Project planning and kickoff - Invoice Builder
Invoice Builder is a web-based application designed to assist freelancers in India with generating invoices compliant with Indian freelancing standards. This document outlines the technical architecture and the technologies chosen for building the website.
Technical Architecture
1. Which technologies should we use for creating website for this project?
1a. Frontend
- React: A powerful JavaScript library for building dynamic user interfaces.
- HTML/CSS: Fundamental web technologies for content structure and styling.
- JavaScript (ES6+): Modern JavaScript for adding interactivity.
- Tailwind CSS: A utility-first CSS framework for efficient UI design.
1b. Backend
- Node.js: A runtime environment for server-side JavaScript.
- Express.js: A minimal and flexible web application framework for Node.js.
- MongoDB: A NoSQL database for storing user data, transaction records, and generated invoices.
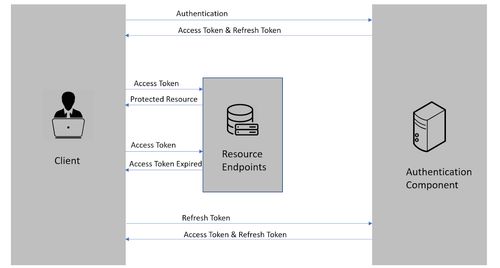
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens): A secure authentication mechanism.
1c. Development and Deployment Tools
- Git: Version control system for collaborative development and code management.
- Deployment Platforms: Options such as Vercel, Netlify, or Heroku for hosting and deploying the web application.
2. What security mechanisms (HTTPS, encryption, OAuth, etc.) will be implemented to ensure data integrity and confidentiality?
2a. HTTPS (SSL/TLS):
Enable HTTPS on your web application to encrypt data transmitted between the user's browser and the server. This prevents eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Obtain an SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA) and configure your web server (e.g., Express.js) to use HTTPS.
A website must have an SSL/TLS certificate for their web server/domain name to use SSL/TLS encryption. Once installed, the certificate enables the client and server to securely negotiate the level of encryption in the following steps:
Both the client and server are now using HTTPS (SSL/TLS + HTTP) for their communication. Web browsers validate this with a lock icon in the browser address bar. HTTPS functions over Port 443.
2b. Secure Data Storage:
Follow best practices for securely storing sensitive user data in your database, including hashing and salting passwords and encrypting sensitive information.
2c. Access Control Lists (ACLs):
Implement granular access control lists to restrict data access within your application, even after a user has been authorized.
2d. Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing:
Conduct security audits and penetration testing to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
2e. Monitoring and Logging:
Implement monitoring and logging to detect and respond to security incidents in real-time.
Database
3. What kind of database and authentication will be most efficient for this application?
3a. Most efficient Database for Invoice builder application : NoSQL Database (e.g., MongoDB)
-
Semi-Structured Data: Invoice Builder also deals with semi-structured or unstructured data, such as invoices and user preferences.
-
Flexibility and Scalability: NoSQL databases like MongoDB provide flexibility and scalability, making them suitable for handling varying data types and accommodating future growth.
-
Efficiency for Unstructured Data: MongoDB efficiently stores and retrieves unstructured data, such as invoice documents.
3b. Most efficient Authentication for Invoice builder application : JSON Web Tokens (JWT)
-
Efficient Authentication: JWTs offer an efficient and stateless way to authenticate users after login.
-
Security: JWTs can securely carry user identity and claims, preventing unauthorized access to application resources.
-
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): JWTs support RBAC, enabling the definition of user roles and permissions for controlled access.
-
Compatibility: JWTs are compatible with web applications, making them a suitable choice for the Invoice Builder application.
3c. Authentication : Bcrypt for Password Hashing
-
Secure Password Storage: Bcrypt ensures secure password hashing and salting before storing passwords in the database.
-
Protection Against Attacks: Bcrypt defends against common password-related vulnerabilities, such as brute-force and rainbow table attacks.
-
Data Confidentiality: Securely stored passwords contribute to data confidentiality by safeguarding user credentials.
4. How will database backups be handled?
Data backup options for MongoDB are as follows:
4a. mongodump and mongorestore:
- Use MongoDB's built-in tools for creating full or partial backups.
- Suitable for routine backup tasks and migrations.
- Simple to use but may impact database performance.
- To create a backup of the MongoDB database, we utilize the
mongodumpcommand.
4b. MongoDB Atlas Backup:
- Offered as part of MongoDB Atlas, the cloud-hosted service.
- Provides automated and managed backups with continuous and point-in-time recovery options.
- Ideal for applications hosted on MongoDB Atlas.
4c. File System Snapshots:
- Involve taking snapshots of the underlying file system where MongoDB data resides.
- Suitable for consistent backups without impacting database performance.
- Requires file system-level access and is not application-aware.
4d. Third-Party Backup Solutions:
- Offered by various vendors with advanced features like compression and deduplication.
- Useful for complex deployments and demanding backup requirements.
- May involve additional costs and complexity.
4e. Custom Backup Scripts:
- Create tailored backup scripts using MongoDB drivers and tools.
- Highly customizable and suitable for unique requirements.
- Requires development effort and ongoing maintenance.
Front-end and User Experience
5. What front-end technologies and libraries should be used?
As i have mentioned in the first question as well, the frontend technologies and libraries which would be useful are as follows:
The front-end of the Invoice Builder application is built using modern web development technologies, ensuring a responsive and user-friendly experience. The core technologies include:
-
React.js: A popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces. React offers a component-based architecture, making it easy to create reusable UI components.
-
HTML5 and CSS3: Used for structuring web content and styling the user interface, respectively.
-
JavaScript (ES6+): Utilized for adding interactivity to the application and enhancing user experience.
Libraries and Frameworks
To streamline development, enhance functionality, and ensure a smooth user experience, several libraries and frameworks are integrated into the front-end:
-
React Router: Provides client-side routing capabilities, enabling navigation between different views or pages of the application.
-
Tailwind CSS: A utility-first CSS framework that simplifies styling and layout, helping create a responsive and visually appealing UI.
-
Axios: Used for making HTTP requests to the backend server to fetch and update data, ensuring seamless communication between the front-end and backend.
-
React Charting Libraries (e.g., Chart.js, D3.js): Used for displaying charts and graphs to visualize data in an easy-to-understand manner.
-
Git: A version control system used for tracking changes and collaborating on the codebase.
6. How will the UI/UX be designed to be intuitive for non-technical users?
The things to keep in mind when creating a UI/UX design for a Invoice Builder app for non tech users are as follows:
6a. User Onboarding:
Implement a user-friendly onboarding process that guides new users through setting up their profiles and understanding how to use the app effectively.
6b. Dashboard:
Create a clear and organized dashboard that provides an overview of the user's account, recent activities, and key actions like creating a new invoice.
6c. Profile Management:
Allow users to easily manage their profile information, including personal details, business information, and payment preferences.
6d. Invoice Creation:
Design an intuitive interface for creating invoices, including options for adding client details, line items, item descriptions, quantities, rates, and due dates.
6e. Preview and Editing:
Provide users with the ability to preview invoices before finalizing them. Include options for editing and making changes.
6f. Invoice List:
Display a list of all created invoices, including their statuses (e.g., draft, sent, paid). Implement sorting and filtering options for easy access.
6g. Responsive Design:
Ensure that the UI adapts to various screen sizes and orientations, making the app usable on desktops, tablets, and mobile devices.
6h. Color Scheme and Branding:
Choose a professional and harmonious color scheme that aligns with your branding. Use colors to highlight important elements and actions.
6i. Icons and Typography:
Select clear and legible fonts for content and headings. Ensure that text is appropriately, Utilize icons and visual elements sized for readability.
Testing and QA
7. What types of testing (unit, integration, etc.) will be most crucial for this project?
Types and classification of testing:
Our "Invoice Builder" project encompasses both functional and non-functional testing aspects, as is typical for most software applications. Let's break down the classification:
7a. Functional Testing: Functional testing focuses on verifying whether the application's features and functions work as intended. It checks that the software performs the tasks it was designed to do correctly. In the context of your project, functional testing includes:
-
Unit Testing: Ensuring that individual functions and components (e.g., invoice generation, data validation) work correctly.
-
Integration Testing: Verifying that different components and modules integrate seamlessly and interact correctly.
-
End-to-End (E2E) Testing: Assessing the entire user journey, from creating invoices to sending and receiving payments.
7b. Non-Functional Testing: Non-functional testing evaluates the performance, usability, and quality attributes of the application. It assesses how the software performs under various conditions. In your project, non-functional testing includes:
- Performance Testing: Analyzing how the application performs under different loads, assessing its responsiveness and speed.
- Security Testing: Identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities and ensuring the application's security.
- Accessibility Testing: Ensuring the application is accessible to users with disabilities.
- Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Testing: Verifying that the application functions correctly across various browsers and devices.
- Load Testing: Assessing the application's ability to handle concurrent users and heavy traffic.
Which Testing Type is Most Useful and Why: The importance of each testing type depends on your project's goals, priorities, and user requirements. However, given the nature of your "Invoice Builder" application and the needs of your users, some testing types are particularly crucial:
-
Functional Testing (Including E2E Testing): Functional testing, including E2E testing, is essential to ensure that the core functionalities of your invoice generation and management system work correctly. It directly impacts user satisfaction and the application's primary purpose.
-
Security Testing: Security testing is paramount, as your application will handle sensitive financial data (invoices, payment information). Ensuring that your application is secure protects both your users and your business from potential data breaches and legal issues.
-
Performance Testing: Performance testing is crucial to providing a seamless user experience. Slow-loading pages or unresponsive interactions can frustrate users. By identifying and addressing performance bottlenecks, you can enhance user satisfaction and retention.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the "Invoice Builder" project is an ambitious endeavor aimed at providing a user-friendly and compliant invoicing solution for freelancers in India. We have outlined a comprehensive technical architecture and chosen a stack of modern technologies to build a robust web application.
On the frontend, I'll leverage React.js, HTML/CSS, JavaScript, and Tailwind CSS to create an intuitive and responsive user interface. For the backend, Node.js, Express.js, and MongoDB will power the application's functionality and data storage, with authentication secured using JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
Security is a top priority, with HTTPS encryption, secure data storage practices, bcrypt for password hashing, and access control lists (ACLs) for data access control.
My choice of a NoSQL database, MongoDB, is ideal for handling semi-structured data such as invoices and user preferences. JWT authentication offers efficiency and security for user access control.
The UI/UX design focuses on user onboarding, an organized dashboard, profile management, intuitive invoice creation, and a responsive layout. Thoughtful choices in color, typography, and icons enhance the overall user experience.
Testing strategies include a combination of functional and non-functional tests, covering everything from unit and integration testing to security, performance, accessibility, and cross-browser/device testing.
In summary, the "Invoice Builder" project is well-planned, prioritizing security, user experience, and functionality. We're committed to delivering a valuable tool for Indian freelancers to simplify their invoicing processes.
Thank you!

Is there an existing Discovery issue on this topic?
Objective
We will start with a new project "Invoice Builder" is a web-based application designed to assist freelancers in India with generating invoices compliant with Indian freelancing standards. Users can log in to add and store their personal details and business transactions, which can then be used to generate invoices. Given the sensitive nature of financial data, the platform will prioritize security at all layers. The software will be open source.
Answer the following questions in comments:
Technical Architecture
Database
Front-end and User Experience
Testing and QA
Reference Materials
Expected Outcome
Answers to each question with clear explainations in the comment section. Research your answers before answering(You can use chatgpt).
Successfully answering these questions will earn you 100 points. You will get 50 extra points if your overall answers are the better than others. In case of similar answers First one to submit will be considered for extra points.
Deadline: 13 Oct, 2023 0900
Have you provided comprehensive details for this discovery task?