class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {
vector<int> res;
if (words.empty()) return res;
int m = words.size(), w = words[0].size(), mw = m * w, cnt = 0;
unordered_map<string, int> wf, wd;
for (auto& word : words) wf[word]++;
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) {
for (int j = i; j + w <= s.size(); j += w) {
if (j >= i + mw) {
string word = s.substr(j - mw, w);
wd[word]--;
if (wd[word] < wf[word]) cnt--;
}
string word = s.substr(j, w);
wd[word]++;
if (wd[word] <= wf[word]) cnt++;
if (cnt == m) res.push_back(j - (m - 1) * w);
}
wd.clear();
cnt = 0;
}
return res;
}
};TC: O(N*Len) SC: O(N)
30. 串联所有单词的子串
入选理由
暂无
题目地址
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/substring-with-concatenation-of-all-words
前置知识
题目描述
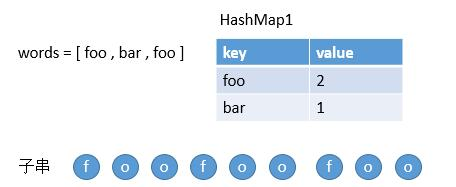
注意子串要与 words 中的单词完全匹配,中间不能有其他字符,但不需要考虑 words 中单词串联的顺序。
示例 1: 输入: s = "barfoothefoobarman", words = ["foo","bar"] 输出:[0,9] 解释: 从索引 0 和 9 开始的子串分别是 "barfoo" 和 "foobar" 。 输出的顺序不重要, [9,0] 也是有效答案。 示例 2:
输入: s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword", words = ["word","good","best","word"] 输出:[]