思路
滑动窗口
代码
var maxSlidingWindow = function(nums, k) {
let res = [];
const n = nums.length;
let left = 0, right = k - 1;
while(right < n) {
let max = -Infinity;
let i = left;
while (i <= right) {
max = Math.max(max, nums[i]);
i++;
}
res.push(max);
left++;
right++;
}
return res;
};复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(n^2)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
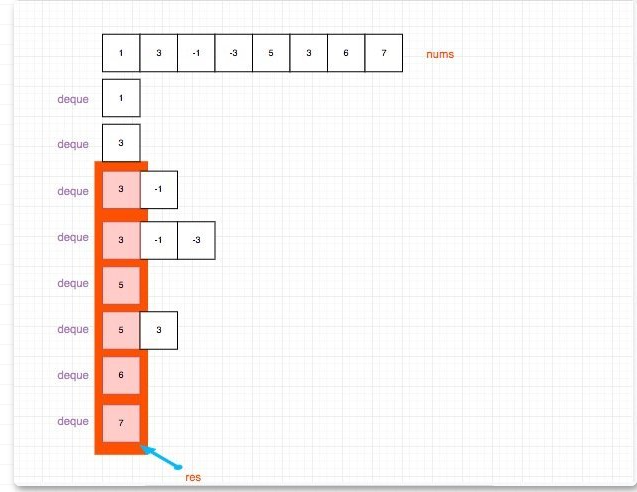
239. 滑动窗口最大值
入选理由
暂无
题目地址
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sliding-window-maximum/
前置知识
题目描述
返回滑动窗口中的最大值。
进阶:
你能在线性时间复杂度内解决此题吗?
示例:
输入: nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], 和 k = 3 输出: [3,3,5,5,6,7] 解释:
滑动窗口的位置 最大值
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3 1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3 1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5 1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5 1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6 1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5 -10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4 1 <= k <= nums.length