In this step, you will be using Postman to test the CataaS API by sending a GET request.
✅ Tasks:
[x] 1: Read and explore the documentation for the Cataas API
[x] 2: With Postman, specify the API Endpoint and set the parameters to send a GET request to the CataaS API and receive a cat picture with "Serverless" written on it
[x] 🚀 Comment the picture you receive from the API in this issue/pull request to move on
1. Exploring the CataaS API
CATAAS is a RESTful API that exclusively delivers images of cats. The main feature is that we can change the properties of images, add text, truncate the image, add a filter and more. It's not an API with many real-world applications, but it's perfect for learning.
Interested in playing around with the API? Documentation is here.
How does the cloud work?
["The cloud"](https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cloud/what-is-the-cloud/) refers to servers that are accessed over the Internet, and the software and databases that run on those servers. Cloud servers are located in data centers all over the world. By using cloud computing, users and companies don't have to manage physical servers themselves or run software applications on their own machines.
What are HTTP Requests?
A [server](https://www.infotech.co.uk/blog/it-infrastructure-what-does-a-server-actually-do) is a computer that provides (serves) data to other computers, called clients. Clients connect to servers through the internet.
Clients communicate with servers with through `HTTP requests`. For example, when you are on your favorite browser and look up YouTube.com, you are making an HTTP "get" request to the server to load the contents from YouTube.com.
:exclamation:What are some examples of request types??
Below are some of the most common HTTP requests. Read through each one, and try to get familiar with their functions!
**Get Request**: gets data from a server (hence the name). The data we want is specified using a URL we call a Request URL. In this case, you will use a Get Request URL from the Catass API to receive a cat picture.
**Post Request**: used to send data to a server, to create or update a resource. The information submitted to the server is archived in the request body of the HTTP request. This is often used to send user-generated data to a server. An example could be uploading a picture to a Post URL.
**Put Request**: similar to a Post Request, but a put request will always have the same result every time you use one, whereas a post request might not. We call this property "idempotency."
**Delete Request**: used to delete resources indicated by the URL and will remove the targeted resources.
What are APIs, and what makes one "RESTful?"
An API is a piece of software that lets two other pieces of software talk to each other! Imagine you're driving a car - the wheel and pedals would be like APIs between you and the car, since they allow you to controll the car easily.
Most of the time, an API will be used to connect an app to an external service. For example, the Twitter API could allow a user to automatically receive updates on tweets concerning a particular topic or event.
Any API that follows these 5 rules is, by definition, RESTful.
**You don't need to worry about the 5 rules**, but if you're curious...
1. Internally, the API should keep the things the user does and the things the server does separate.
2. The server shouldn't ever need to store the user's data to function.
3. All output data from the API should mark itself as either "cacheable" or "non-cacheable" (cacheable data can be stored and reused later by the user, while non-cacheable data should be discarded and recomputed by the API every time).
4. The user shouldn't be able to tell whether or not they're communicating with the API's server, or an intermediary server.
5. The interface of the API should conform to a few agreed-upon conventions (that we won't be going over here).
2. Sending Requests with Postman
In this step, we'll be using a software called Postman to test an API. Postman is a debugging tool for RESTful APIs, which allows you to test both pre-existing, community made APIs, or your own self-made APIs, without having to write any HTML test code!
Parameters: color (color of the text) and size (font size)
:question: How do I specify the API Endpoint?
Enter https://cataas.com/cat/cute/says/Serverless, which is the API endpoint, into the text box next to GET
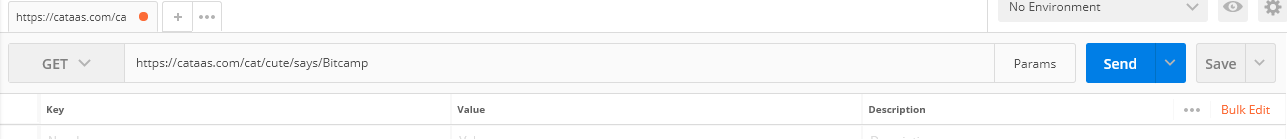
:question: How do I set the parameters?
Click on "Params" and enter `color` into Key and the color you want (eg. blue) into Value. Enter `size` into the next Key row and a number (eg. 50) into Value.
> **Note on parameters:**
> * the `size` parameter refers to the font size of your caption. It has a limit at around 1,200.
> * Colors are pretty hit or miss; since the Cat API is on the web, but it generally adheres to HTML color names. Expect values such as "blue, green, yellow" to work.
> * The API can take very large words as input for the caption, however only **34** characters can be seen on the picture at one time .
Week 1 Step 3 ⬤⬤⬤◯◯◯◯◯◯ | 🕐 Estimated completion: 10-15 minutes
Getting Cat Pics with Postman 🐱
In this step, you will be using Postman to test the CataaS API by sending a GET request.
✅ Tasks:
1. Exploring the CataaS API
CATAAS is a RESTful API that exclusively delivers images of cats. The main feature is that we can change the properties of images, add text, truncate the image, add a filter and more. It's not an API with many real-world applications, but it's perfect for learning.
Interested in playing around with the API? Documentation is here.
How does the cloud work?
["The cloud"](https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/cloud/what-is-the-cloud/) refers to servers that are accessed over the Internet, and the software and databases that run on those servers. Cloud servers are located in data centers all over the world. By using cloud computing, users and companies don't have to manage physical servers themselves or run software applications on their own machines.What are HTTP Requests?
A [server](https://www.infotech.co.uk/blog/it-infrastructure-what-does-a-server-actually-do) is a computer that provides (serves) data to other computers, called clients. Clients connect to servers through the internet. Clients communicate with servers with through `HTTP requests`. For example, when you are on your favorite browser and look up YouTube.com, you are making an HTTP "get" request to the server to load the contents from YouTube.com.:exclamation:What are some examples of request types??
Below are some of the most common HTTP requests. Read through each one, and try to get familiar with their functions! **Get Request**: gets data from a server (hence the name). The data we want is specified using a URL we call a Request URL. In this case, you will use a Get Request URL from the Catass API to receive a cat picture. **Post Request**: used to send data to a server, to create or update a resource. The information submitted to the server is archived in the request body of the HTTP request. This is often used to send user-generated data to a server. An example could be uploading a picture to a Post URL. **Put Request**: similar to a Post Request, but a put request will always have the same result every time you use one, whereas a post request might not. We call this property "idempotency." **Delete Request**: used to delete resources indicated by the URL and will remove the targeted resources.What are APIs, and what makes one "RESTful?"
An API is a piece of software that lets two other pieces of software talk to each other! Imagine you're driving a car - the wheel and pedals would be like APIs between you and the car, since they allow you to controll the car easily. Most of the time, an API will be used to connect an app to an external service. For example, the Twitter API could allow a user to automatically receive updates on tweets concerning a particular topic or event. Any API that follows these 5 rules is, by definition, RESTful. **You don't need to worry about the 5 rules**, but if you're curious... 1. Internally, the API should keep the things the user does and the things the server does separate. 2. The server shouldn't ever need to store the user's data to function. 3. All output data from the API should mark itself as either "cacheable" or "non-cacheable" (cacheable data can be stored and reused later by the user, while non-cacheable data should be discarded and recomputed by the API every time). 4. The user shouldn't be able to tell whether or not they're communicating with the API's server, or an intermediary server. 5. The interface of the API should conform to a few agreed-upon conventions (that we won't be going over here).2. Sending Requests with Postman
In this step, we'll be using a software called Postman to test an API. Postman is a debugging tool for RESTful APIs, which allows you to test both pre-existing, community made APIs, or your own self-made APIs, without having to write any HTML test code!
You can sign up for Postman here.
:question: How do we build requests?
The [Postman documentation](https://learning.postman.com/docs/sending-requests/requests/) covers: * Creating requests * Adding request detail * Setting request URLs * Selecting request methods * Sending parameters * Sending body data * Authenticating requests * Configuring request headersOpen up Postman and try it out yourself:
color(color of the text) andsize(font size):question: How do I specify the API Endpoint?
Enter https://cataas.com/cat/cute/says/Serverless, which is the API endpoint, into the text box next to GET 
:question: How do I set the parameters?
Click on "Params" and enter `color` into Key and the color you want (eg. blue) into Value. Enter `size` into the next Key row and a number (eg. 50) into Value. > **Note on parameters:** > * the `size` parameter refers to the font size of your caption. It has a limit at around 1,200. > * Colors are pretty hit or miss; since the Cat API is on the web, but it generally adheres to HTML color names. Expect values such as "blue, green, yellow" to work. > * The API can take very large words as input for the caption, however only **34** characters can be seen on the picture at one time .
Click
Sendto get your cat picture