我想在补充一下babel compiler是如何将Component类型,Function类型和HTML标签(React没有对它们进行区分,本质上都作为一类进行处理)转换成为ReactElement的。
首先来说说HTML标签:
例如:
<div class="somestylesheet">This is a html standard div tag</div>
先来看看ReactElement的createElement函数:
/**
* Create and return a new ReactElement of the given type.
* See https://reactjs.org/docs/react-api.html#createelement
*/
//这里type就对应的是"div",传入的是个字符串
//config就是该div所包含的属性
//children就是该div所包含的子标签
export function createElement(type, config, children) {
let propName;
// Reserved names are extracted
const props = {};
let key = null;
let ref = null;
let self = null;
let source = null;
if (config != null) {
if (hasValidRef(config)) {
ref = config.ref;
}
if (hasValidKey(config)) {
key = '' + config.key;
}
self = config.__self === undefined ? null : config.__self;
source = config.__source === undefined ? null : config.__source;
// Remaining properties are added to a new props object
for (propName in config) {
if (
hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) &&
!RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)
) {
props[propName] = config[propName];
}
}
}
// Children can be more than one argument, and those are transferred onto
// the newly allocated props object.
const childrenLength = arguments.length - 2;
if (childrenLength === 1) {
props.children = children;
} else if (childrenLength > 1) {
const childArray = Array(childrenLength);
for (let i = 0; i < childrenLength; i++) {
childArray[i] = arguments[i + 2];
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(childArray);
}
}
props.children = childArray;
}
// Resolve default props
if (type && type.defaultProps) {
const defaultProps = type.defaultProps;
for (propName in defaultProps) {
if (props[propName] === undefined) {
props[propName] = defaultProps[propName];
}
}
}
if (__DEV__) {
if (key || ref) {
const displayName =
typeof type === 'function'
? type.displayName || type.name || 'Unknown'
: type;
if (key) {
defineKeyPropWarningGetter(props, displayName);
}
if (ref) {
defineRefPropWarningGetter(props, displayName);
}
}
}
return ReactElement(
type,
key,
ref,
self,
source,
ReactCurrentOwner.current,
props,
);
}
//可见在执行ReactDOM.render()之前,先要createElement
function createElementWithValidation(type, props, children) {
//判断传入的元素类型是否有效
var validType = isValidElementType(type); // We warn in this case but don't throw. We expect the element creation to
// succeed and there will likely be errors in render.
if (!validType) {
var info = '';
if (type === undefined || typeof type === 'object' && type !== null && Object.keys(type).length === 0) {
info += ' You likely forgot to export your component from the file ' + "it's defined in, or you might have mixed up default and named imports.";
}
var sourceInfo = getSourceInfoErrorAddendum(props);
if (sourceInfo) {
info += sourceInfo;
} else {
info += getDeclarationErrorAddendum();
}
var typeString = void 0;
if (type === null) {
typeString = 'null';
} else if (Array.isArray(type)) {
typeString = 'array';
} else if (type !== undefined && type.$$typeof === REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE) {
typeString = '<' + (getComponentName(type.type) || 'Unknown') + ' />';
info = ' Did you accidentally export a JSX literal instead of a component?';
} else {
typeString = typeof type;
}
warning$1(false, 'React.createElement: type is invalid -- expected a string (for ' + 'built-in components) or a class/function (for composite ' + 'components) but got: %s.%s', typeString, info);
}
//这里用到了js function的apply方法,不知道怎么用的话请看这篇[教程]
(https://www.cnblogs.com/coco1s/p/4833199.html)
// 这里this跟进去看是个React对象(为什么,我还没想明白,希望有知道的大神能解释一下,也就是createElement这个函数执行的上下文是在React对象中
var element = createElement.apply(this, arguments); // The result can be nullish if a mock or a custom function is used.
// TODO: Drop this when these are no longer allowed as the type argument.
if (element == null) {
return element;
} // Skip key warning if the type isn't valid since our key validation logic
// doesn't expect a non-string/function type and can throw confusing errors.
// We don't want exception behavior to differ between dev and prod.
// (Rendering will throw with a helpful message and as soon as the type is
// fixed, the key warnings will appear.)
if (validType) {
for (var i = 2; i < arguments.length; i++) {
validateChildKeys(arguments[i], type);
}
}
if (type === REACT_FRAGMENT_TYPE) {
validateFragmentProps(element);
} else {
validatePropTypes(element);
}
return element;
}
如果元素类型有效,则调用:
function createElement(type, config, children) {
var propName = void 0; // Reserved names are extracted
var props = {};
var key = null;
var ref = null;
var self = null;
var source = null;
if (config != null) {
if (hasValidRef(config)) {
ref = config.ref;
}
if (hasValidKey(config)) {
key = '' + config.key;
}
self = config.__self === undefined ? null : config.__self;
source = config.__source === undefined ? null : config.__source; // Remaining properties are added to a new props object
for (propName in config) {
if (hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) && !RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)) {
props[propName] = config[propName];
}
}
} // Children can be more than one argument, and those are transferred onto
// the newly allocated props object.
var childrenLength = arguments.length - 2;
if (childrenLength === 1) {
props.children = children;
} else if (childrenLength > 1) {
var childArray = Array(childrenLength);
for (var i = 0; i < childrenLength; i++) {
childArray[i] = arguments[i + 2];
}
{
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(childArray);
}
}
props.children = childArray;
} // Resolve default props
if (type && type.defaultProps) {
var defaultProps = type.defaultProps;
for (propName in defaultProps) {
if (props[propName] === undefined) {
props[propName] = defaultProps[propName];
}
}
}
{
if (key || ref) {
var displayName = typeof type === 'function' ? type.displayName || type.name || 'Unknown' : type;
if (key) {
defineKeyPropWarningGetter(props, displayName);
}
if (ref) {
defineRefPropWarningGetter(props, displayName);
}
}
}
return ReactElement(type, key, ref, self, source, ReactCurrentOwner.current, props);
}
render: function render(element, container, callback) {
//判断container是否为合法容器
!isValidContainer(container) ? invariant(false, 'Target container is not a DOM element.') : void 0;
{
!!container._reactHasBeenPassedToCreateRootDEV ? warningWithoutStack$1(false, 'You are calling ReactDOM.render() on a container that was previously ' + 'passed to ReactDOM.%s(). This is not supported. ' + 'Did you mean to call root.render(element)?', enableStableConcurrentModeAPIs ? 'createRoot' : 'unstable_createRoot') : void 0;
}
return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(null, element, container, false, callback);
},
继续看:
function legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(parentComponent, children, container, forceHydrate, callback) {
{
topLevelUpdateWarnings(container);
} // TODO: Without `any` type, Flow says "Property cannot be accessed on any
// member of intersection type." Whyyyyyy.
var root = container._reactRootContainer;
if (!root) {
// Initial mount,
// 如果reactRootContainer不存在,那么创建一个,其实是创建了一个FiberNode
root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(container, forceHydrate);
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
var originalCallback = callback;
callback = function callback() {
var instance = getPublicRootInstance(root._internalRoot);
originalCallback.call(instance);
};
} // Initial mount should not be batched.
unbatchedUpdates(function () {
if (parentComponent != null) {
root.legacy_renderSubtreeIntoContainer(parentComponent, children, callback);
} else {
root.render(children, callback);
}
});
} else {
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
var _originalCallback = callback;
callback = function callback() {
var instance = getPublicRootInstance(root._internalRoot);
_originalCallback.call(instance);
};
} // Update
if (parentComponent != null) {
root.legacy_renderSubtreeIntoContainer(parentComponent, children, callback);
} else {
root.render(children, callback);
}
}
return getPublicRootInstance(root._internalRoot);
}
这篇文章已经把Component和Element 解释的很清楚了: https://github.com/creeperyang/blog/issues/30
我想在补充一下babel compiler是如何将Component类型,Function类型和HTML标签(React没有对它们进行区分,本质上都作为一类进行处理)转换成为ReactElement的。 首先来说说HTML标签: 例如:
<div class="somestylesheet">This is a html standard div tag</div>先来看看ReactElement的createElement函数:这里我们用chrome跟下源码(我用的是React Developer Tools,是chrome的一个插件,具体用法可以参考:这里。 示例程序在Repo.
在这里加断点: 点击图中的红框中的箭头,跳到下一个函数调用,来到下面这个函数:
点击图中的红框中的箭头,跳到下一个函数调用,来到下面这个函数:
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, document.getElementById('root'));运行之后的Call Stack信息:如果元素类型有效,则调用:
至此,App元素创建完毕,见下图: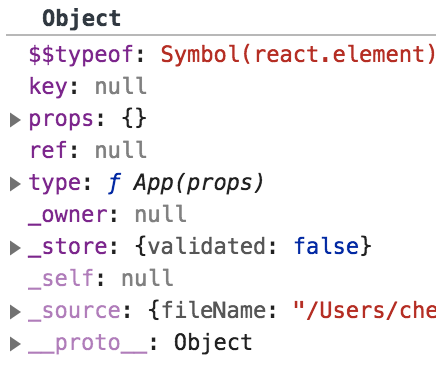
继续下一个函数调用,来到了这里,看来要对App元素进行渲染了,这里并非真实浏览器渲染,而是加入到virtual DOM里面(真的是这样吗?带着这个问题,继续看):
继续看:
legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer函数最终调用的是new了一个FiberNode, react-fiber的具体内容可参考这里
可以看到FiberNode里面有child return sibling三个属性,相当从一个FiberNode 可以找到它的子节点,父节点和兄弟节点。
看了这么多,是不是有点乱?没关系,先小结一下: React的入口是ReactDom.render(element, container, callback), render 之前,babel compiler 会调用createElement函数,将Component | Function 和HTML tag转换成一个ReactElement Object。 然后根据element 和 container 创建ReactRoot对象其中包含了FiberNode节点。然后调用ReactRoot.render函数,然后通过reconciller 进行调度,最终调用真实的renderer进行渲染(这个暂且不论,有兴趣的可以看下React16源码之React Fiber架构)。
未完待续。。。