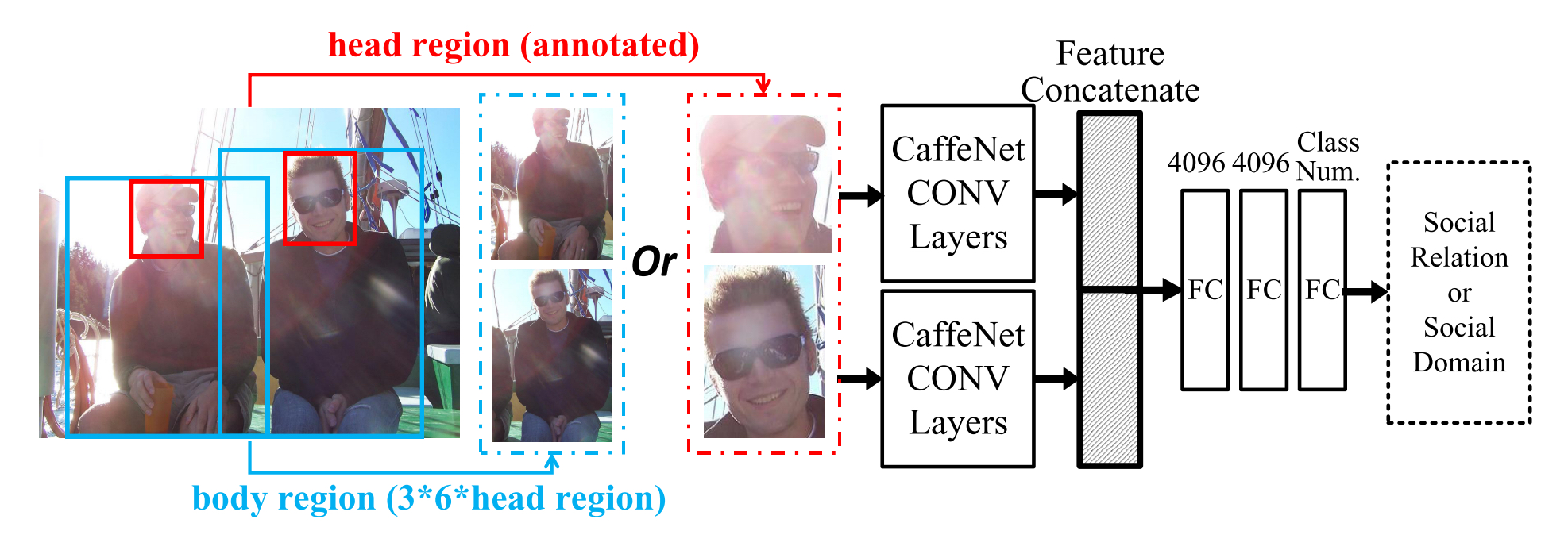
Summary:
Introduction
Social relations are the foundation of human daily life. Developing techniques to analyze such relations from visual data bears great potential to build machines that better understand us and are capable of interacting with us at a social level. Previous investigations have remained partial due to the overwhelming diversity and complexity of the topic and consequently have only focused on a handful of social relations. In this paper, we argue that the domain-based theory from social psychology is a great starting point to systematically approach this problem. The theory provides coverage of all aspects of social relations and equally is concrete and predictive about the visual attributes and behaviors defining the relations included in each domain. We provide the first dataset built on this holistic conceptualization of social life that is composed of a hierarchical label space of social domains and social relations. We also contribute the first models to recognize such domains and relations and find superior performance for attribute based features. Beyond the encouraging performance of the attribute based approach, we also find interpretable features that are in accordance with the predictions from social psychology literature. Beyond our findings, we believe that our contributions more tightly interleave visual recognition and social psychology theory that has the potential to complement the theoretical work in the area with empirical and data-driven models of social life.
Installation
In order to run this repo, we advise you to install python 2.7 and TensorFlow 1.3.0 with Anaconda.
You may download Anaconda and read the installation instruction on their official website: https://www.anaconda.com/download/
Then create a new environment and install tensorflow on it:
conda create --name tensorflow_1.3.0_gpu python=2.7
source activate tensorflow_1.3.0_gpu
pip install --ignore-installed --upgrade https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/tensorflow/linux/gpu/tensorflow_gpu-1.3.0-cp27-none-linux_x86_64.whlThen clone the repo install the requirements:
git clone https://github.com/Y2L/social-relation-tensorflow.git
cd social-relation-tensorflow-master
pip install scipy
pip install tqdmDataset
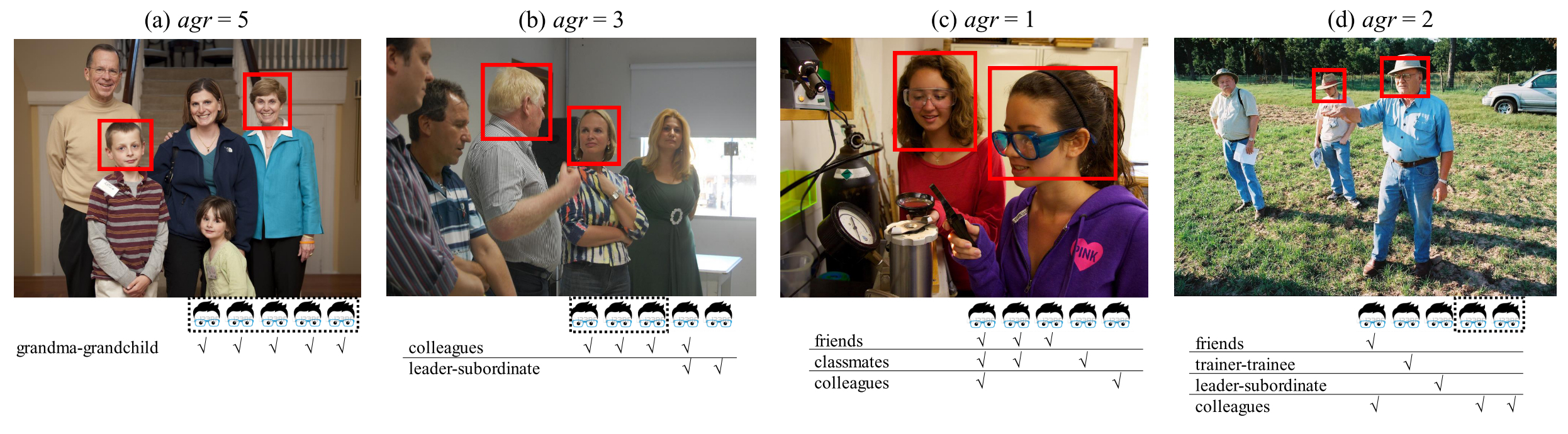
Figure: Person pair counting in terms of agreement agr.
Image resource
The image resource People in Photo Album (PIPA) was collected from Flickr photo albums for the task of person recognition. Photos from Flickr cover a wide range of social situations and are thus a good starting point for social relations. The same person often appears in different social scenarios and interacting with different people which make it ideal for our purpose. Identity information is used for selecting person pairs and defining train-validation-test splits. In summary, PIPA contains 37,107 photos with 63,188 instances of 2,356 identities. We extend the dataset by 26,915 person pair annotations for social relations.
Annotators
Annotating social relations might be subjective and ambiguous. One reason is that a person pair may have multiple plausible relations, as shown in the figure. Another reason is that the definition of the same social relation might differ, depending on the cultural backgrounds of the annotators. We selected 5 annotators from Asia, Africa, Europe and America and gave them detailed explanations and photo examples to help them keep a basic consistency.
Annotation protocol
- For each annotated person, the head bounding box and identity number are available.
- The label space is hierarchical, by assigning social domain labels that partition the data into 5 domain classes as well as assigning a label for the particular relation that two persons appear to be in.
- Annotators are asked to individually annotate all person pairs for which we present pairs of head bounding boxes.
- For each pair the annotator can either pick a relation from our list or, if they are too uncertain, can skip this pair. For example, two people wearing uniforms and working in the factory should be labeled as "colleagues", as the cues of action "working", clothing "uniforms" and environment "factory" are obvious. If the annotators are uncertain they are asked to indicate this by clicking "maybe" for this relation.
- Based on our pre-annotation phase, we allowed at most 3 relation labels per person pair.
Single body/face data and train-test-eval splits can be download here: data, splits
Usage
Train models:
python main.py --train=True --net_arch=vgg19 --double_stream_mode=True --epoch_num=10 --batch_size=10 --cls_num=16 --learning_rate=1e-4 --shuffle_dataset=True --img_list1=${DATA_LIST1} --img_list2=${DATA_LIST2}Run the test:
python main.py --train=False --net_arch=vgg19 --double_stream_mode=True --batch_size=10 --cls_num=16 --img_list1=${TEST_DATA_LIST1} --img_list2=${TEST_DATA_LIST2}Citation
Please cite our paper if it is helpful to your work:
@inproceedings{sun2017socialrelation,
title={A domain based approach to social relation recognition},
author={Sun, Qianru and Schiele, Bernt and Fritz, Mario},
booktitle={CVPR},
pages={21--26},
year={2017}
}

