Dwelling-database-index
Background
During the course of the cooperation with MSF, the humanitarian working group has generated thousands of dwelling polygons. The polygons were generated based on satellite images. Every polygon that represents a dwelling has certain characteristics, such as its location and the date the respective satellite image was taken. Other characteristics include its size, ...[add more]. The polygons are currently stored in a database. Recent activities include that the dwelling polygons shall function as samples for convolutional neural networks (CNN), which aim at automatized dewlling extraction from satellite imagery.
Objective
All the dwelling data in the database is supposed to receive an identifier which is not only unique but also descriptive. It should contain:
- a consecutive number
- a timestamp
- its location, based on a DGGS
(Question from me: Why can we not have the timestamp and the location stored as an attribute of the dwelling? Why must it be in the identifier?)
DGGS
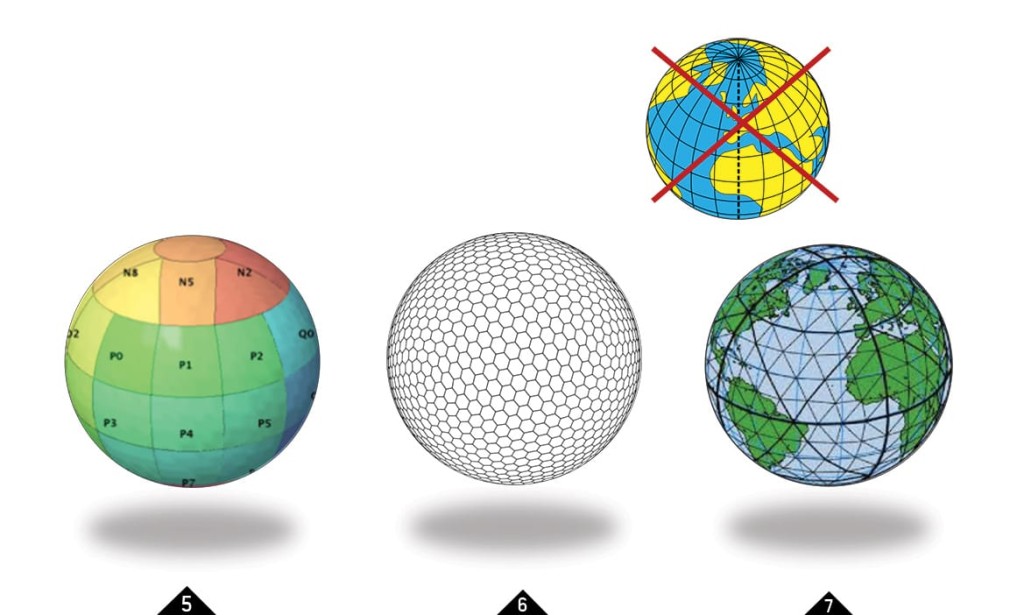
DGGS stands for discrete global grid system. By now, DGGS is an Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) standard. It is defined as "a spatial reference system that uses a hierarchical tesselation of cells to partition and address the globe." (Purss, 2015). Each cell has an unique adress and can be repeatedly subdivided for finer resolutions.
DGGSs could replace projected reference systems, as they avoid some of their known shortcomings. They are not meant for navigation (like latitude and longitude) but for tasks such as:
- data modeling
- processing
- storage
- transmission
- visualization
- analysis
Some advantages are:
- If everyone would use this standard, the same fixed cells could be used to record and analyze all location specific data
- It allows raster, vector and point cloud data to be combined into a common, globally consistent framework (OGC, 2017)
- It can analyze large amounts of data very quickly
- Multiple data sources can be integrated and analyzed without converting or changing the spatial reference system (Peterson, 2016)
- Users can work with many types of data at once, which is beneficial when working in large projects or with time-series data
- Accurately portrais polar regions, as well as all other regions of the earth
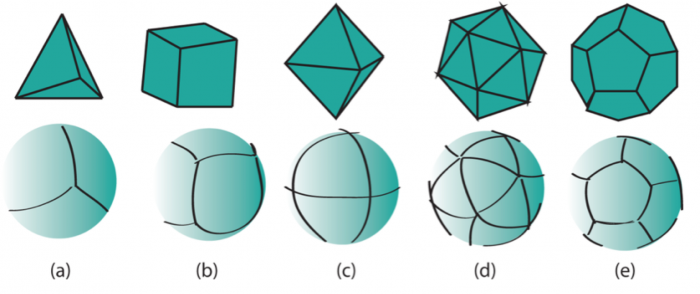
There is not the one DGGS, but many different implementations. They have in common that they are based on platonic solids with corresponding equal area tesselations. Click on the images below for further information.
Interesting introductory reads
https://apogeospatial.com/2079-2/
http://geoawesomeness.com/discrete-global-grid-system-dggs-new-reference-system/
https://ecce.esri.ca/cogs-blog/2018/11/09/dggs-a-new-way-to-model-geospatial-information/
http://docs.opengeospatial.org/as/15-104r5/15-104r5.html
DGGS Implementations
H3: Uber's Hexagonal Hierarchical Spatial Index
dggridR: Discrete Global Grids for R
Click here for some examples I did using dggridR
Development of a data harvesting strategy, including the identification of global data sets to exploit the full potential of freely available big data for humanitarian applications.