/**
- Definition for a binary tree node.
- function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
- this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
- this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
- this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
- } */ /**
- @param {TreeNode} root
- @return {number} */
var traves = (node,depth)=>{ if(!node){ return null } const left = traves(node.left,depth+1) const right = traves(node.right,depth+1) if(!left && !right){ node.depth = depth } else if(!right || (left && left.depth >= right.depth)){ node.depth = left.depth node.val = left.val } else { node.depth = right.depth node.val = right.val }
return node } var findBottomLeftValue = function(root) { return traves(root,0).val };
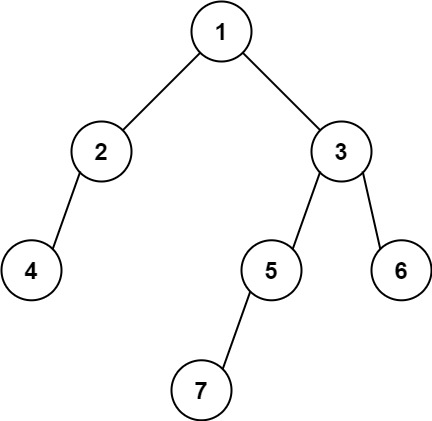
513. 找树左下角的值
入选理由
暂无
题目地址
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/
前置知识
暂无
题目描述