export function enqueueUpdate<State>(fiber: Fiber, update: Update<State>) {
// Update queues are created lazily.
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
let queue1;
let queue2;
// 通过 ReactDOM.render 初次渲染
if (alternate === null) {
// There's only one fiber.
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue;
queue2 = null;
// 创建一个updateQueue
if (queue1 === null) {
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue = createUpdateQueue(fiber.memoizedState);
}
} else {
// There are two owners.
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue;
queue2 = alternate.updateQueue;
if (queue1 === null) {
if (queue2 === null) {
// Neither fiber has an update queue. Create new ones.
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue = createUpdateQueue(fiber.memoizedState);
queue2 = alternate.updateQueue = createUpdateQueue(
alternate.memoizedState,
);
} else {
// Only one fiber has an update queue. Clone to create a new one.
queue1 = fiber.updateQueue = cloneUpdateQueue(queue2);
}
} else {
if (queue2 === null) {
// Only one fiber has an update queue. Clone to create a new one.
queue2 = alternate.updateQueue = cloneUpdateQueue(queue1);
} else {
// Both owners have an update queue.
}
}
}
// 初次渲染 queue2 为null
if (queue2 === null || queue1 === queue2) {
// There's only a single queue.
// 将 update 加入到 updateQueue 里
// fiber.updateQueue.firstUpdate = fiber.updateQueue.lastUpdate = update;
appendUpdateToQueue(queue1, update);
} else {
// There are two queues. We need to append the update to both queues,
// while accounting for the persistent structure of the list — we don't
// want the same update to be added multiple times.
if (queue1.lastUpdate === null || queue2.lastUpdate === null) {
// One of the queues is not empty. We must add the update to both queues.
appendUpdateToQueue(queue1, update);
appendUpdateToQueue(queue2, update);
} else {
// Both queues are non-empty. The last update is the same in both lists,
// because of structural sharing. So, only append to one of the lists.
appendUpdateToQueue(queue1, update);
// But we still need to update the `lastUpdate` pointer of queue2.
queue2.lastUpdate = update;
}
}
}
function computeExpirationForFiber(currentTime: ExpirationTime, fiber: Fiber) {
let expirationTime;
// 外部强制的情况
// 两种情况赋值 expirationContext ,
// 1、deferredUpdates 计算出 Async 方式的优先级时间
// 2、syncUpdates <- flushSync <- ReactDOM.flushSync , syncUpdates 在执行 fn 之前将
// expirationContext 修改为 Sync,通过外部强制某个更新必须使用那种 expirationTime 的行为
if (expirationContext !== NoWork) {
// An explicit expiration context was set;
expirationTime = expirationContext;
} else if (isWorking) {
// 有任务更新的情况
if (isCommitting) {
// Updates that occur during the commit phase should have sync priority
// by default.
expirationTime = Sync;
} else {
// Updates during the render phase should expire at the same time as
// the work that is being rendered.
expirationTime = nextRenderExpirationTime;
}
} else {
// No explicit expiration context was set, and we're not currently
// performing work. Calculate a new expiration time.
// ConcurrentMode = 0b001; 通过 与 / 或运算便于组合和判断不同的mode
// 异步 mode 才计算 expirationTime
if (fiber.mode & ConcurrentMode) {
// interactiveUpdates 函数里置为true,即计算高优先级的expirationTime
if (isBatchingInteractiveUpdates) {
// This is an interactive update
expirationTime = computeInteractiveExpiration(currentTime);
} else {
// This is an async update
expirationTime = computeAsyncExpiration(currentTime);
}
// If we're in the middle of rendering a tree, do not update at the same
// expiration time that is already rendering.
if (nextRoot !== null && expirationTime === nextRenderExpirationTime) {
expirationTime += 1;
}
// 同步的更新
} else {
// This is a sync update
expirationTime = Sync;
}
}
if (isBatchingInteractiveUpdates) {
// ...
}
return expirationTime;
}
FiberRoot 与 RootFiber
FiberRoot
FiberRoot对象
FiberRoot是ReactRoot生成实例时调用ReactFiberReconciler.js的createContainer传入getElementById(root)执行ReactFiberRoot.js中的createFiberRoot函数生成的Fiber
ReactElement对应一个Fiber对象class Component中的this.state、this.props,在 Fiber 更新后才会更新class Component上的this.state,props,也是hooks实现的原理,functional Component是没有this.statethis.props的,Fiber有能力记录这些状态之后在functional Component更新后拿到这些状态。ReactElement对应的树结构Fiber数据结构ReactElement 对应的Fiber的结构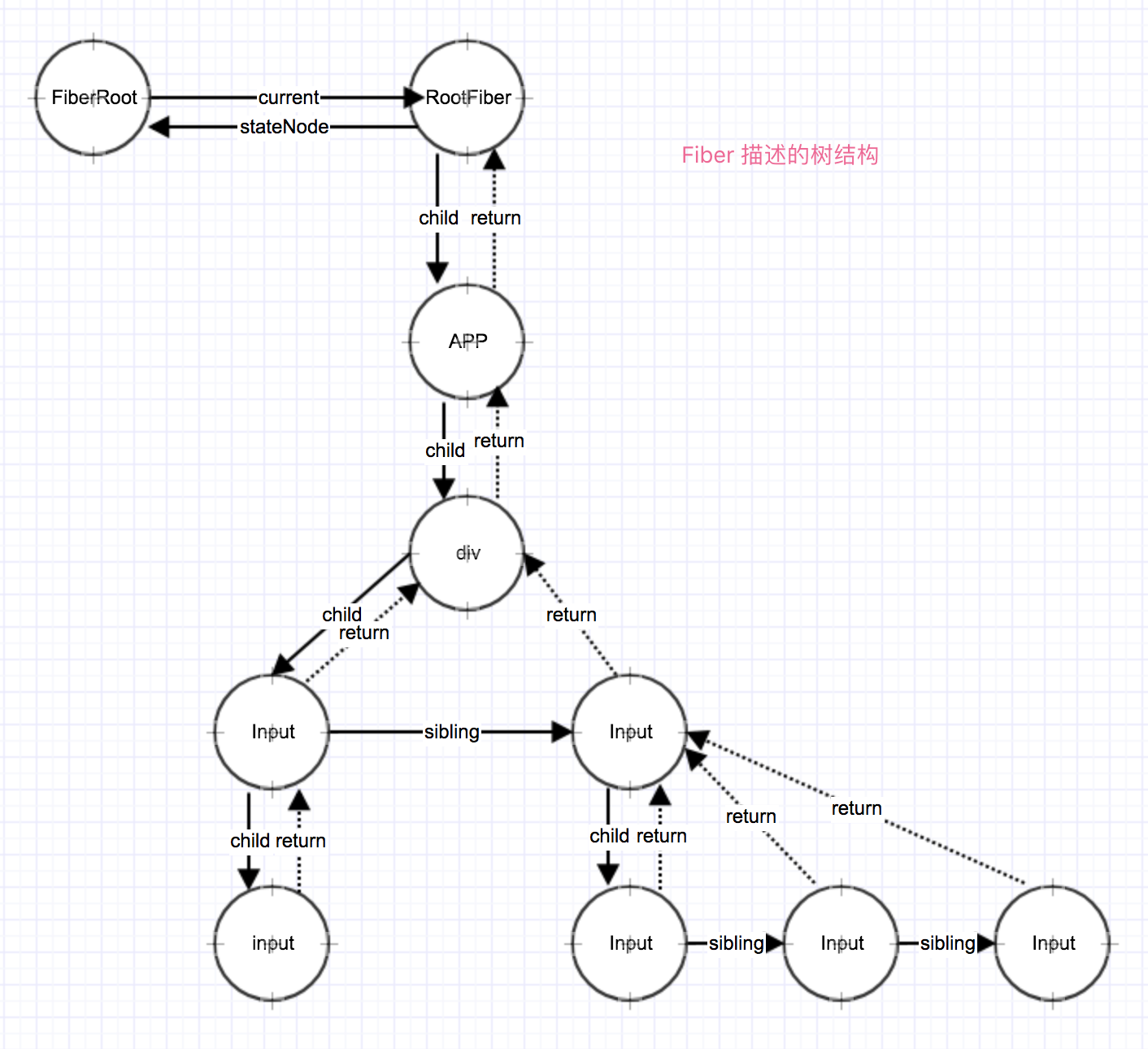
update 和 updateQueue
用于记录组件状态的改变,记录改变的方式和内容
存放于
updateQueue中,存放多个update用来计算出最终改变的结果多个
update可以同时存在,setState三次会创建三个update,放到updateQueue里,在进行更新的操作update 数据结构
ReactDOM.render最终调用ReactRoot.prototype.render时会执行到scheduleRootUpdate方法里执行createUpdateupdateQueue 数据结构
enqueueUpdate 方法
enqueueUpdated就是在fiber对象上创建一个updateQueue,然后把update对象传入到这个queue里appendUpdateToQueue方法,初次渲染将queue的firstUpdate和lastUpdate都指向update,之后的每有更新创建都将lastUpdate.next指向新的update,将lastUpdate指向新的update构建链表结构expirationTime
在
updateContainer方法中会计算一个expirationTime然后用这个时间创建update对象推入updateQueue内requestCurrentTime方法返回一个固定的常量,调用recomputeCurrentRendererTime计算js加载完成到当前渲染时间的时间差值,这个差值范围小(没超过一个单位UNIT_SIZE)的值会在msToExpirationTime内被计算成同一个常数,最后赋值全局变量currentRendererTimecomputeExpirationForFiber方法会根据当前渲染的 currentTime 计算出一个优先级时间,核心就是根据渲染方式的 mode 不同来创建不同优先级的 expirationTime, 区别在于传入computeExpirationBucket 的参数不同。computeExpirationBucket最终的公式为((((currentTime - 2 + 5000(或者150) / 10) / 25(或者10)) | 0) + 1) * 25(或者10),用| 0向下取整,使得在没超过一个单位 25(10)范围内的时间计算出来的值都相同,这样在很短时间内多次 setState 调用更新时,也可以保证是同一优先级的更新。上一篇 下一篇