react test
React test utils
- showRender
- renderIntoDocument `
- findRendered DOMComponentWithTag
- scryRenderedDOMComponents With Tag
- Simulate Clicks Keypresses Etc.`
Open kurtzace opened 5 months ago
React test utils
pkellner/pluralsight-using-hooks-in-react18 and the books
Sapling to view React component tree
useEffect(() => { return () => {} }, [])
Basic Hooks useState, useEffect, useContext Additional Hooks useReducer, useCallback, useMemo, useRef, uselmperativeHandle, useLayoutEffect, useDebugValue, useDeferredValue, useTransition, useld Library Hooks useSyncExternalStore, uselnsertionEffect
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer (reducer, initialArg, init); reducer: A function that takes in 2 parameters, state and action and returns a new state. initialArg: The starting value of state. init: A function that returns the starting state
const imgRef = useRef();
return (
<div className="container">
<img src="/images/Speaker-1124.jpg"
ref={imgRef}
style={{ filter: "grayscale (100%)" }} onMouseOver={() => {
}}
imgRef.current.style.filter = "grayscale (0%)";|
/>In a controlled component, the from values are managed by React and not the DOM. They do not require us to use refs. They do not require us to write imperative code. const [title, setTitle] = useState("");
<input value={title} onChange={event => setTitle(event.target.value)}
or even better - make input hook
export const useInput = initialValue => {
const [value, setValue] = useState(initialValue);
return [
{ value, onChange: e => setValue(e.target.value) },
() => setValue(initialValue)
];
};
// then
const [titleProps, resetTitle] = useInput("");
<input {...titleProps}usecontext usage image
prop drilling
- Train from San Francisco to DC
vs useContext
- Flight from San Francisco to DC
export const ColorContext = createContext();
render( <ColorContext.Provider value={{ colors }}> <App />later somewhere in middle of app
const { colors } = useContext(ColorContext);
old way was
<ColorContext.Consumer>
{context => {stateful providers
ColorProvider ({ children }) {
const [colors, setColors] = useState(colorData);
return (
<ColorContext.Provider value={{ colors, setColors }}>
{children}
</ColorContext.Provider>Instead of exposing the ColorContext instance, we can create a hook called useColors that returns the colors from context:
const ColorContext = createContext();
export const useColors = () => useContext(ColorContext);
// then things will be as simple as
<ColorProvider>
<App />
</ColorProvider>
//later
const { colors } = useColors();useEffect(() => {
console.log(`saved phrase: "${phrase}"`);
}, [phrase]);but cautions - phrase is not a deep dependency
instead of
useEffect(() => {
console.log(`saved phrase: "${phrase}"`);
});also remember to destroy, remove event listeners
useEffect(() => {
newsFeed.subscribe(addPost);
window.addEventListener("keydown", forceRender);
return () => {
newsFeed.unsubscribe(addPost);
window.removeEventListener("keydown", forceRender);
};
}, []);another lifecycle
useLayoutEffect is called at a specific moment in the render cycle. The series of events is as follows:
Render
useLayoutEffect is called
Browser paint: the time when the component’s elements are actually added to the DOM
useEffect is calledexample things inside useLayoutEffect
setWidth(window.innerWidth);
setHeight(window.innerHeight);words are calculated with every render? how about
const words = useMemo(() => children.split(" "), [children]);
even memo pure components
const Cat = ({ name }) => {
console.log(`rendering ${name}`);
return <p>{name}</p>;
};
const PureCat = memo(Cat);
const RenderCatOnce = memo(Cat, () => true);
const AlwaysRenderCat = memo(Cat, (prevProps, nextProps) => false);useCallback can be used like useMemo, but it memoizes functions instead of values. For example:
const memoizedCallback = useCallback(() => { //.. do something with a & b }, [a, b])
useCallback is to prevent a component from re-rendering unless its props have changed.
above both replaces shouldComponentUpdate
const [checked, setChecked] = useState(false);
function toggle() {
setChecked(checked => !checked);
}
return (
<>
<input type="checkbox" value={checked} onChange={toggle} />better is
const [checked, toggle] = useReducer(checked => !checked, false);
const [number, setNumber] = useReducer(
(number, newNumber) => number + newNumber,
0
);some have habit of doing const [user, setUser] = useState(firstUser);
then setUser({ ...user, admin: true }); //imagine bug is there when developer forgets spread
or better is
const [user, setUser] = useReducer(
(user, newDetails) => ({ ...user, ...newDetails }),
firstUser
);then setUser becomes as simple as setUser({ admin: true });
AMUL Butter: Teach everyone to spread, they’ll spread for a day. Teach everyone to useReducer and they’ll spread for life.
function counterReducer(state = { count: 0 }, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return { count: state.count + 1 };
case 'DECREMENT':
return { count: state.count - 1 };
default:
return state;
}
}
const store = createStore(counterReducer);
store.subscribe(() => console.log(store.getState()));
store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' });
store.dispatch({ type: 'DECREMENT' });redux-thunk is a middleware that allows you to call action creator functions that return a function instead of an action object.
function fetchUserData() {
return (dispatch) => {
dispatch({ type: 'LOADING_USER_DATA' });
fetch('/api/user')
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => dispatch({ type: 'FETCH_USER_DATA_SUCCESS', payload: data }))
.catch((error) => ....;
};
}
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk));
store.dispatch(fetchUserData());hooks
const count = useSelector((state) => state.count);
const dispatch = useDispatch();for lighter weight / libraries
class Store {
@observable count = 0;
@action increment() {
this.count += 1;
}
@action async fetchCountFromServer() {
const response = await fetch('/count');
const data = await response.json();
this.count = data.count;
}
}
const myStore = new Store();
//later
import { observer } from 'mobx-react';
import myStore from './myStore';
const Counter = observer(() => {
return (
<div>
<div>Count: {myStore.count}</div>
3rd party: redux, mobx, recoil
Remote: react query, swr, relay/Apollo
Webstore: local, session , index db
Local state
Lifted state
Derived : length of array
Refs : dom, uncontrolled components, non react libs , hold timer, track of component is mounted, store prev state value, undo ,redo
Url
npm install eslint-plugin-jsx-a11ynpm install eslint-plugin-react-hooks --save-dev or npx eslint --init / npx eslint sample.js sudo npm install -g prettier / prettier --write "sample.js" or Prettier in VSCode - may cause nightmare to code reviewer unless entire project has enabled it through prettier rc filenpm install prop-types --save-dev
import PropTypes from "prop-types";
App.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string
};
npm install --save flow-bin//@flow
type Props = { item: string };
function App(props: Props) { //... }
3. TypeScript
class/enum/types/interfaces/primitieves/tuple/ OOPS
## Testing
jestdescribe("Math functions", () => { test("Multiplies by two", () => { expect(timesTwo(4)).toBe(8); });
simple reactconst div = document.createElement("div");
ReactDOM.render(
react testing libraryimport { toHaveAttribute } from "@testing-library/jest-dom"; expect.extend({ toHaveAttribute });
test("renders a star", () => {
const div = document.createElement("div");
ReactDOM.render(
//or better
import { render, fireEvent } from "@testing-library/react";
test("renders an h1", () => {
const { getByText } = render(
const { getByLabelText } = render(
});
or include all matchersimport * as matchers from "@testing-library/jest-dom/matchers"; expect.extend(matchers); afterEach(() => { cleanup(); });
reduce the getBy... with
<input ... data-testid="checkbox" // Add the data-testid= attribute />
getByTestId("checkbox");
Jest ships with Istanbul for code coverage
const { result } = renderHook(() => useCounter()); expect(result.current.count).toBe(0);
#### vite test
"npm install -D vitest"import { beforeAll, describe, expect, it, vi } from 'vitest'; import { getSteps } from './ios-health-kit'; describe('IOS Health Kit', () => { beforeAll(() => { vi.mock('./ios-health-kit', () => ({ getSteps: vi.fn().mockImplementation(() => 2000), })); }); it('should return steps', () => { expect(getSteps()).toBe(2000); expect(getSteps).toHaveBeenCalled(); }); });
Mock Service Worker for mocking server requests. It allows you to mock REST and GraphQL requests very flexibly.
import { http, HttpResponse } from 'msw'; import { setupServer } from 'msw/node'; import { describe, it, expect, beforeAll, afterEach, afterAll } from 'vitest'; const server = setupServer( http.get('https://api.github.com/users', () => { return HttpResponse.json({ firstName: '.... }); }) ); describe('Mocked fetch', () => { beforeAll(() => server.listen()); afterEach(() => server.resetHandlers()); afterAll(() => server.close()); it('should returns test data', async () => { const response = await fetch('https://api.github.com/u
fake timers
describe('delayed execution', () => { beforeEach(() => { vi.useFakeTimers() }) afterEach(() => { vi.restoreAllMocks() }) it('should execute the function', () => { executeInMinute(mock) vi.runAllTimers() expect(mock).toHaveBeenCalledTimes(1) }) it('should not execute the function', () => { executeInMinute(mock) vi.advanceTimersByTime(2) expect(mock).not.toHaveBeenCalled() })
spyable fake functions
exampleconst selector = (onSelect: (value: string) => void) => { onSelect('1'); onSelect('2'); onSelect('3'); };
test('selector', () => { const onSelect = vi.fn(); selector(onSelect); expect(onSelect).toBeCalledTimes(3); expect(onSelect).toHaveBeenLastCalledWith('3'); });
const spy = vi.spyOn(cart, 'getProducts');
#### React test utils
- showRender
- renderIntoDocument
`
- findRendered DOMComponentWithTag
- scryRenderedDOMComponents With Tag
- Simulate
Clicks
Keypresses
Etc.`
## Playwright - Automated Software testing
[Automated Software Testing with Playwright](https://cisco.udemy.com/course/automated-software-testing-with-playwright/)
BDD cucumber
Page object model
by Microsoft
headless vs headful
python, java, net, javascript*
Fast
no need to wait
------
.prettierrc
`{ semi false, singleQuote true}`
`npm i @playwright/test`
`npx playwright install` installs chromium, webkit, firefox, ffmpeg
import {test, expect} from @playwright/test test('...', async ({page})=> { await page.goto("https://...") const pt = await page.locator('h1') await expect(pt).toContainText('.....') })
`npx playwright test` or `npx playwright test --headed` or `npx playwright test --browser=firefox` or `...--browser=all`
or `.... tests/example.spec.ts`
-----
page.click('#btnId') page.click('text=Sign In') const err= await page.locator('.myClassName') expect(err).toContainText('...') page.click('//button') page.fill('#username', '........') //to type expect(page).toHaveUrl('https://...'). to HaveTitle
expect(elem).toHaveCount(1)
----
to skip `test.skip`, test.only
test.describe('',()=> {
}
`npx playright test --grep @myTag` if `test('asse.. @myTag'`. -grep-invert to ignore
playright.config.tsimport {PlaywrightTestConfig} from @.../test
config config:playwrightTestConfig = { timeout: retries: use { headless: true viewport:{width:1280,} actionTimeout ignoreHttpsErrors: video: 'off' screenshot: off' projects:[{name: uses:{browserName:'webkit'}}] } ...test --config=```
--reporter=html/junit/lline
npx playwright show-report
await page.screenshot({path:'screen.png', fullPage:true})
const elem = await page.$('h1')
await elem.screnshot({path:})beforeEach, afterAll
export async function loadHomepage(page) {await page.togo('')}
React Fiber in 2017. Fiber was a rewrite of React’s rendering algorithm that was sort of magical in its execution. It was a full rewrite of React’s internals that changed barely anything about the public API
The compose function is a higher-order function. It takes functions as arguments and returns a single value:
const compose = (...fns) => arg =>
fns.reduce((composed, f) => f(composed), arg);converts const both = date => appendAMPM(civilianHours(date)); to
const both = compose(
civilianHours,
appendAMPM
);
both(new Date());const dan = {
type: "person",
data: {
gender: "male",
info: {
id: 22,
fullname: {
first: "Dan",
last: "Deacon"
}
}
}
};
deepPick("type", dan); // "person"
deepPick("data.info.fullname.first", dan); // "Dan"
const deepPick = (fields, object = {}) => {
const [first, ...remaining] = fields.split(".");
return remaining.length
? deepPick(remaining.join("."), object[first])
: object[first];
};event.preventDefault() , event.stopPropagation()
const max = ages.reduce((max, value) => (value > max ? value : max), 0);
or
when we want to add hash to array
const colors = [
{
id: "wfsfs",
title: "myTitle",
rating: 4
},.....]
const hashColors = colors.reduce((hash, { id, title, rating }) => {
hash[id] = { title, rating };
return hash;
}, {});
will give {"wfsfs": {title, rating}}Array.reduceRight end to begin
React.createElement(
"ul",
{ className: "ingredients" },
React.createElement("li", null, "2 lb salmon"),or create class
const IngredientsList = React.createClass({
displayName: "IngredientsList",
render() {
return React.createElement(or classbased
class IngredientsList extends React.Component {
render() {
return React.createElement(to be replaced by
ReactDOM.render(
<Menu recipes={data} title="Delicious Recipes" />,
document.getElementById("root")
);
and
function Menu({ title, recipes }) {
return (
<article>
<header>
<h1>{title}</h1>
and newer way is Render is now become createRoot in react 18
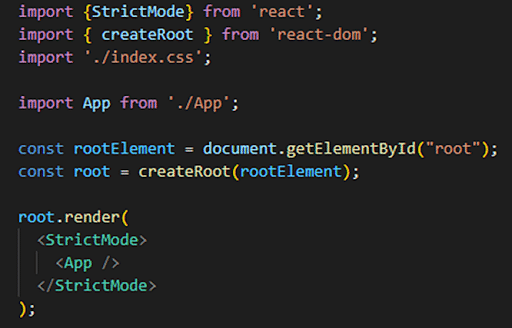
npm install --save-dev webpack webpack-cli @babel/preset-env @babel/preset-react
.babelrc:
{
"presets": ["@babel/preset-env", "@babel/preset-react"]
}simplest // ./webpack.config.js
var path = require("path");
module.exports = {
entry: "./src/index.js",
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, "dist", "assets"),
filename: "bundle.js"
},
module: {
rules: [{ test: /\.js$/, exclude: /node_modules/, loader: "babel-loader" }]
},
devtool: "#source-map" // Add this option for source mapping
};instead of all of above
npm install -g create-react-app
function handleClick() { setIsFetching(false); setError(null); setFormStatus('Success'); }to force a refresh to specific state
import { flushSync } from "react-dom";
function handleClickWithFlush() {
// will force a render
flushSync(() => {
setCount((c) => c + 1);
});
// will cause another render
setIsEven((count + 1) % 2 === 0);
}// Urgent: Show what was typed
setInputValue(input);
//Mark any state updates inside as transitions
startTransitions (() => { // Transition: Show the results
setSearchQuery(input); }); const specialPromiseResource = getSpecialProgisetofetchlteas();
return ( <Suspense fallback={<div>Loading Itens</div>)>
<FoodList resource={specialPromiseResource} />
</Suspense> instead of
{loading ? (
<p>Loading please wait...</p>
) : (
<ListUniversities list={data} />
)}after
image
also see Render is now become createRoot in react 18

new hooks a. useId : like uuid b. useDeferredValue : debouncing
New way to create
npm create vite@latest my-react-app -- --template react
best to use in useEffect
fetch(`https://api.github.com/users/moonhighway`)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(console.log)or
const response = await fetch(
`https://api.github.com/users/${githubLogin}`
);
const userData = await response.json();images
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append("username", "moontahoe");
formData.append("fullname", "Alex Banks");
forData.append("avatar", imgFile);how about make a hook
export function useFetch(uri) {
const [data, setData] = useState();
const [error, setError] = useState();
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
...useEffect(() => { .....fetch
...
return {
loading,
data,
error
};waterFall
<Fetch
uri={`https://api.github.com/users/${login}/repos`}
renderSuccess={({ data }) => (
<RepoMenu repositories={data} onSelect={onSelect} />
)}
/>
vs parallel
<>
<SearchForm value={login} onSearch={setLogin} />
<GitHubUser login={login} />
<UserRepositories login={login} repo={repo} onSelect={setRepo} />
<RepositoryReadme login={login} repo={repo} />
</>Waiting for Values {login && <GitHubUser login={login} />}
GraphQL API
const query = `
query findRepos($login: String!) {
user(login: $login) {
login
name
location
avatar_url: avatarUrl
repositories(first: 100) {
totalCount
nodes {
name
} } } }
`import { GraphQLClient } from "graphql-request";
const client = new GraphQLClient(url, {headers ...)
client
.request(query, { login: "moontahoe" })react-window and react-virtualized. Virtualized lists are so important that React Native even ships with one: the FlatList
import { FixedSizeList } from "react-window";
<FixedSizeList
height={window.innerHeight}
width={window.innerWidth - 20}
itemCount={bigList.length}
itemSize={50}
>{renderRow}
</FixedSizeList>export default class ErrorBoundary extends Component {
state = { error: null };
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
return { error };
}
render() {
const { error } = this.state;
const { children, fallback } = this.props;
if (error) return <fallback error={error} />;
return children;
}
}
function ErrorScreen({ error }) {....
<ErrorBoundary fallback={ErrorScreen}>
<App />
</ErrorBoundary>;const Main = React.lazy(() => import("./Main"));
then
<Suspense fallback={<ClimbingBoxLoader />}>
<Main />
</Suspense>
axios.get('http://example.com/data')
.then(response => console.log(response.data))interceptors
this.apiInstance = axios.create({
baseURL: "https://api.github.com",
});
this.apiInstance.interceptors.request.use((config) => {
console.log("Request:", '${config.method?.toUpperCase()} ${config.url}');
return config;
});
this.apiInstance.interceptors.response.use(
(response) => {
const queryClient = new QueryClient();
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root")!).render(
<QueryClientProvider client={queryClient}>
const userFetcher = (username: string) =>
fetch("https://api.github.com/users/sakhnyuk")
.then((response) => response.json());
const {
data: user,
isPending,
isError,
} = useQuery({
queryKey: ["githubUser"],
queryFn: () => userFetcher("sakhnyuk"),
});
// naive
import { useQuery } from 'react-query';
function UserProfile({ userId }) {
const { data, error, isLoading } = useQuery(userId, fetchUser);
const socket = new WebSocket('ws://example.com');
socket.onopen = function(event) {
console.log('Connection established');
};import { BrowserRouter as Router, Link } from "react-router-dom";
render(
<Router>
<App />
</Router>,
App() {
return (
<div>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<Home />} />
<Route
path="/about"
element={<About />}
/>
<Route
path=":id"
element={<ColorDetails />}
/>
<Redirect
from="services"
to="about/services"
/>
<Route path="*" element={<Whoops404 />} />
<Link to="about">About</Link>
and inside Whoops404 let location = useLocation(); {location.pathname}
or how about
let element = useRoutes([
{ path: "/", element: <Home /> },
{
path: "about",
element: <About />,
children: [Params
ColorDetails() { let params = useParams();
to go navigate from inside js
let navigate = useNavigate(); navigate(/${id})}
const query = new URLSearchParams({ msg: "From Query" });
React frameworks include Next.js, Gatsby, and Remix.
Why? Seo/static/
npm install isomorphic-fetch
and
ReactDOM.renderToString, ReactDOM.hydrate instead of ReactDOM.render.
example
app.get("/*", (req, res) => {
const app = ReactDOMServer.renderToString(
<Menu />
);
});const nodeExternals = require("webpack-node-externals");
Server Rendering with Next.jsPets.getInitialProps = async function() {
Rehydration: Loading JavaScript views on the client to reuse the server-rendered HTML’s DOM tree and data.
Prerendering Running a client-side application at build time and capturing initial state as static HTML.
force-dynamic value. This parameter explicitly tells Next.js that we want to generate a new page for each request.
Expo now supports web development, allowing you to run your app on the web using React Native for Web. This means that you can develop apps that work on Android, iOS, and the web using a single code base. Additionally, the Tamagui UI kit
JS engines such as V8, SpiderMonkey, and others, React Native also contains a JS virtual machine.
React Native started using the new Hermes virtual machine, and from 0.64
Our entire application structure is packaged into a single file using the Metro bundler. It is also responsible for transpiling JSX code into JS. If we want to use TypeScript, Babel can support it. It
React 18
course1 And book React and React Native - Fifth Edition -Adam
And Book learning-react-2nd Edition - Alex Banks
Useful courses
Book
PluralSight and Udemy
Concurrent features:
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}><div>UI...</div> </Suspense>, lifecycle with useTransitionimport { useTransition, useState } from 'react'; function App() { } const [isPending, startTransition] = useTransition(); const [someState, setSomeState] = useState(); const someEvent = (event) => { } startTransition (() => { }); setSomeState(event.target.value); return <SlowComponent value={someState} />;Online course editors: CodeSandbox, StackBlitz, and Replit.
React frameworks include Next.js, Gatsby, and Remix
Vite generate:
npm create vite@latest my-react-app -- --template reactRenderers: React DOM, React Native, React PDF, and React Unity.
useCallback and useMemo: These Hooks are used for performance optimization. useCallback memoizes a function, preventing it from being recreated on every render, while useMemo memoizes a value, recomputing it only when its dependencies change.
"const inputRef = React.useRef(null);"
nav and routes
declare async routes
then use loaded data
children
lazy component
or better use
Lazy components need to be rendered inside of a Suspense component.
Material UI React library
import Typography from "@mui/material/Typography"; import Container from "@mui/material/Container";grid stack
useLocation()
to get the current pathnameMUI menu
<FormControl> <InputLabel id="select-label">My Select</InputLabel> <Select..<MenuItem ..<Button variant="contained"/outlinedCompose function
const both = date => appendAMPM(civilianHours(date));orconst both = compose( civilianHours, appendAMPM); both(new Date());const compose = (...fns) => arg => fns.reduce((composed, f) => f(composed), arg);Long form of JSX
React.createElement( "ul", { className: "ingredients" }, React.createElement("li", null, "2 lb salmon")input pattern
instead of copying pasting
value={title} onChange={event => setTitle(event.target.value)}then use it like<input {...colorProps}Context
retrieve it later using
const { colors } = useContext(ColorContext);instead of<ColorContext.Consumer>{context => {Context + Hook
imagine we have a ColorProvider
we can have a hook
const ColorContext = createContext(); export const useColors = () => useContext(ColorContext);wrapped under `,`
later
const { colors } = useColors();orconst { rateColor, removeColor } = useColors();useLayoutEffect
useLayoutEffect is called at a specific moment in the render cycle. The series of events is as follows: