The below code makes the 60 LEDs light white color. ✅
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding: utf8
from time import sleep
from rpi_ws281x import PixelStrip, Color
# LED strip configuration:
LED_COUNT = 60 # Number of LED pixels.
LED_PIN = 18 # GPIO pin connected to the pixels (18 uses PWM!).
# LED_PIN = 10 # GPIO pin connected to the pixels (10 uses SPI /dev/spidev0.0).
LED_FREQ_HZ = 800000 # LED signal frequency in hertz (usually 800khz)
LED_DMA = 10 # DMA channel to use for generating signal (try 10)
LED_BRIGHTNESS = 20 # Set to 0 for darkest and 255 for brightest
LED_INVERT = True # True to invert the signal (when using NPN transistor level shift)
LED_CHANNEL = 0 # set to '1' for GPIOs 13, 19, 41, 45 or 53
# Create NeoPixel object with appropriate configuration.
strip = PixelStrip(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, LED_FREQ_HZ, LED_DMA, LED_INVERT, LED_BRIGHTNESS, LED_CHANNEL)
# Intialize the library (must be called once before other functions).
strip.begin()
print("Test ✅")
# clear
for i in range(strip.numPixels()):
strip.setPixelColor(i, Color(0, 0, 0))
strip.show()
sleep(1)
# Switch all pixels on
for i in range(strip.numPixels()):
# here work as expect ✅
strip.setPixelColor(i, Color(255, 255, 255))
strip.show()
print("Test finished 🎉")
exit()
But after running once the above code, the below code did not change the LED's lighting result anymore. ❌
All 60 LED colors remain white color.
So, what's wrong with this?
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding: utf8
from time import sleep
from rpi_ws281x import PixelStrip, Color
# LED strip configuration:
LED_COUNT = 60 # Number of LED pixels.
LED_PIN = 18 # GPIO pin connected to the pixels (18 uses PWM!).
# LED_PIN = 10 # GPIO pin connected to the pixels (10 uses SPI /dev/spidev0.0).
LED_FREQ_HZ = 800000 # LED signal frequency in hertz (usually 800khz)
LED_DMA = 10 # DMA channel to use for generating signal (try 10)
LED_BRIGHTNESS = 20 # Set to 0 for darkest and 255 for brightest
LED_INVERT = True # True to invert the signal (when using NPN transistor level shift)
LED_CHANNEL = 0 # set to '1' for GPIOs 13, 19, 41, 45 or 53
# Create NeoPixel object with appropriate configuration.
strip = PixelStrip(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, LED_FREQ_HZ, LED_DMA, LED_INVERT, LED_BRIGHTNESS, LED_CHANNEL)
# Intialize the library (must be called once before other functions).
strip.begin()
print("Test ✅")
# clear
for i in range(strip.numPixels()):
strip.setPixelColor(i, Color(0, 0, 0))
strip.show()
sleep(1)
# Switch all pixels on
for i in range(strip.numPixels()):
# here not work as expect ❌
strip.setPixelColor(i, Color(255, 0, 0))
strip.show()
print("Test finished 🎉")
exit()
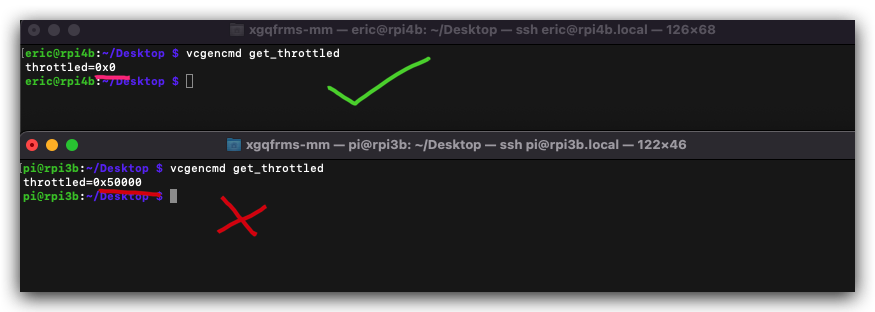
Where can I find the API for the rpi-ws281x-python library?
https://github.com/rpi-ws281x/rpi-ws281x-python/blob/master/library/rpi_ws281x/rpi_ws281x.py#L102