思路: 快慢指针 先处理边界条件,若为空,返回nil for fast.Next != nil && fast.Next.Next != nil 慢指针走一步,快指针走两步。当快慢指针相遇,快指针从头开始移动。 当快慢指针相等时返回对应指针。 如果没有环,for循环结束,直接返回nil
func detectCycle(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil{
return nil
}
slow := head
fast := head
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil{
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
if slow == fast{
fast = head
for slow != fast{
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next
}
return slow
}
}
return nil
}时间复杂度:O(n) 空间复杂度:O(1)
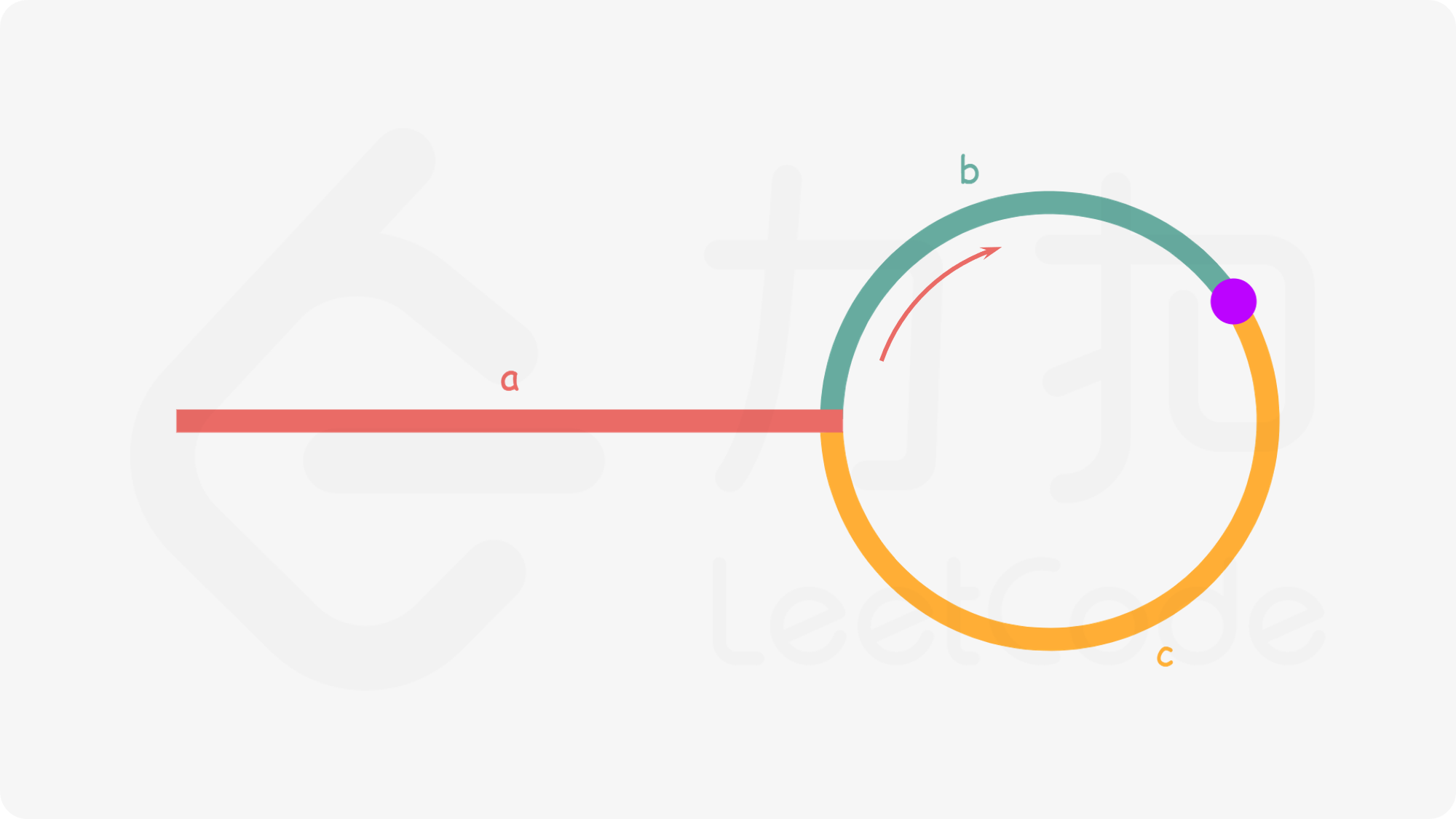
142. 环形链表 II
入选理由
暂无
题目地址
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
前置知识
暂无
题目描述