- [x] Geoprogressing Tools
- [x] Geospatial Analysis
- [x] Basic Editing Geoprocessing Tools in QGIS
Open Rylynnn opened 7 years ago
The Buffer Tool is a proximity function. When you use this geoprocessing tool, it creates a polygon at a set distance surrounding the feature(s). A buffer is a polygon or collection of cells that are within a specified proximity of a set of features.
 The buffer tool is a proximity function that sets a fixed or variable distance surrounding the feature(s).
The buffer tool is a proximity function that sets a fixed or variable distance surrounding the feature(s).
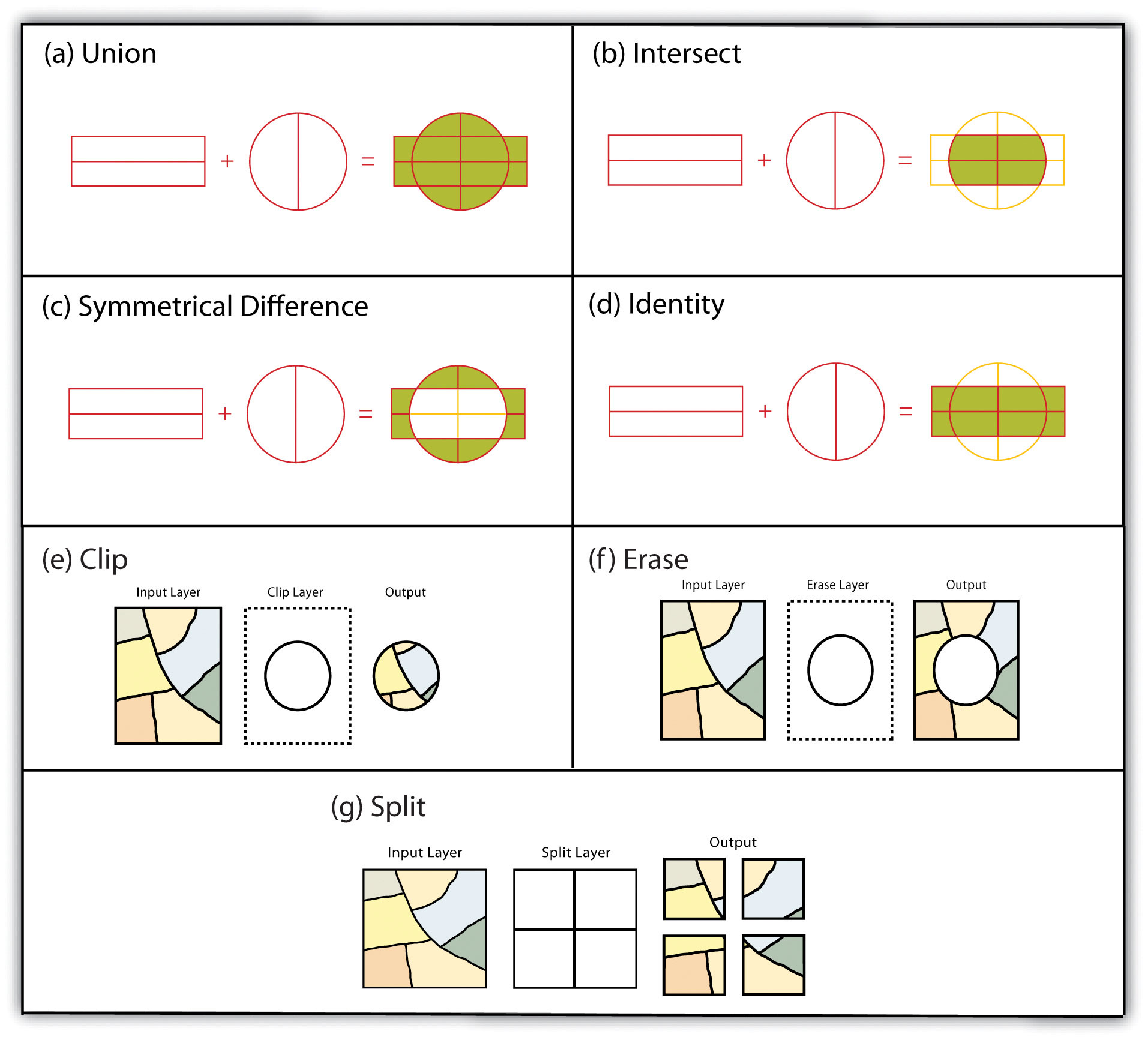
A clip is an overlay tool that cuts out an input layer with the extent of a defined feature boundary. The result of this tool is a new clipped output layer.
 The Clip Tool is a geoprocessing tool that extracts the input feature based on the extent of another polygon feature.
The Clip Tool is a geoprocessing tool that extracts the input feature based on the extent of another polygon feature.
global horizontal irradiance (GHI)
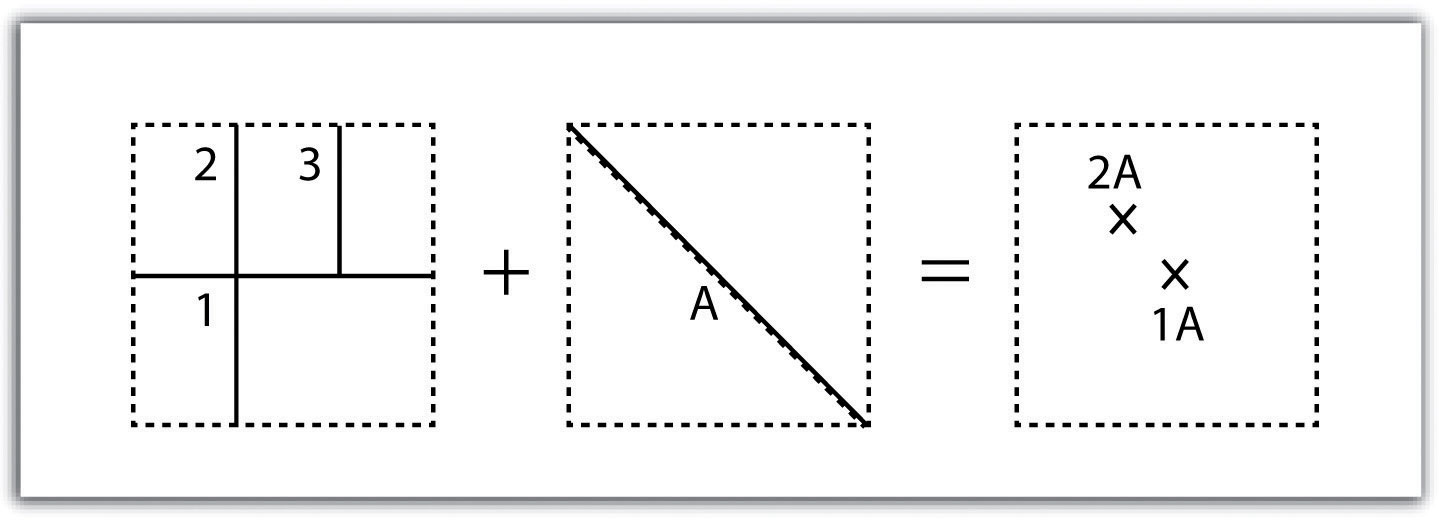
The merge geoprocessing tool combines data sets that are the same data type (points, lines or polygons). When you run the merge tool, the resulting data will be merged into one.
 The Merge Tool combines input features from multiple input sources. It creates a single, new, output feature class.
The Merge Tool combines input features from multiple input sources. It creates a single, new, output feature class.
The Dissolve Tool unifies boundaries based on common attribute values.
 The dissolve tool aggregates neighboring boundaries based on common attribute values.
The dissolve tool aggregates neighboring boundaries based on common attribute values.
The only exception is that attributes from all the data sets that overlap each other are preserved in the final data set.
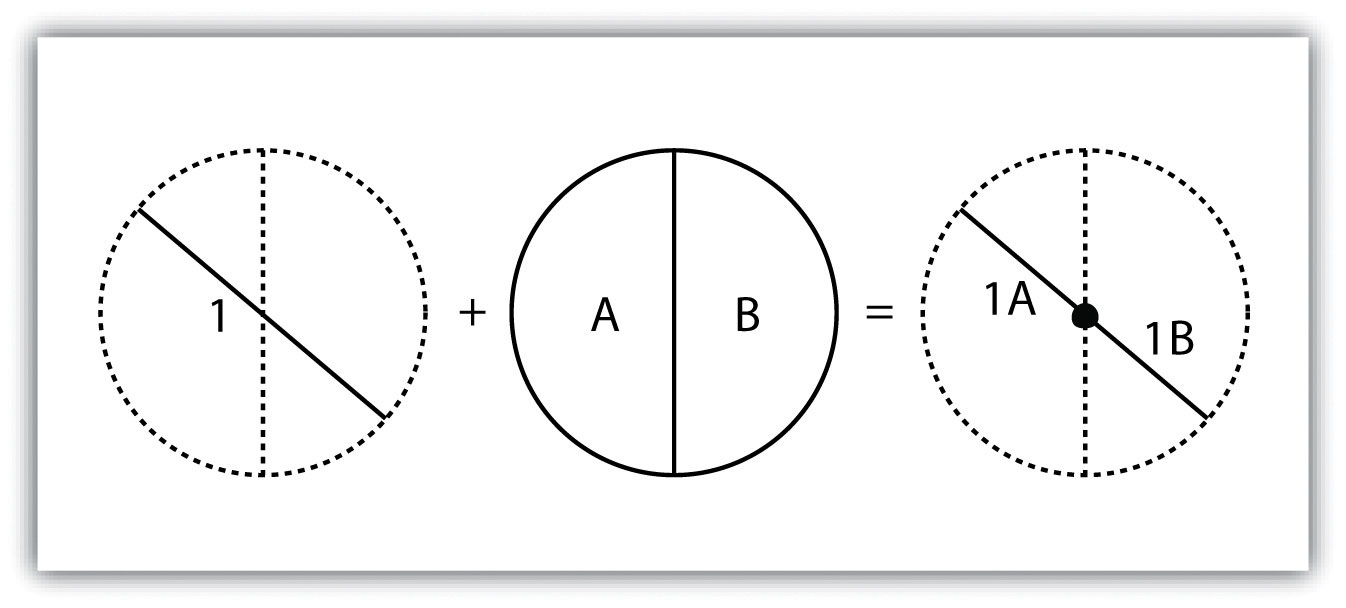
 The Intersect Tool performs a geometric overlap. All features that overlap in all layers will be part of the output feature class – attributes preserved.
The Intersect Tool performs a geometric overlap. All features that overlap in all layers will be part of the output feature class – attributes preserved.
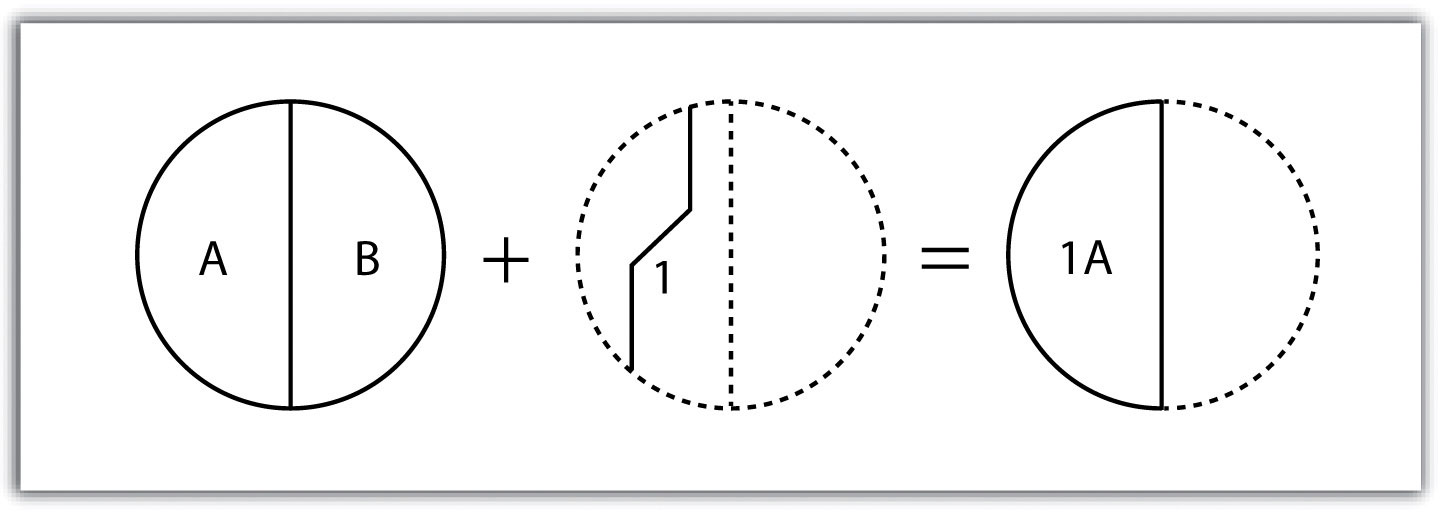
The Union tool spatially combines two data layers. It preserves features from both layers at the same extents.
 The Union Tool maintains all input features boundaries and attributes when it is written to the output feature class.
The Union Tool maintains all input features boundaries and attributes when it is written to the output feature class.
The input layer is what will be erased. The erase feature determines what will be erased.
 The Erase Tool removes features that overlap the erase features. This geoprocessing tool maintains portions of input features falling outside the erase features extent.
The Erase Tool removes features that overlap the erase features. This geoprocessing tool maintains portions of input features falling outside the erase features extent.
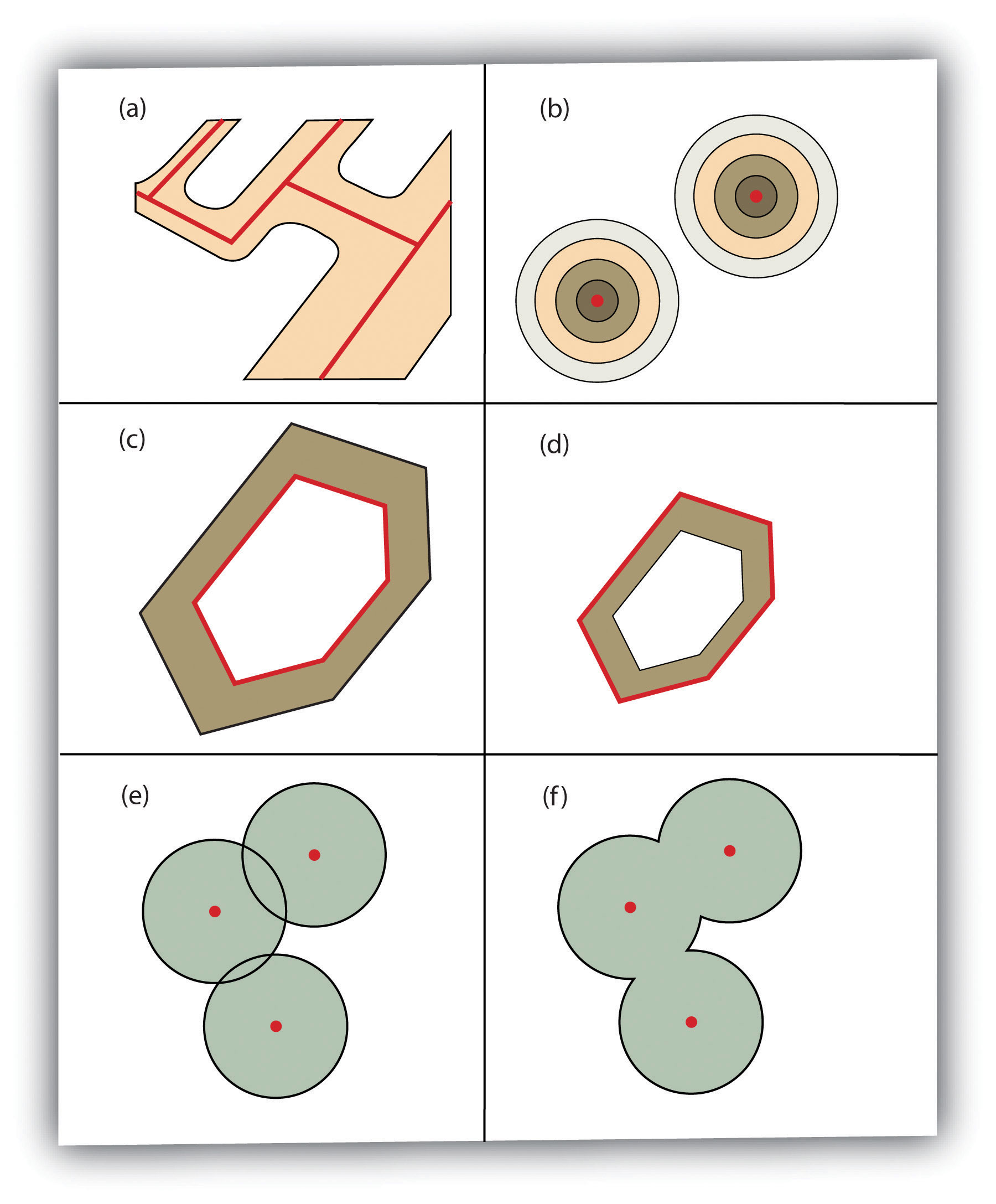 Additional Buffer Options around Red Features: (a) Variable Width Buffers, (b) Multiple Ring Buffers, (c) Doughnut Buffer, (d) Setback Buffer, (e) Nondissolved Buffer, (f) Dissolved Buffer
Additional Buffer Options around Red Features: (a) Variable Width Buffers, (b) Multiple Ring Buffers, (c) Doughnut Buffer, (d) Setback Buffer, (e) Nondissolved Buffer, (f) Dissolved Buffer
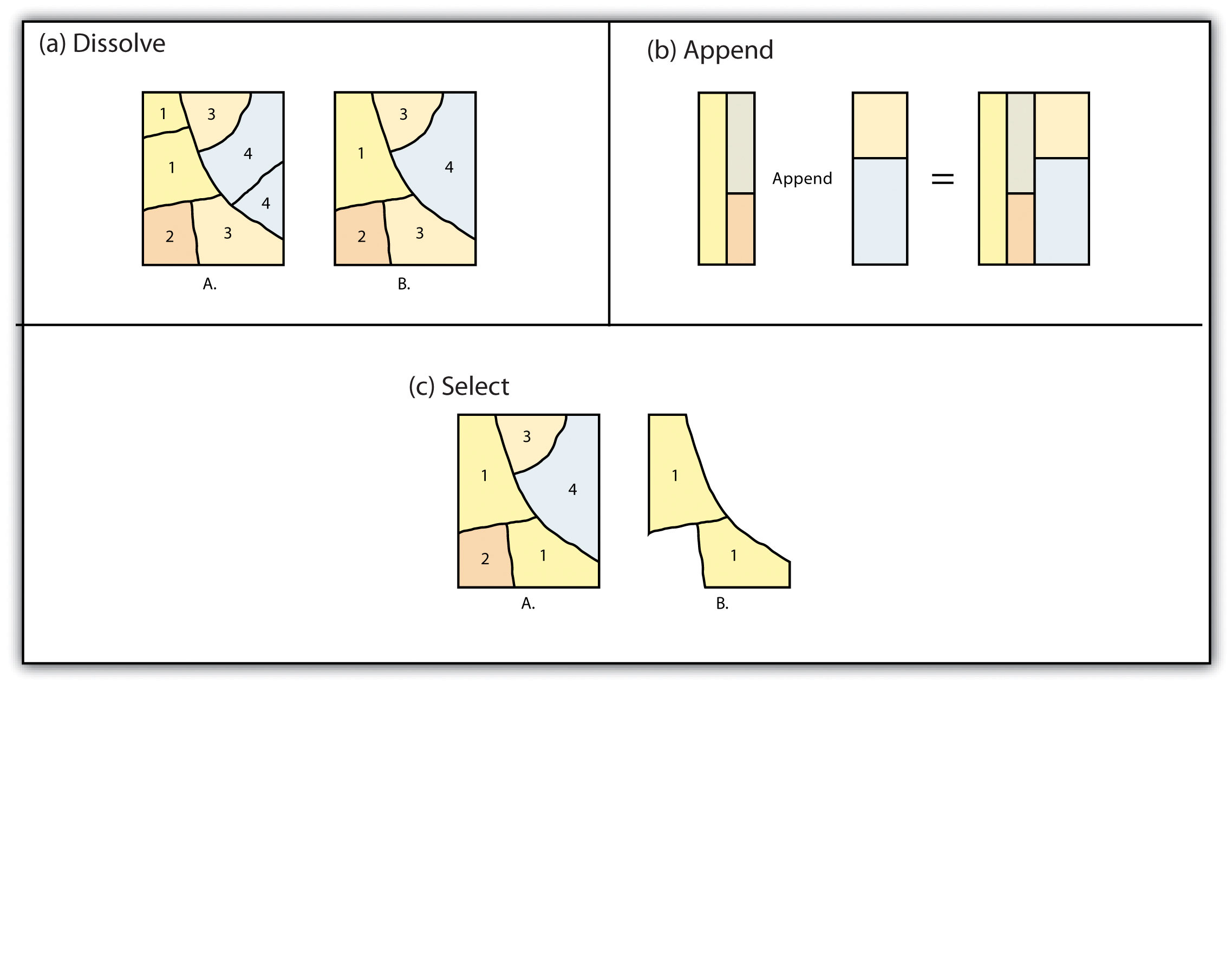 Single Layer Geoprocessing Functions
Single Layer Geoprocessing Functions
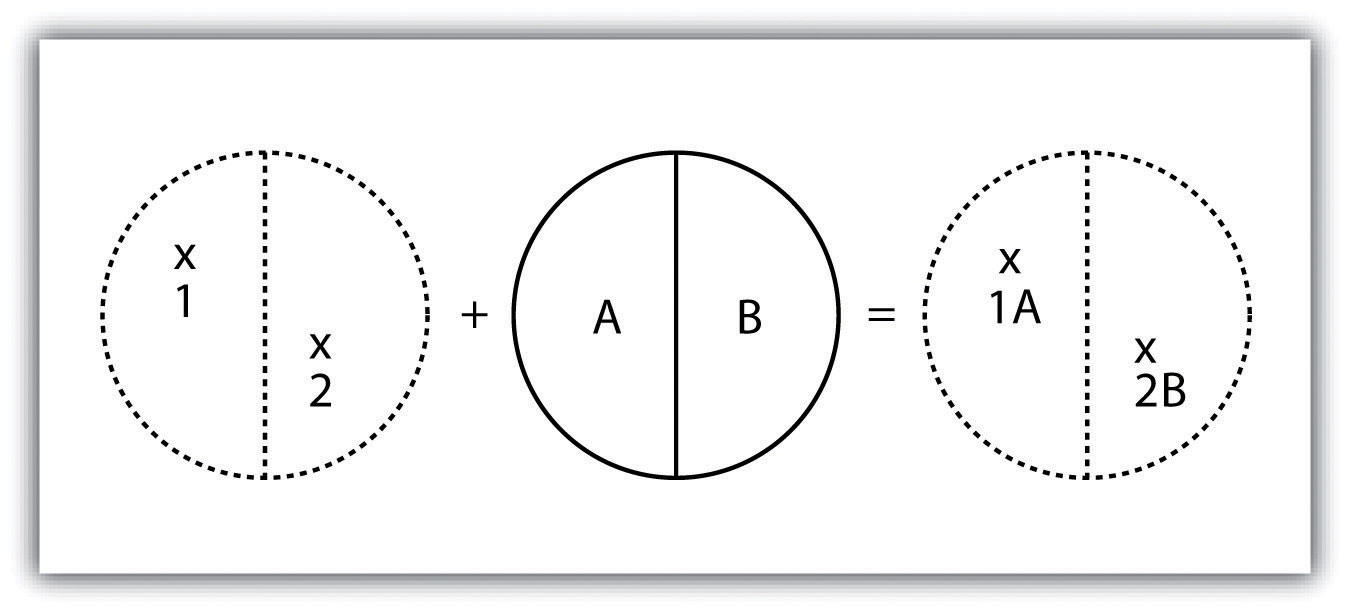
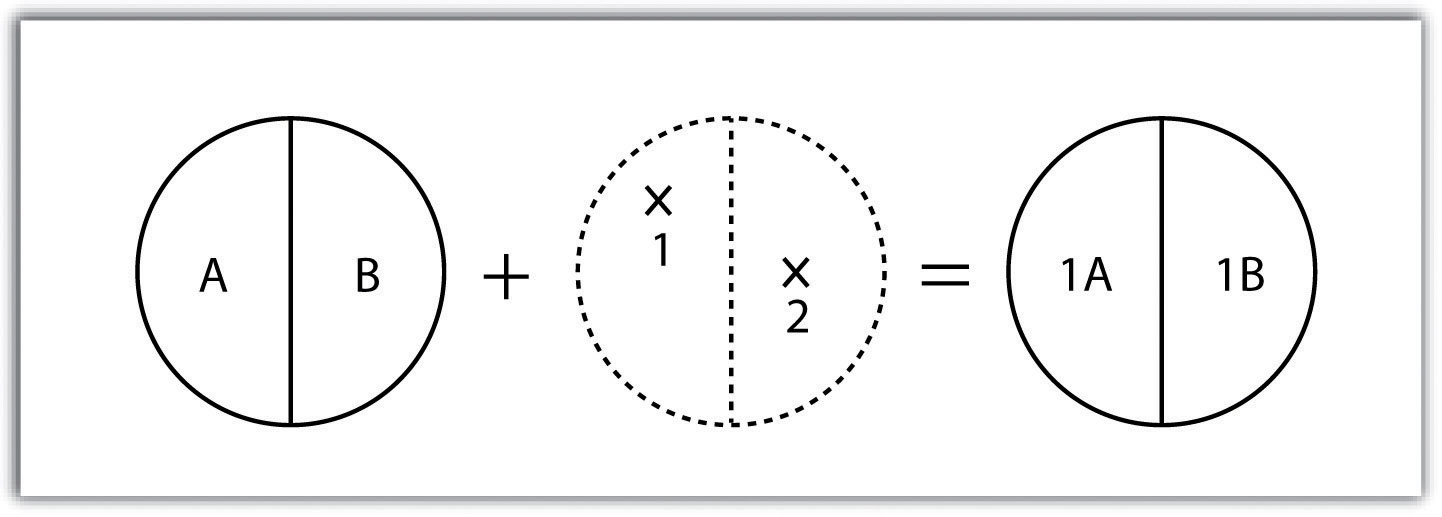
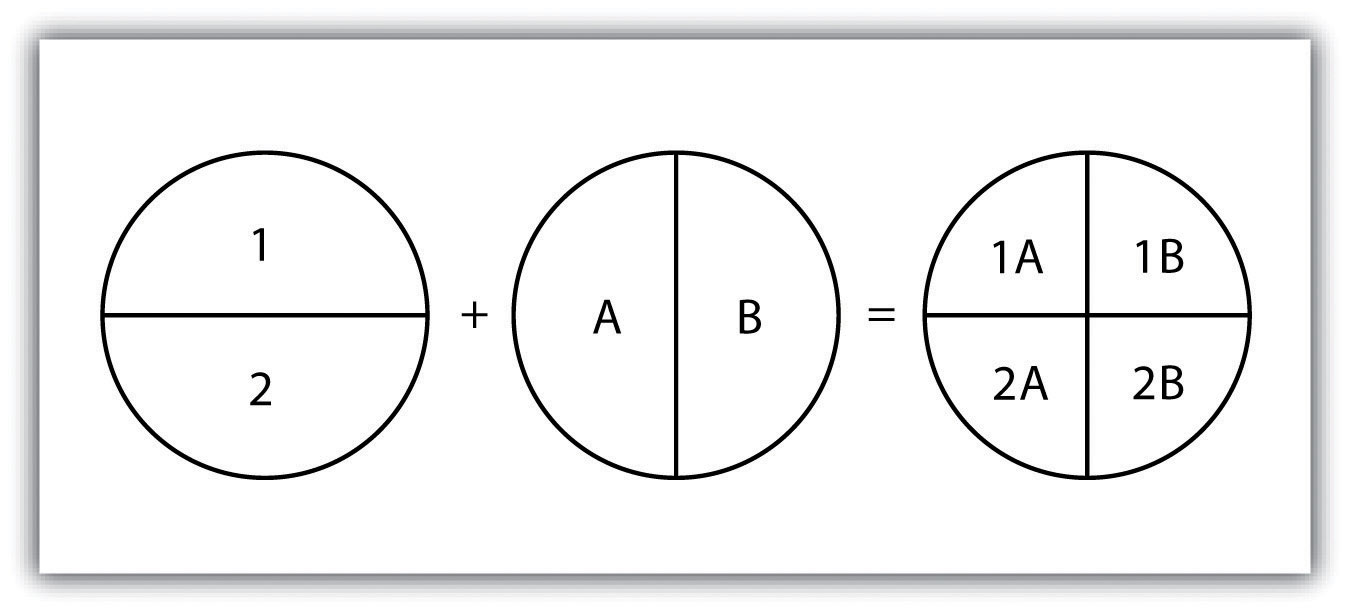
A spatial join is a hybrid between an attribute operation and a vector overlay operation.Unlike the attribute operation, a spatial join determines which fields from a source layer’s attribute table are appended to the destination layer’s attribute table based on the relative locations of selected features.
Although overlays are one of the most important tools in a GIS analyst’s toolbox, there are some problems that can arise when using this methodology.