const codeGen = (node) => {
let type = node.type
if (type === 'Program') {
let body = node.body
let s = body.map(b => codeGen(b)).join('\n')
return s
}
}
const codeGen = (node) => {
let type = node.type
if (type === 'Program') {
let body = node.body
let s = body.map(b => codeGen(b)).join('\n')
return s
} else if (type === 'ImportDeclaration') {
let specifiers = node.specifiers
let source = node.source
// 引入用逗号分隔,所以返回结果 join(',')
let s = specifiers.map(s => codeGen(s)).join(', ')
let v = codeGen(source)
// 检查是否勾选对应选项
let es6_import_or_export_braces_space = toggleSpace('es6_import_or_export_braces')
// 拼接返回内容
let r = `import {${es6_import_or_export_braces_space}${s}${es6_import_or_export_braces_space}} from ${v}`
return r
}
}
// 补全缩进
const fillIndent = (count) => {
// padStart 是在字符串前补全长度的方法,默认用空格补全
return ''.padStart(count)
}
const codeGen = (node) => {
let type = node.type
...
} else if (type === 'ClassBody') {
let body = node.body
let startSpace = fillIndent(indentConfig.indent * node.indentCount)
body = body.map(e=> {
let b = startSpace + codeGen(e)
return b
}).join('\n')
let r = `${body}`
return r
} else if (type === 'BlockStatement') {
let body = node.body
let startSpace = fillIndent(indentConfig.indent * node.indentCount)
let endSpace = fillIndent(indentConfig.indent * (node.indentCount - 1))
let b = body.map(b => codeGen(b)).join(', ')
let r = `{\n${startSpace}${b}\n${endSpace}}`
return r
}
...
}
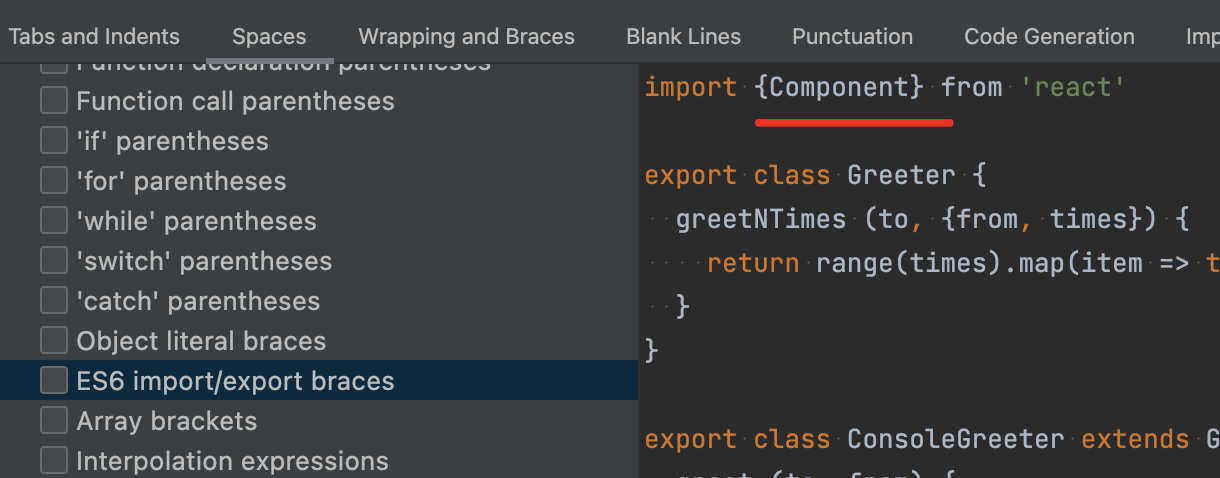
当同时选中空格配置 function_declaration 和 function_expression 时,发现 function 有多余空格,如图所示:
检查 AST 可见,function_declaration 是处理 MethodDefinition 情况的空格,function_expression 是处理 VariableDeclarator 情况的空格。
而处理的节点 type 都是 FunctionExpression,所以需要根据父节点的 type 进行判断。由于需要增加传参,则将之前 codeGen() 里的 if-else 判断拆分为独立的函数。
const codeGen = (node, parent) => {
let type = node.type
let result = ''
result = typeMap[type] && typeMap[type](node, parent)
return result
}
const typeMap = {
Program(node) {
let body = node.body
let s = body.map(b => codeGen(b)).join('\n\n')
return s
},
MethodDefinition(node) {
let key = node.key
let value = node.value
let k = codeGen(key)
let v= codeGen(value, 'MethodDefinition')
let function_declaration = toggleSpace('function_declaration')
let r = `${k}${function_declaration}${v}`
return r
},
VariableDeclarator(node) {
let id = node.id
let init = node.init
let name = codeGen(id)
let i = codeGen(init, 'VariableDeclarator')
let r = `${name} = ${i}`
return r
},
FunctionExpression(node, parentType) {
let params = node.params
let body = node.body
let before_comma = toggleSpace('before_comma')
let after_comma = toggleSpace('after_comma')
let p = params.map(p => codeGen(p)).join(`${before_comma},${after_comma}`)
let b = codeGen(body)
let function_expression = toggleSpace('function_expression')
let function_left_brace = toggleSpace('function_left_brace')
let function_declaration_parentheses = toggleSpace('function_declaration_parentheses')
let r = ''
if (parentType === 'MethodDefinition') {
r = `(${function_declaration_parentheses}${p}${function_declaration_parentheses})${function_left_brace}${b}`
} else {
r = `function${function_expression}(${function_declaration_parentheses}${p}${function_declaration_parentheses})${function_left_brace}${b}`
}
return r
},
....
}
JS Formatter 是什么
JS Formatter 是可以对 JavaScript 代码进行格式化的工具,可参考 WebStorm 的配置 Preferences -> Editor -> Code Style -> JavaScript 实现加减空格、缩进和分号的功能。
步骤拆解
本项目技术方案采用 Vue3 + ElementPlus + highlightjs + espree + Webpack。 拆解思维导图如下: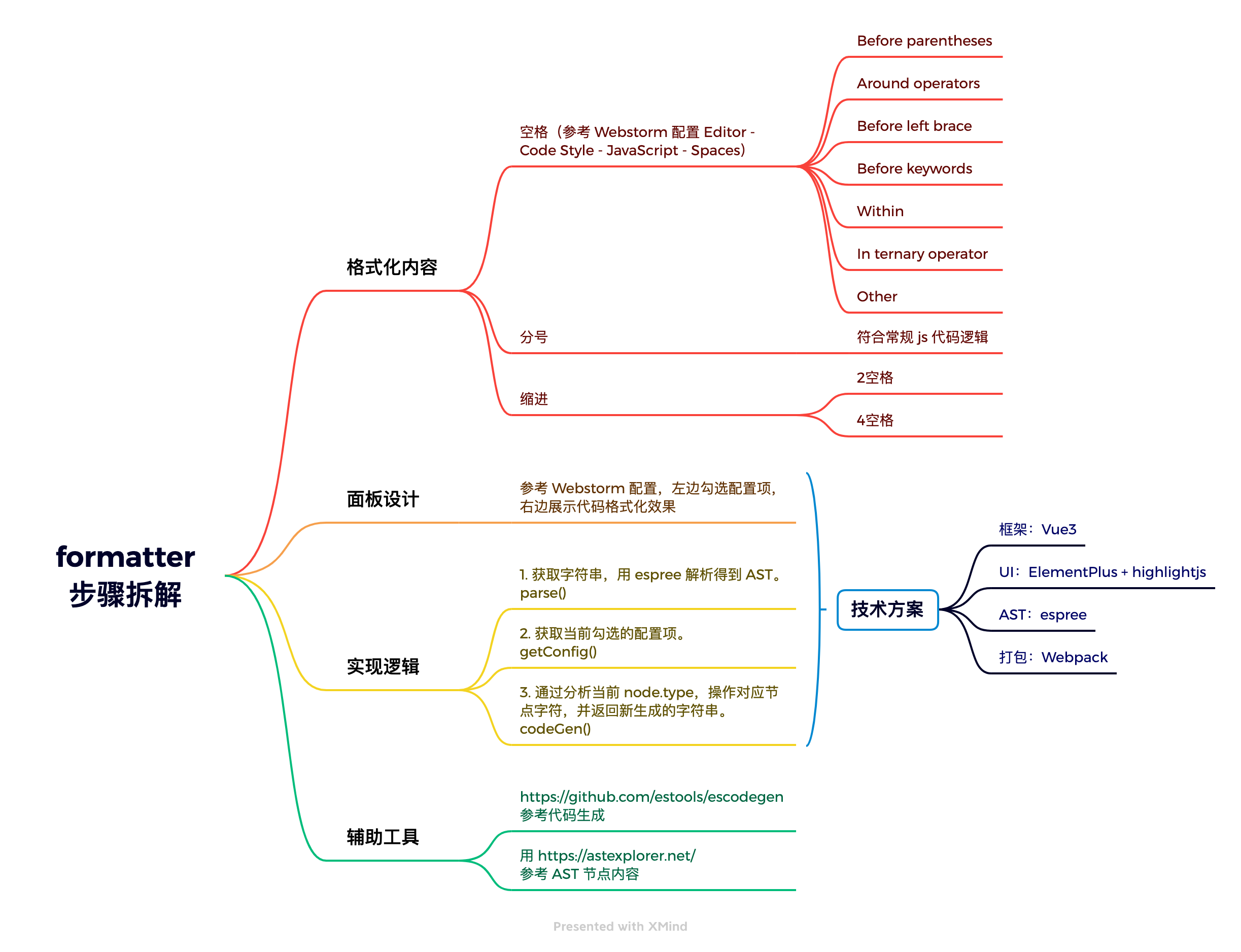 接下来按步骤实现代码。
接下来按步骤实现代码。
代码实现
parse():提取 AST
使用 espree.parse() 提取 AST。
根据 espree 官方说明配置,适用于本次格式化的源码(使用 WebStorm 的示例代码)。
getConfig():获取当前勾选的格式化配置
使用 ElementPlus 的 ElCheckboxGroup 和 ElCheckbox 组件,用 checkList 获取当前配置。
codeGen():生成格式化后的代码
此处需用到 https://astexplorer.net/,便于观察生成的 AST 抽象语法树。 先举个简单的例子,取待格式化的第一行代码进行演示。
将上述代码粘贴到 astexplorer 左边输入框,上方语言选 JavaScript,解析器选 espree,右边生成的即是左边代码对应的 AST tree。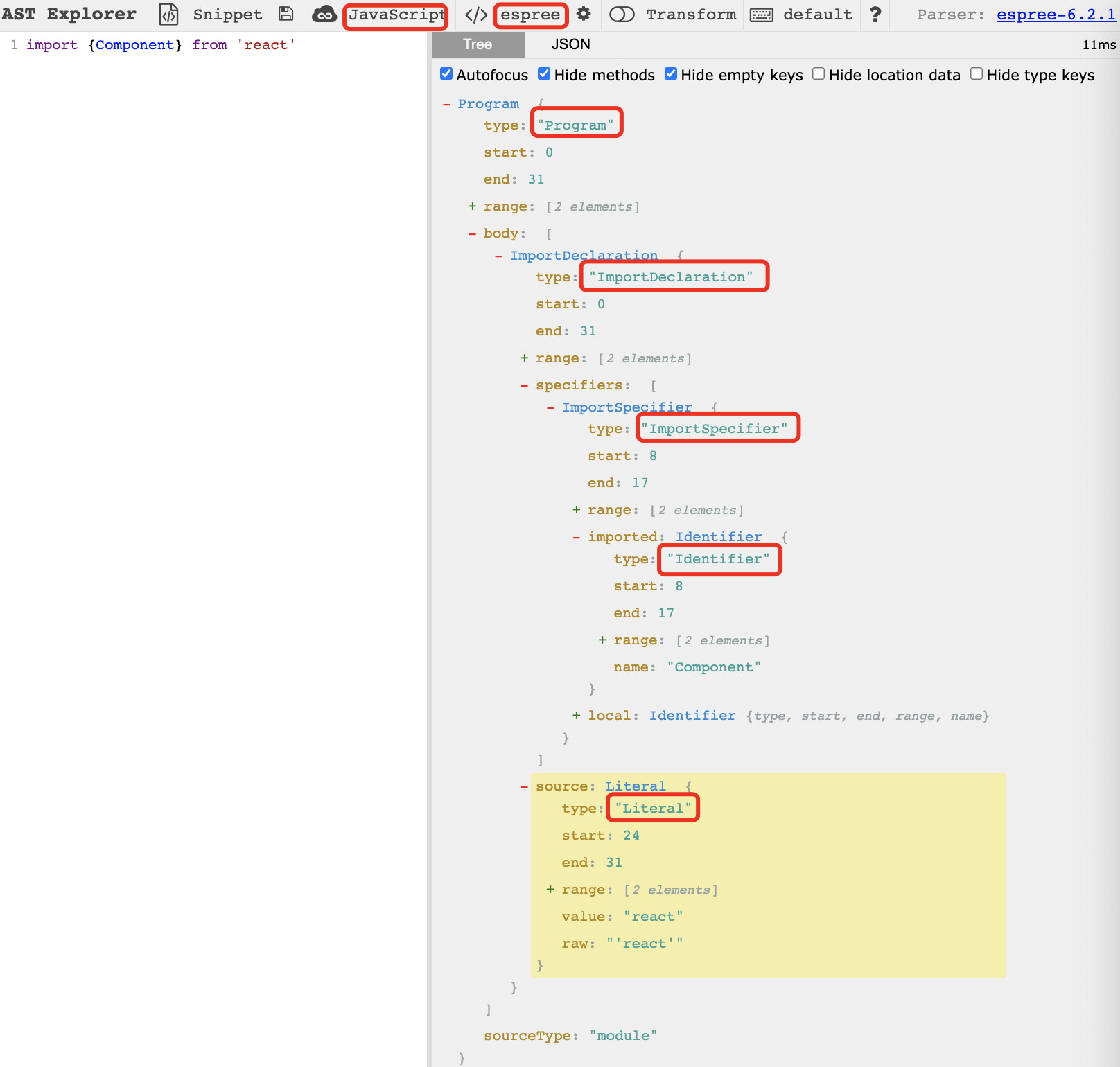 将鼠标移到左边代码上,右边 AST tree 会高亮显示对应的节点。我们需要遍历这些节点,对其进行相应处理,并返回新的代码字符串,这个过程即实现格式化。
而需要生成怎样的字符串呢?这时可以去上方所说的 WebStorm 配置里,勾选对应的格式化配置,观察格式化后的代码。
格式化前:
将鼠标移到左边代码上,右边 AST tree 会高亮显示对应的节点。我们需要遍历这些节点,对其进行相应处理,并返回新的代码字符串,这个过程即实现格式化。
而需要生成怎样的字符串呢?这时可以去上方所说的 WebStorm 配置里,勾选对应的格式化配置,观察格式化后的代码。
格式化前:
 格式化后:
格式化后:
 可见格式化后的代码,在花括号内两边增加了空格。那么如何用代码实现呢?
可见格式化后的代码,在花括号内两边增加了空格。那么如何用代码实现呢?
处理空格
将 parse() 生成的 AST 传入 codeGen(),由上述 astexplorer 中所见,可以用 node.type 来判断当前节点。整个 AST 开始的节点是 'Program',而我们需要获取的是 body 中的内容,所以递归调用 codeGen() 传入 body,而 body 是数组结构,所以用上述 map 写法调用。 第一次递归调用时,判断到当前 type 为'ImportDeclaration',在该节点 AST 中可见,需要用到 specifiers 和 source 节点,分别对应了源代码的 {Component} 和 'react' 部分。我们需要获取这两个值。
而 specifiers 和 source 里还有其他节点,所以需要继续递归调用 codeGen(),同理 specifiers 是数组结构,用 map 调用,返回值用逗号拼接即可。 然后,需要检查当前是否勾选 es6_import_or_export_braces_space,有勾选则返回空格,没有则返回空。 由上述格式化图片可见,我们需要生成 import { Component } from 'react' 这段字符串,所以返回的拼接内容即 r 变量所示。 接下来,则是继续递归调用 codeGen() 以获取所需值。
当遍历到 type 为 Identifier 和 Literal 时,即可获取所需值。此时即可生成格式化后的字符串。 其他源代码处理逻辑同上。 将格式化后的代码显示在面板中即可。
处理缩进
接下来我们处理 WebStorm 示例代码中的第二段代码:
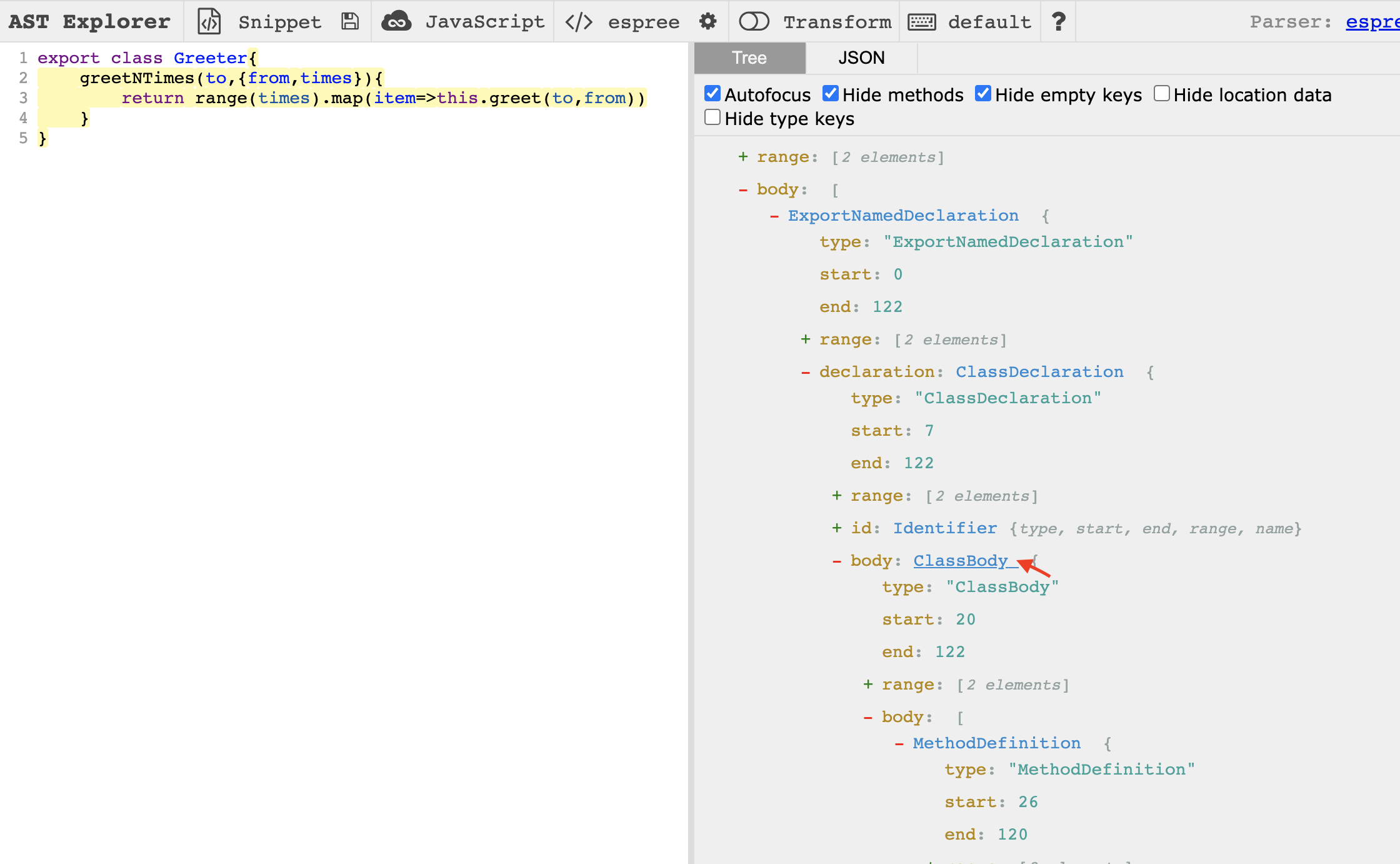
按照上述 codeGen() 的原理,将代码复制到 https://astexplorer.net/ 中,生成 AST tree,然后根据判断 AST 节点的 node.type 类型,对每个节点内容进行解析,并返回相应字符串。结果如下图所示。 很明显,生成的代码缺少缩进。如何按层级结构添加相应数量的缩进呢?
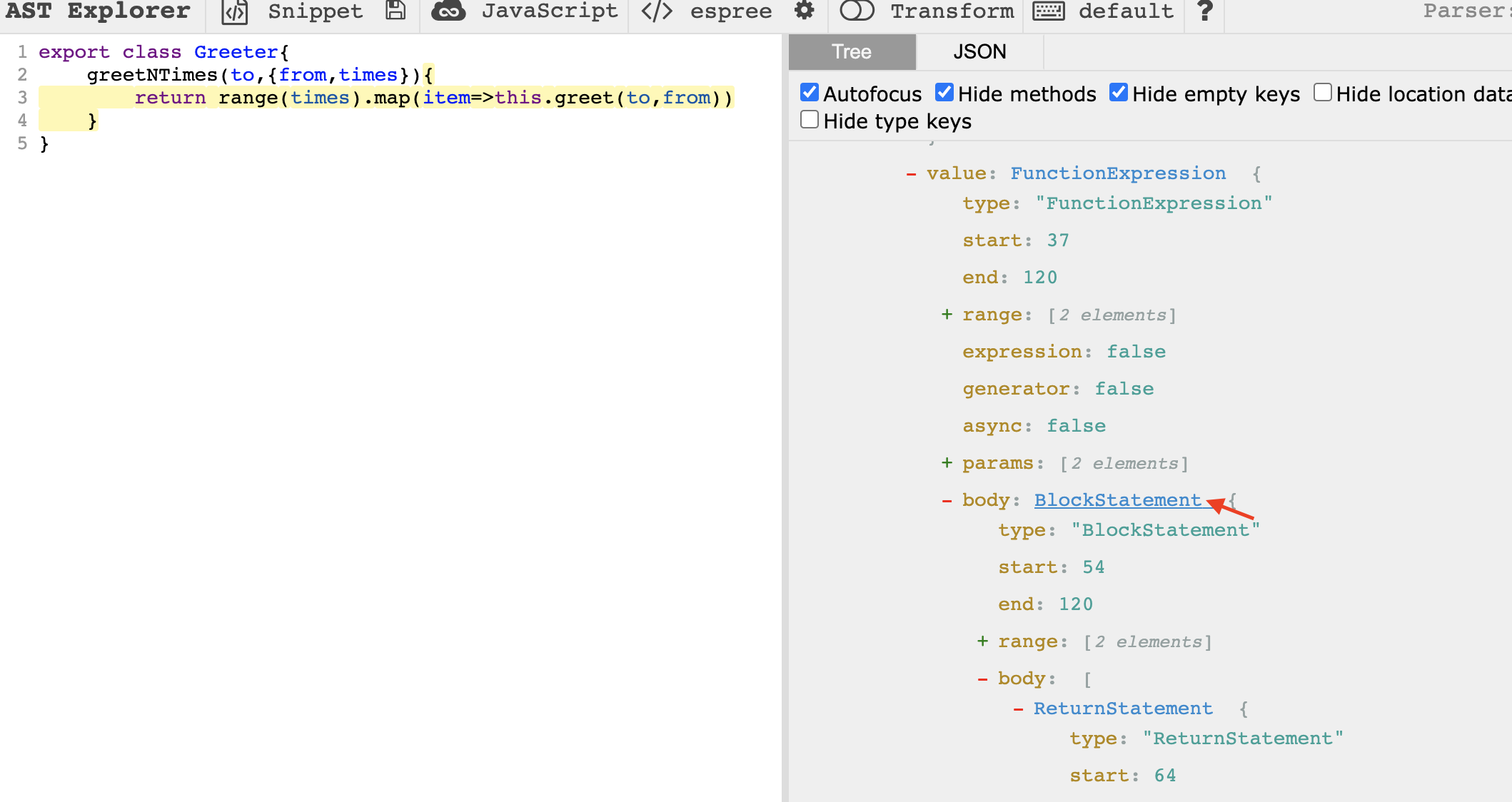
我们先去 astexplorer 观察下缩进的结构。
将鼠标移动到 AST 对应的节点上,左边面板的相应代码会高亮,可以观察到需要处理缩进的是 ClassBody 和 BlockStatement 里的内容。
很明显,生成的代码缺少缩进。如何按层级结构添加相应数量的缩进呢?
我们先去 astexplorer 观察下缩进的结构。
将鼠标移动到 AST 对应的节点上,左边面板的相应代码会高亮,可以观察到需要处理缩进的是 ClassBody 和 BlockStatement 里的内容。
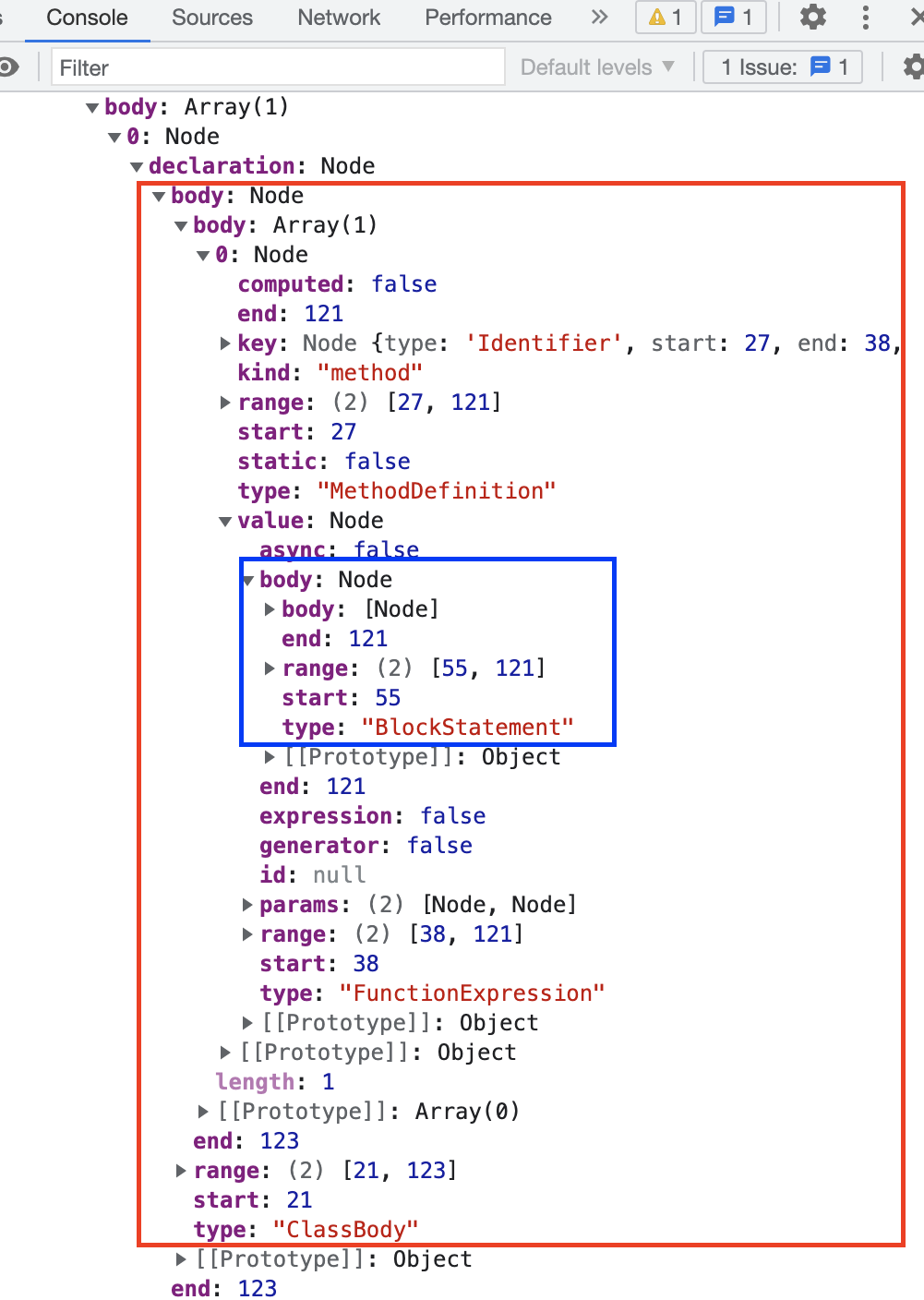
 在控制台将 ast 打印出来,发现节点里没有记录嵌套层级的字段:
在控制台将 ast 打印出来,发现节点里没有记录嵌套层级的字段:
 而判断缩进则需要知道对应的层级关系,所以我们要对 ast 进行遍历处理,添加字段 indentCount。
实现 astAddIndentCount()
将 ast.body 传入函数。
而判断缩进则需要知道对应的层级关系,所以我们要对 ast 进行遍历处理,添加字段 indentCount。
实现 astAddIndentCount()
将 ast.body 传入函数。
可以将上述初始化 indentCount 和处理 class 内缩进的代码提取出来,单独封装成函数,功能独立。
经过 astAddIndentCount() 处理后的 ast 节点如下图所示: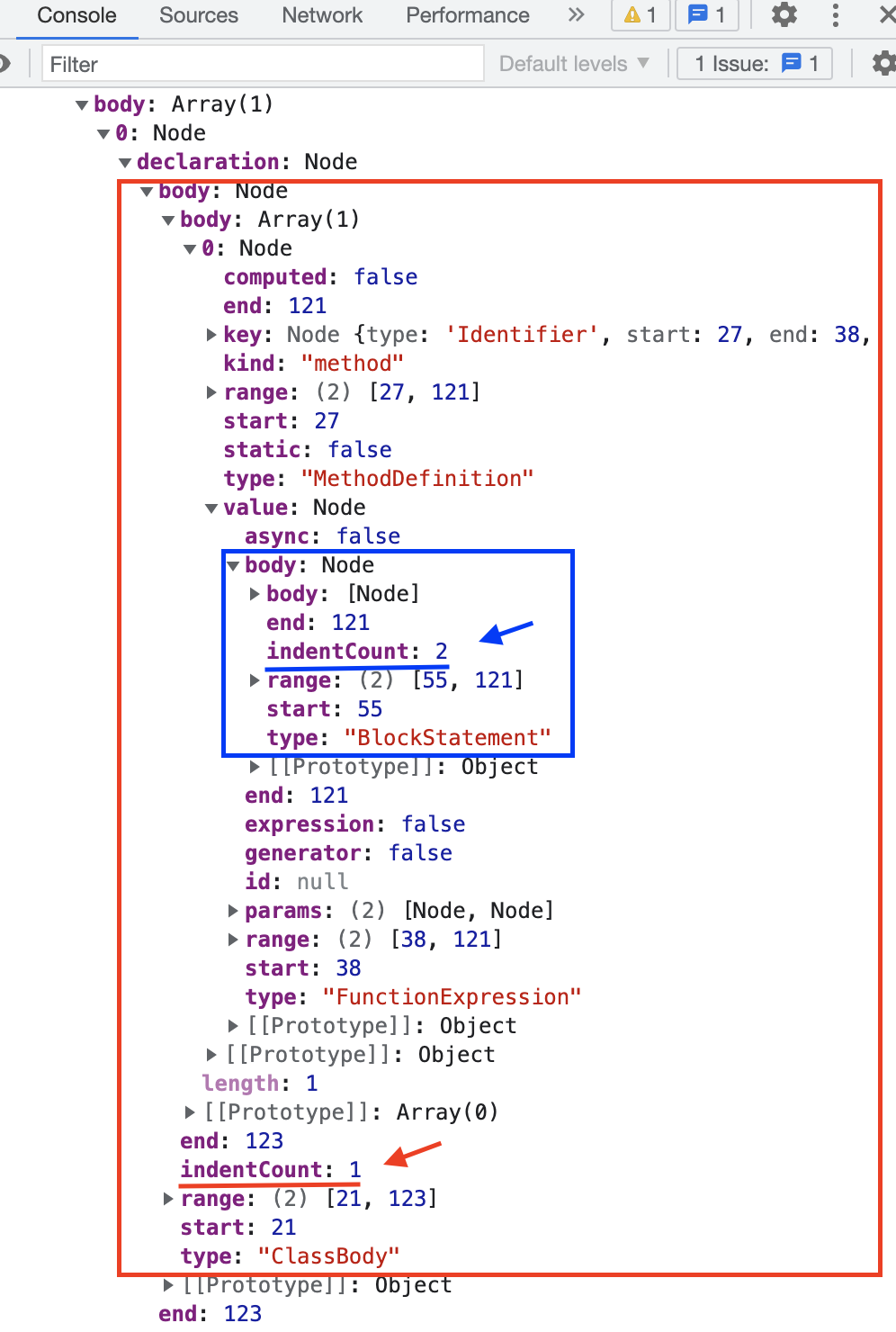 这时我们就可以用 indentCount 字段来添加缩进了。观察代码结构可得,ClassBody 内容单行需添加一个缩进,BlockStatement 内容单行需添加两个缩进,末尾花括号前添加一个缩进。
这时我们就可以用 indentCount 字段来添加缩进了。观察代码结构可得,ClassBody 内容单行需添加一个缩进,BlockStatement 内容单行需添加两个缩进,末尾花括号前添加一个缩进。
 回到 codeGen() 函数,对 'ClassBody' 和 'BlockStatement' 进行缩进处理。
回到 codeGen() 函数,对 'ClassBody' 和 'BlockStatement' 进行缩进处理。
此时便实现了补全缩进处理,其他节点处理逻辑同理。 在选项面板中添加 indent 配置,控制单个 indent 的空格数。
添加事件之后,便可实现如下格式化效果: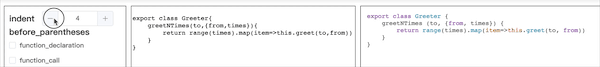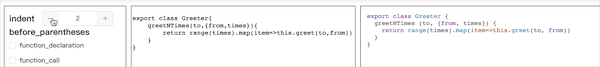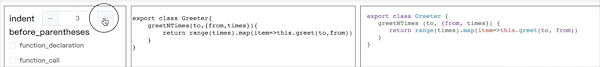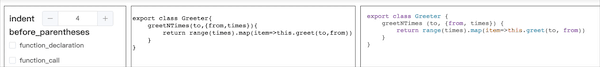
处理细节
处理完缩进和空格之后,对着 Webstorm 的配置进行检查。发现如下细节问题。
Function 多余空格
当同时选中空格配置 function_declaration 和 function_expression 时,发现 function 有多余空格,如图所示: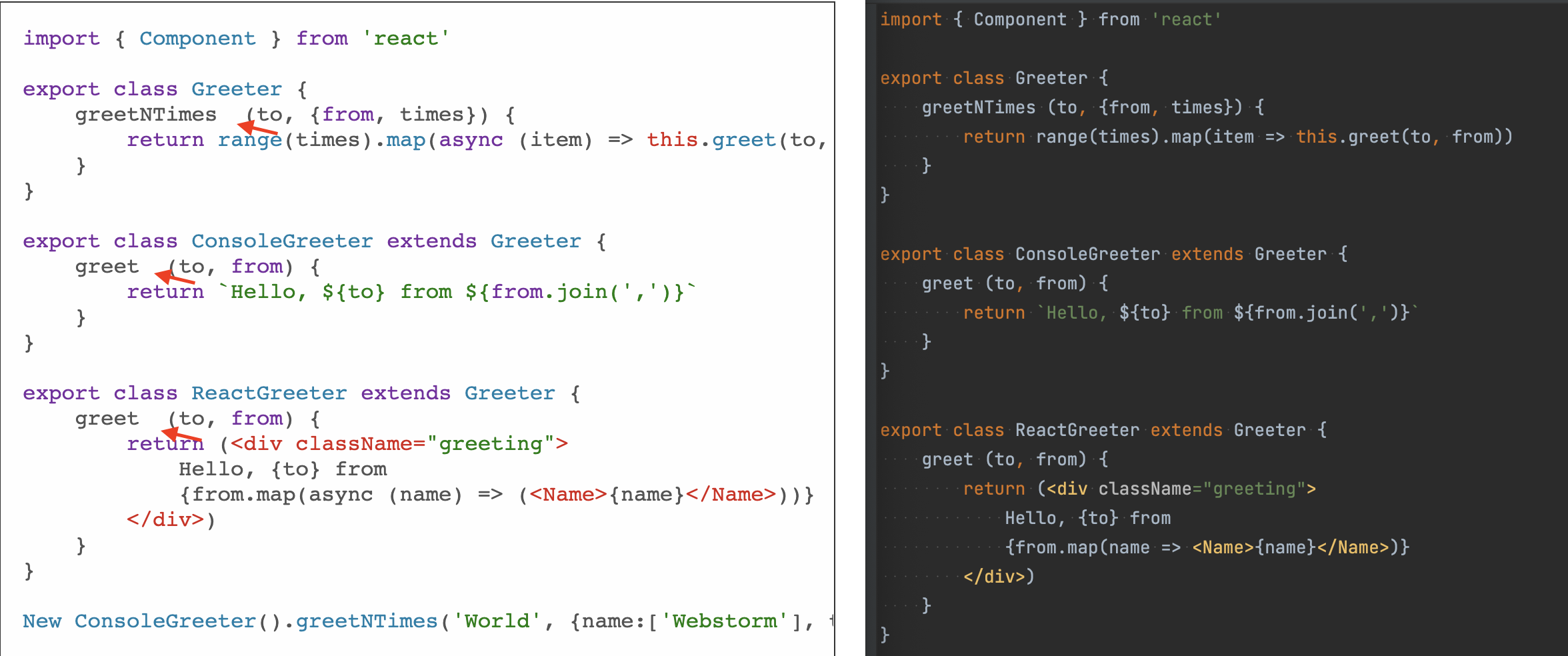 检查 AST 可见,function_declaration 是处理 MethodDefinition 情况的空格,function_expression 是处理 VariableDeclarator 情况的空格。
检查 AST 可见,function_declaration 是处理 MethodDefinition 情况的空格,function_expression 是处理 VariableDeclarator 情况的空格。
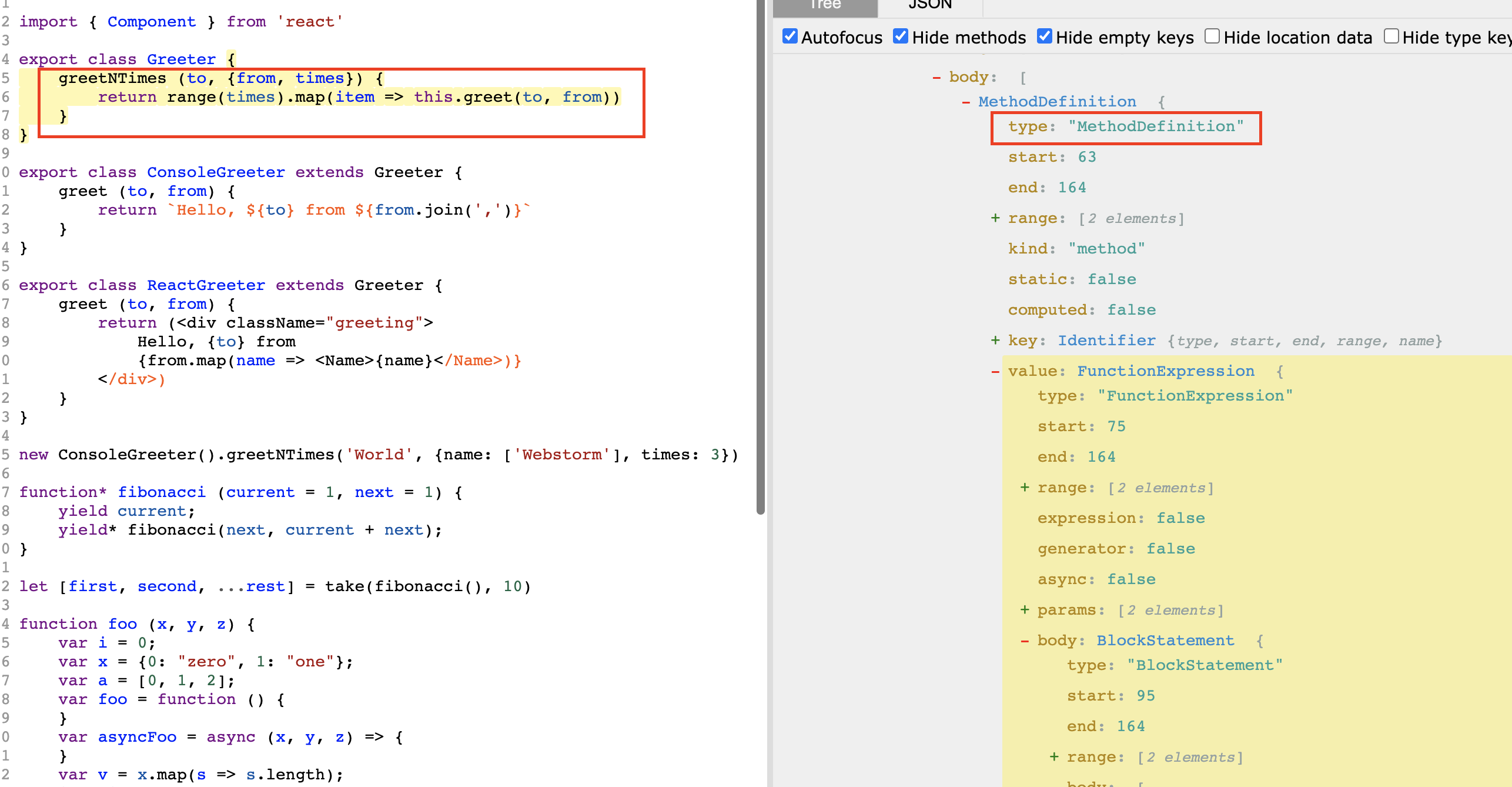
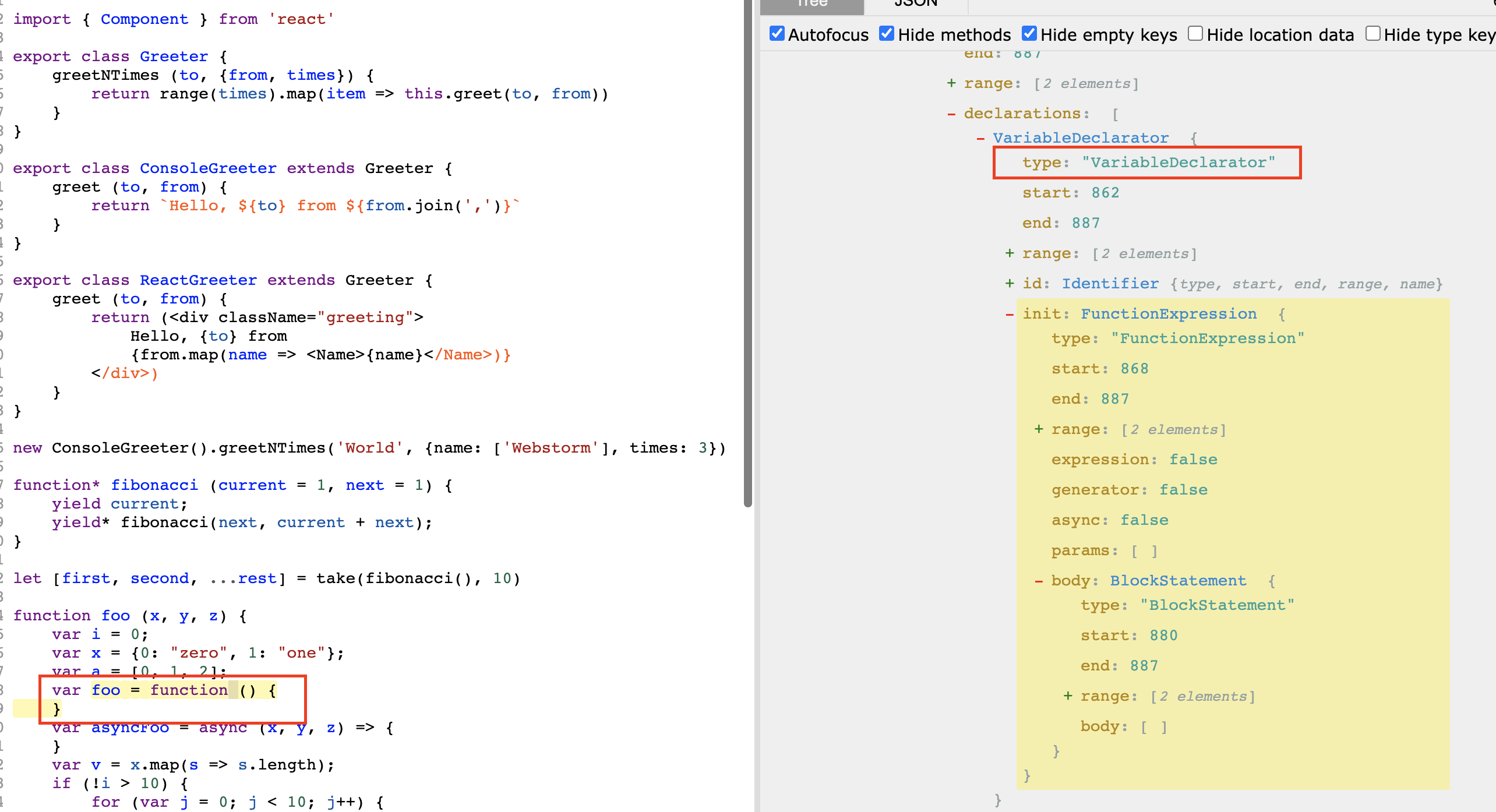 而处理的节点 type 都是 FunctionExpression,所以需要根据父节点的 type 进行判断。由于需要增加传参,则将之前 codeGen() 里的 if-else 判断拆分为独立的函数。
而处理的节点 type 都是 FunctionExpression,所以需要根据父节点的 type 进行判断。由于需要增加传参,则将之前 codeGen() 里的 if-else 判断拆分为独立的函数。
处理完即可正常显示: