class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode* p = head;
if (p == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
int n = 1;
while (p->next)
{
p = p->next;
n++;
}
p->next = head;
k = k % n;
p = head;
int i = 1;
while (i < n - k)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
ListNode* newHead = p->next;
p->next = nullptr;
return newHead;
}
};
61. 旋转链表
入选理由
暂无
题目地址
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-list/
前置知识
题目描述
示例 1:
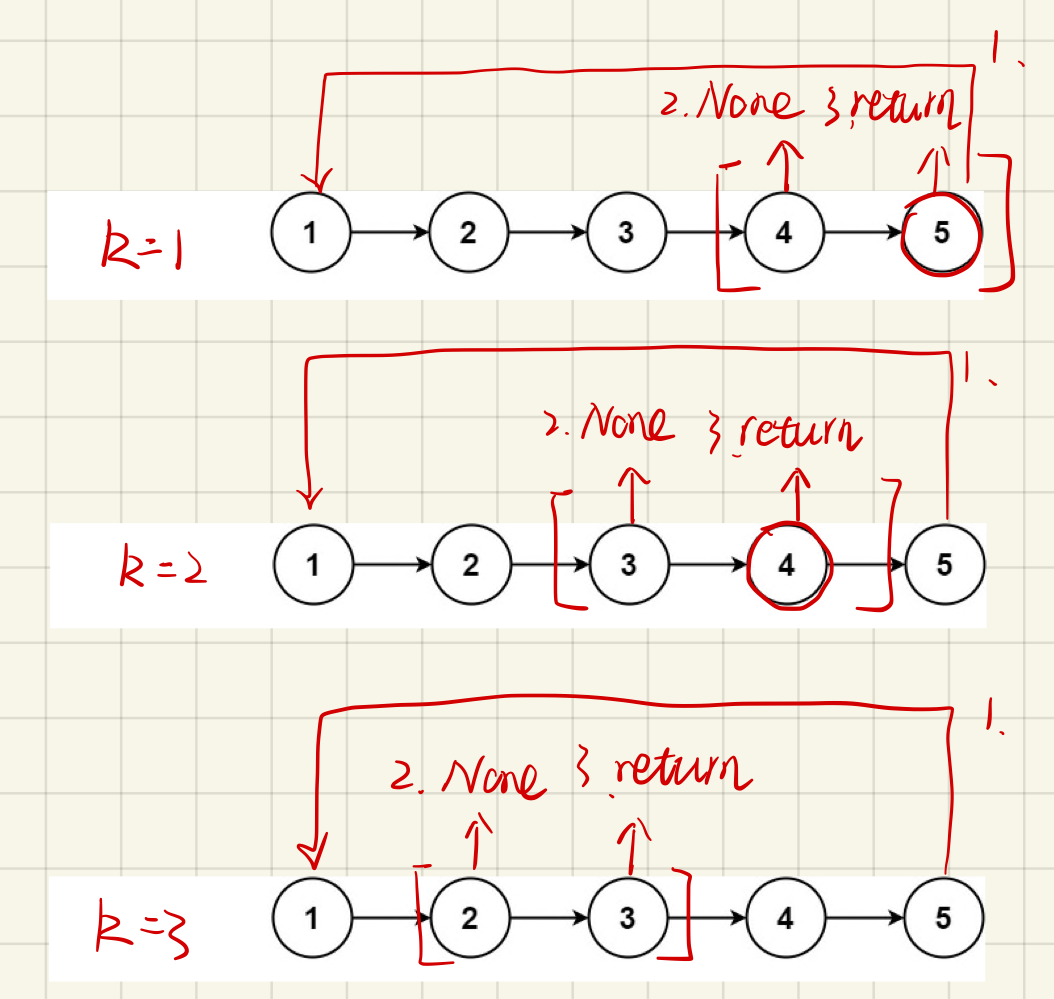
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2 输出: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL 解释: 向右旋转 1 步: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL 向右旋转 2 步: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL 示例 2:
输入: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4 输出: 2->0->1->NULL 解释: 向右旋转 1 步: 2->0->1->NULL 向右旋转 2 步: 1->2->0->NULL 向右旋转 3 步: 0->1->2->NULL 向右旋转 4 步: 2->0->1->NULL