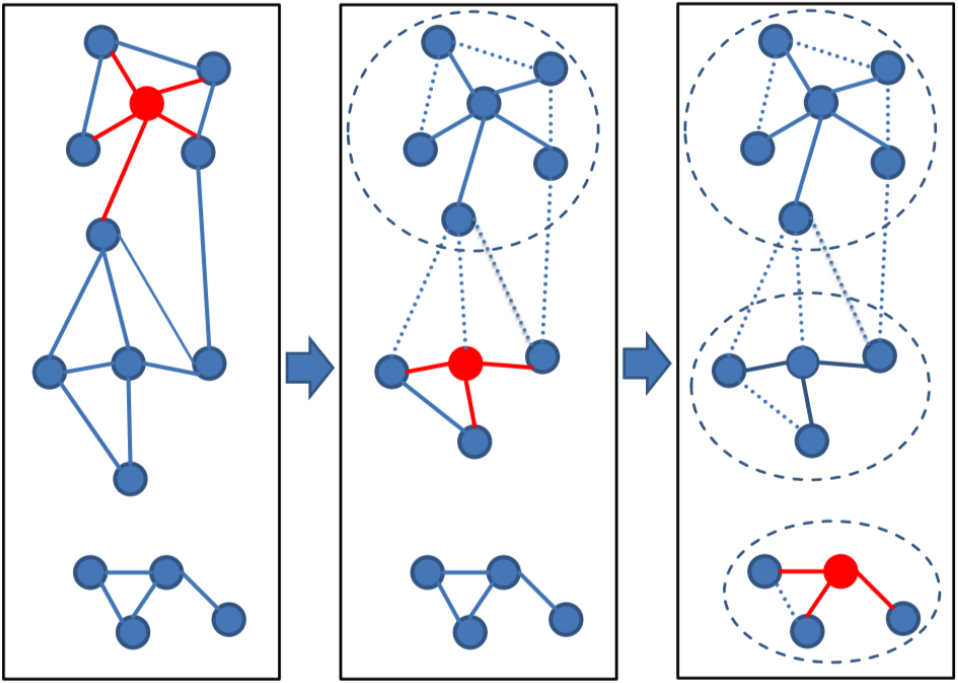
@taylorreiter In default we use the greedy set cover algorithm for clustering. It picks the representative with the most alignments as the center. See the figure below. We use the longest sequence if you switch the --cov-mode 1 to uni-directional.
Open taylorreiter opened 1 year ago
@taylorreiter In default we use the greedy set cover algorithm for clustering. It picks the representative with the most alignments as the center. See the figure below. We use the longest sequence if you switch the --cov-mode 1 to uni-directional.

To slightly expand on this, easy-cluster just calls cluster and a few modules to make the clustering tsv file and the FASTA files. It itself doesn't do anything special, however generating the cluster FASTA files is a bit tricky with the currently available MMseqs2 modules, so the easy-cluster workflow does that for you.
The clustering procedure should be mostly the same since the Linclust paper (the combined Linclust+MMseqs2 clustering). The --cluster-reassign parameter to fix hits with sequence-identity/coverages below the given thresholds that were allowed due to the cascading is not described in the paper and the nucleotide clustering was also not available then.
Thank you both so much, these were incredibly helpful explanations!
If I use the command:
How will mmseqs determine the representative cluster? I've tried reading through the documentation, issues, and papers, but it wasn't clear to me how the representative was selected for
easy-cluster...I'm sorry if I missed something! I think in the linclust paper it's mentioned that the longest sequence is selected as the representative, but I couldn't find a similar citation foreasy-cluster.