I have the exact same issue and this whole package is useless without this function.
Open bettyliao776 opened 4 years ago
I have the exact same issue and this whole package is useless without this function.
Hey, I'm sorry about this. I'm transitioning most of this functionality over to timetk so you may have better luck with that. I'm not in a position to work on anomalize (my apologies). I'd try:
library(timetk)
library(tidyverse)
# Get Anomaly Data
walmart_sales_weekly %>%
group_by(id) %>%
tk_anomaly_diagnostics(
.date_var = Date,
.value = Weekly_Sales
)
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> # A tibble: 1,001 x 12
#> # Groups: id [7]
#> id Date observed season trend remainder seasadj remainder_l1
#> <fct> <date> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1_1 2010-02-05 24924. 874. 19967. 4083. 24050. -15981.
#> 2 1_1 2010-02-12 46039. -698. 19835. 26902. 46737. -15981.
#> 3 1_1 2010-02-19 41596. -1216. 19703. 23108. 42812. -15981.
#> 4 1_1 2010-02-26 19404. -821. 19571. 653. 20224. -15981.
#> 5 1_1 2010-03-05 21828. 324. 19439. 2064. 21504. -15981.
#> 6 1_1 2010-03-12 21043. 471. 19307. 1265. 20572. -15981.
#> 7 1_1 2010-03-19 22137. 920. 19175. 2041. 21217. -15981.
#> 8 1_1 2010-03-26 26229. 752. 19069. 6409. 25478. -15981.
#> 9 1_1 2010-04-02 57258. 503. 18962. 37794. 56755. -15981.
#> 10 1_1 2010-04-09 42961. 1132. 18855. 22974. 41829. -15981.
#> # … with 991 more rows, and 4 more variables: remainder_l2 <dbl>,
#> # anomaly <chr>, recomposed_l1 <dbl>, recomposed_l2 <dbl>
# Plot Anomalies
walmart_sales_weekly %>%
group_by(id) %>%
plot_anomaly_diagnostics(
.date_var = Date,
.value = Weekly_Sales,
.facet_ncol = 2,
.interactive = FALSE
)
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
#> frequency = 13 observations per 1 quarter
#> trend = 52 observations per 1 year
Created on 2020-11-13 by the reprex package (v0.3.0)
Hi, I run the sample code from https://github.com/business-science/anomalize and there's an issue. Please see below: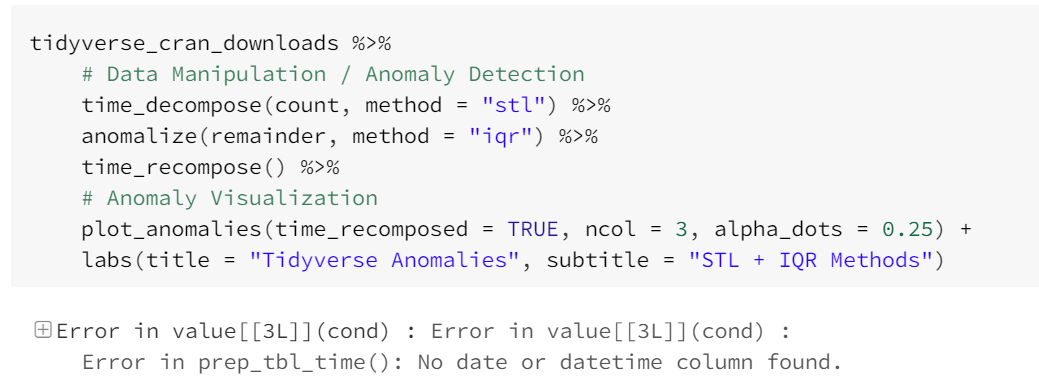
I tried the same code on my own tibble table and I got the same error: Error in value[3L] : Error in value[3L] : Error in prep_tbl_time(): No date or datetime column found.