class Solution:
def sortedListToBST(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not head:
return head
pre ,slow , quick = None,head,head
while quick and quick.next:
pre = slow
slow = slow.next
quick = quick.next.next
#print(pre==head)
if pre:
pre.next = None
a = TreeNode(slow.val)
if quick == slow:
return a
a.left = self.sortedListToBST(head)
a.right = self.sortedListToBST(slow.next)
return a
![计算机生成了可选文字: Python 函 数 可 以 返 回 多 种 类 型 的 值 与 其 他 编 程 语 言 不 同 , python 函 数 不 限 于 返 回 单 一 类 型 的 值 。 如 果 您 昏 它 没 有 任 何 有 关 它 可 以 返 回 的 内 容 的 信 息 。 让 我 们 看 一 个 示 例 , 其 中 函 数 将 返 回 多 种 类 型 的 值 。 def get_demo_data(object_type): if ' s t r ' object_type : return 'test' elif 'tuple' object_type: ( 1 , 2 , 3 ) object_type: [ 1 , 2 , 3 ] object_type : None return elif ' 1 i s t ' return elif ' d i c t ' return else: return](file:///C:/Users/lx2019/AppData/Local/Temp/msohtmlclip1/01/clip_image001.png)
109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树
入选理由
暂无
题目地址
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-sorted-list-to-binary-search-tree/
前置知识
题目描述
本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
示例:
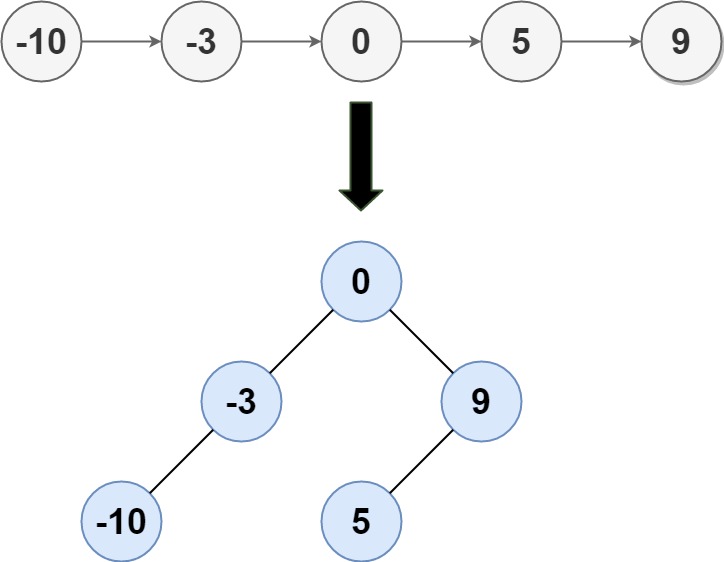
给定的有序链表: [-10, -3, 0, 5, 9],
一个可能的答案是:[0, -3, 9, -10, null, 5], 它可以表示下面这个高度平衡二叉搜索树:
-3 9 / / -10 5