- Error:
Error: Error 127 occurred creating conda environment r-reticulate - fix from: https://github.com/metrumresearchgroup/mrgsolve/issues/160#issuecomment-258655845
- First had to manually install Rtools (from: https://cran.r-project.org/bin/windows/Rtools/rtools40.html)
- put it in
/usr/local/bin/rtoolspath <- Sys.getenv("PATH") # original: # path <- c("C:\\RBuildTools\\3.3\\bin", "C:\\RBuildTools\\3.3\\gcc-4.6.3\\bin", path) # mine path <- c("C:\\usr\\local\bin\\rtools40", "C:\\usr\\local\bin\\rtools40\\ucrt64\\bin", path) path <- paste(path,collapse=";") Sys.setenv(PATH=path)
- put it in
Hydro modeling in tensorflow
Running a tensorflow on deq2
Tensorflow basics
Installation / Platform Info
Windows
.bash_profile) - use: https://tensorflow.rstudio.com/installation//usr/local/binPATH="$PATH:/usr/local/bin/Miniconda3/Scripts"conda config --set ssl_verify Falselibrary(tensorflow)library(reticulate)conda_create("r-reticulate", conda = "c:\\usr\\local\\bin\\Miniconda3")install_tensorflow(method = "conda", conda = "/usr/local/bin/Miniconda3")Image 1 Search for "Edit environment variables for your account".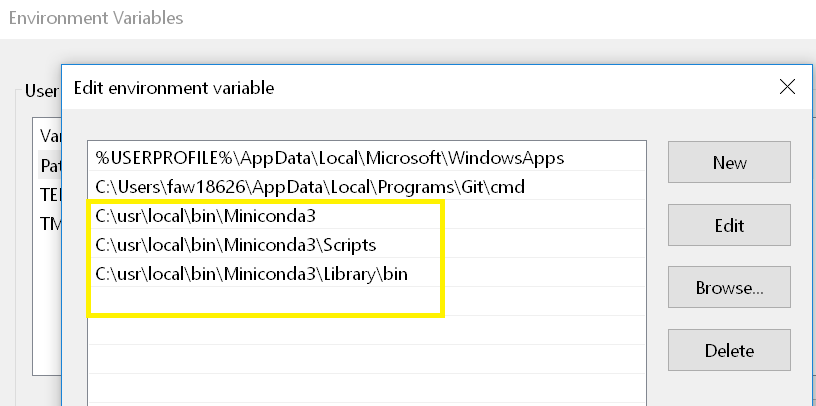
Linux
Install tensorflow on ubuntu 20.04 (used https://www.linode.com/docs/guides/how-to-install-tensorflow/)
sudo apt install python3.8-venpython3 -m venv --system-site-packages ./tfsource ./tf/bin/activatedeactivatepython -c 'import tensorflow as tf; print(tf.__version__)'...libcudart.so.11.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directorypythonimport os;os.environ["TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL"]="3";print("TensorFlow version:", tf.__version__)Command line linux testing
file-based testing
python test1.pytest1.pyCode 1: Command line testingimport tensorflow as tf import os os.environ["TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL"]="3"; print("TensorFlow version:", tf.version)
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D from tensorflow.keras import Model
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data() x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
Add a channels dimension
x_train = x_train[..., tf.newaxis].astype("float32") x_test = x_test[..., tf.newaxis].astype("float32")
train_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices( (x_train, y_train)).shuffle(10000).batch(32)
test_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test)).batch(32)
class MyModel(Model): def init(self): super(MyModel, self).init() self.conv1 = Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu') self.flatten = Flatten() self.d1 = Dense(128, activation='relu') self.d2 = Dense(10)
def call(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) x = self.flatten(x) x = self.d1(x) return self.d2(x)
Create an instance of the model
model = MyModel()
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
train_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='train_loss') train_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='train_accuracy')
test_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='test_loss') test_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy(name='test_accuracy')
@tf.function def train_step(images, labels): with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
training=True is only needed if there are layers with different
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables) optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model.trainable_variables))
train_loss(loss) train_accuracy(labels, predictions)
@tf.function def test_step(images, labels):
training=False is only needed if there are layers with different
behavior during training versus inference (e.g. Dropout).
predictions = model(images, training=False) t_loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)
test_loss(t_loss) test_accuracy(labels, predictions)
EPOCHS = 5
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
Reset the metrics at the start of the next epoch
train_loss.reset_states() train_accuracy.reset_states() test_loss.reset_states() test_accuracy.reset_states()
for images, labels in train_ds: train_step(images, labels)
for test_images, test_labels in test_ds: test_step(test_images, test_labels)
print( f'Epoch {epoch + 1}, ' f'Loss: {train_loss.result()}, ' f'Accuracy: {train_accuracy.result() 100}, ' f'Test Loss: {test_loss.result()}, ' f'Test Accuracy: {test_accuracy.result() 100}' )