@SelenIT wrote:
Wouldn't the Masonry concept better fit into the overall Grid logic if masonry becomes a new grid-auto-flow modifier rather than the separate value of grid-template-*?
Sure that would work too I guess. I chose grid-template-* somewhat arbitrarily. Note that dense is used though - it affects step 1 in grid item placement (that step determines which items contributes to intrinsic track sizing). But yeah, we could allow grid-auto-flow: row masonry dense to solve that.
The obvious downside of that approach is the impossibility to enable the Masonry behavior on both directions at once (grid-template: masonry / masonry), but I believe that such case has low practical value anyway.
Yeah, I don't really see how that would be useful.
since the grid remains two-dimensional, it becomes possible to combine regular grid items with masonry items flowing around them
That seems like a more complex model to me. Also, I don't see how that would work with the new track alignment if some items are attached to grid lines and some not. Fragmentation probably becomes hairy too.
Note also that you can force items to attach to line 1 in the masonry axis with the current proposal (with grid-row:1 for example), which sort of have the same effect as stamping. Only for line 1 though, since all other item positions in the masonry axis are treated as auto. But, perhaps most use cases for stamping is at the top of the container anyway? (it seems their example could be implemented with my proposal)
When I play around with their stamping example you linked to it seems they never place any items above the stamped items anyway, so I think being able to place items at line 1 is good enough to emulate the stamping feature they have. (I could be mistaken though.)
before starting Masonry layout, place all grid items assigned to explicit grid areas as usually, and then during the Masonry placement check not only the top position, but also the available space between the previous masonry item and the next grid item in each track
Well, you need to determine the item's position before starting to layout the item, so you don't know the item's size yet when you position it. And then I'm not sure what should happen if the item was too big to fit between the last masonry item and a grid item.
Your model is an interesting thought experiment. But I don't really understand how item layout should work and the track alignment feature seems incompatible with it.
Overview
This is a proposal to extend CSS Grid to support masonry layout in one of the axes while doing normal grid layout in the other. I'll use
grid-template-rows/columns: masonryto specify the masonry-axis in the examples (and I'll call the other axis the grid-axis). Here's a simple example:Result:
The grid-axis behaves pretty much the same as in a normal grid container. Line names and track sizes can be specified and items can be placed and span multiple tracks using
grid-column/row. CSS Box Alignment works normally etc. In the masonry-axis, items are placed into the grid-axis track(s) with the most space (typically) after the margin-box of the last item in those tracks.Line name resolution and grid item placement
Grid items are formed and blockified the same as in a normal grid container. Line name resolution works the same as if
masonrywere replaced withnone, i.e. names resolve in both axes. Grid item placement is done normally as well, although most of this result is discarded. Any items that were placed in the first hypothetical "track" in the masonry-axis keep their placement. Other items that have a definite position in the grid-axis keep that. Other placement results are ignored. These items will instead be placed according to the Masonry layout algorithm. (This implies that items can only be placed into the same grid area in this first hypothetical "track"). The flow axis specified bygrid-auto-flowis ignored - items are always placed by filling the grid-axis.direction:rtlworks as usual (reverses the grid) if the grid-axis is the inline-axis.Containing block
The containing block for a grid item is formed by the grid area in the grid-axis and the grid container's content-box in the masonry-axis. Self-alignment works normally in the grid-axis, but is ignored in the masonry-axis. Margins do not collapse in either axis.
Track sizing
The Track Sizing Algorithm works as usual in the grid-axis, except only the subset of items with a definite placement in the grid-axis, or which span all tracks, contribute to the intrinsic sizing. This makes the first (implicit grid) "track" in the masonry-axis special since those items always contribute to the intrinsic sizing.
auto-placed items which don't end up in the first track don't contribute (since which track they end up in depends on layout results). The min/max-content size of a grid container in the masonry-axis is the largest distance between the item margin-edges in each of the tracks in the grid-axis, when sized under a min/max-content constraint.Grid container alignment and gutters
Alignment etc works normally in the grid-axis. Gutters are supported in both axes. In the masonry-axis the relevant gap is applied between each item. Content alignment ( (Item "1" has a 5px bottom margin here.)
Note that there is only ever one alignment subject for these properties in the masonry axis, so the unique alignments boil down to
(Item "1" has a 5px bottom margin here.)
Note that there is only ever one alignment subject for these properties in the masonry axis, so the unique alignments boil down to  (Here's the testcase for that.)
There's one difference for these new properties though:
(Here's the testcase for that.)
There's one difference for these new properties though:
align/justify-content) in the masonry-axis is applied "to the content as a whole". More specifically, the alignment subject is the "masonry box", which has the extent from the content box edge of the grid container to the margin-box end edge of the item that is the furthest away, as indicated by the dashed border here:start,center,endandstretch. (normalbehaves asstretchas usual for grid containers). The above image shows the alignment subject withalign-content:start. By default the masonry box is the same as the content box due to being stretched. This doesn't affect the items' alignment within the masonry box in any way though (which is what I meant by "to the content as a whole"). So I've added two properties to allow authors to align the items within the masonry box:align/justify-trackswhich have the same values as the corresponding-contentproperty (EDIT: I've extended it to accept a list of values, see below). Here's a screenshot showing a few alignment possibilities:normalbehaves asstart. So if all these properties have their initial values, the rendering is the expected "packed" masonry layout as shown in the top left corner above.align/justify-tracks:stretch
align/justify-tracks:stretchcan be used to fill the tracks in the masonry axis by stretching items individually. Items can opt out from stretching process by settingalign/justify-selfto something other thannormal/stretchin the relevant axis. Items that have either a definite size or anautomargin in the masonry axis are excluded from this stretching. An item only grows up to itsmax-size.automargins can be used to align the item inside its new larger space instead of changing its size. I made a testcase and a video to illustrate. Only the purple items haveheight:auto, so they are the ones that may grow by default. A few items worth noting: item 4 hasmax-height:40pxso it only grows up to that size and then the other items in its track picks up the remaining size. Item 16 opts out from resizing by settingalign-self:end. Item 18 hasmargin-top/bottom:autoso it's centered in its allotted space instead of growing. Item 20 hasmargin-top:autoso it's aligned to the end. (Here's the corresponding testcase with a masonry inline-axis instead, with video.) It should be noted that this is an alignment step only - all items keep their pre-alignment track placement.align/justify-tracks alignment values can be specified per track
The (highly tentative) syntax is a comma-separated list of alignment values - the start track takes the first value, etc. If there are fewer values than tracks then the last value is used for all the remaining tracks. If there are more values than tracks then the remaining values have no effect on rendering. Here's an example, which renders like this: Note that the
Note that the
align-trackvalue intentionally has one value less than the number of tracks to illustrate that the remaining track(s) use the last value (i.e. the right-most track also usespace-evenly). (baselinevalues are also supported but excluded in this test, but see below...)Baselines
Item baseline alignment inside the tracks in the grid-axis works as usual, as defined in Grid and Box Alignment specs, and the grid container's baseline is determined the same as for a regular grid in that axis.
Baseline alignment is supported also in the masonry axis, on the first and last item in each track (but not on items "in the middle" of the track). Only tracks with the
align/justify-tracksvaluesstart,endorstretch, support baseline alignment. There are four different sets of baseline groups:starttrack + the first item in eachstretchtrackstarttrackendtrackendtrack + the last item in eachstretchtrackEach of those sets can have a first baseline group or a last baseline group, resulting in eight unique baseline groups. Here's an example illustrating all eight possibilities, which renders as: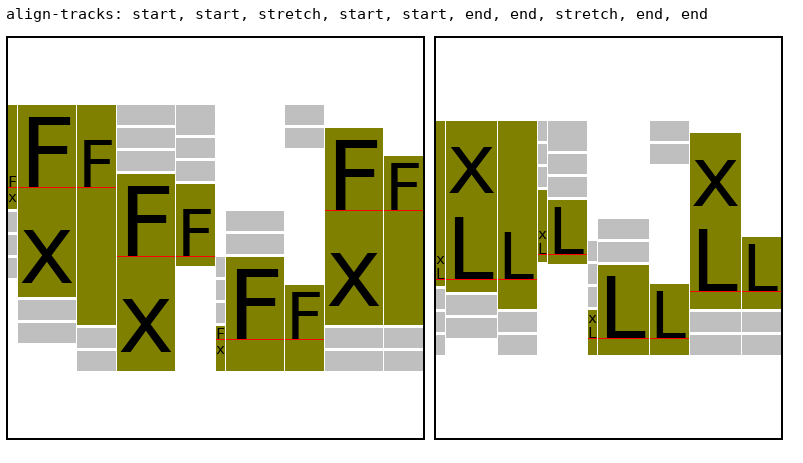 I used two separate grid containers to illustrate first ("F") and last ("L") baseline groups to unclutter it. You can use all eight groups in the same container if you wish. The aligned baselines are indicated in red color. Note that the tracks that are attached to the end side of the masonry box adjust the padding (or margin in the case of
I used two separate grid containers to illustrate first ("F") and last ("L") baseline groups to unclutter it. You can use all eight groups in the same container if you wish. The aligned baselines are indicated in red color. Note that the tracks that are attached to the end side of the masonry box adjust the padding (or margin in the case of
align-self) on the end side, whereas tracks attached to the start side adjust the start padding/margin. (I only usedalign-content:[last] baselineon the items in the example above, which adjusts the padding, since it's easier to see the adjustment. You can also usealign-self:[last] baseline, or a mix of the two, as usual.)ISSUE: this needs more details about edge cases, caveat about misalignment in stretch, etc
Masonry layout algorithm
Items are placed in order-modifed document order but items with a definite placement are placed before items with an indefinite position (as for a normal grid). For each of the tracks in the grid-axis, keep a running position initialized to zero. For each item that has an indefinite placement:
min_posmin_posas the definite placementCalculate the size of the containing block and flow the item. Then calculate its resulting margin-box size in the masonry-axis. Set the running position of the tracks the item spans to
min_pos+ margin-box + grid-gap.There are a few variations of this algorithm that might be useful to authors. First, the "definite items first" might be useful to skip in some cases, so that a plain order-modifed document order is used instead. Also, opting out from the packing behavior described above and instead placing each item in order (a couple of existing masonry JS packages provides this option). So, perhaps something like this:
masonry-auto-flow: [ definite-first | ordered ] || [ pack | next ]. Example:Result: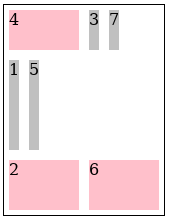
(Without
masonry-auto-flow: next, 1,3,5,6 are placed in the middle row.)Fragmentation
Fragmentation in the masonry-axis is supported. Each grid-axis track is fragmented independently. If an item is fragmented, or has a forced break before/after it, then the running position for the tracks that it spans in the grid-axis are set to the size of the fragmentainer so that no further items will be placed in those tracks. Placement continues until all items are placed or pushed.
Subgrid
Masonry layout is supported also in subgrids (e.g.
grid: subgrid / masonry). However, only a parent grid-axis can be subgridded. Asubgridaxis with a parent masonry-axis will behave asmasonry, unless the subgrid's other axis is alsomasonryin which case it behaves asnone. (A grid container can only have one masonry-axis).auto-placed subgrids don't inherit any line names from their parent grid, but are aligned to the parent's tracks as usual. Here's a subgrid example:Result:
Note how the subgrid's first item ("subgrid.1") contributes to the intrinsic size of the 2nd row in the parent grid. This is possible since the subgrid specified a definite placement so we know which tracks it will occupy. Note also that it's subgridding the masonry-axis of the parent which falls back to masonry layout in the inline-axis for the subgrid.
Absolute Positioning
Grid-aligned absolute positioned children are supported. The containing block is the grid-area in the grid-axis and the grid container padding edges in the masonry-axis, except for line 1 in the masonry-axis which corresponds to the start of the "grid" (the content-box start edge usually). It might be useful to define a static position in the masonry-axis though, given that we only have a one line in that axis to align to. Maybe it could defined as the max (or min?) current running position of the grid-axis tracks at that point?
repeat(auto-fit)
I don't see a way to support
repeat(auto-fit)sinceauto-placed items depend on the layout size of its siblings. Removing empty tracks after layout wouldn't be possible in most cases since it might affect any intrinsic track sizes. Even if all track sizes are definite the containing block size could change for grid-aligned abs.pos. descendants. Sorepeat(auto-fit)behaves asrepeat(auto-fill)when the other axis is a masonry-axis.Performance notes
In general, masonry layout should have significantly better performance than the equivalent (2-axis) grid layout, particularly when the masonry-axis is the block-axis since the intrinsic sizing of grid rows is typically quite expensive. Any intrinsic track sizing in the grid-axis should be cheaper too, because, typically, only a subset of items contribute to the intrinsic sizing in a masonry layout, contrary to a 2-axis grid where all items spanning the intrinsic track contributes. That said,
justify/align-tracks:stretchspecifically adds a cost proportionate to the number of items that are resized. (Note thatstretchisn't the default value for these properties though.) Stretched items do a second layout (size reflow) with the new size (when it actually changed) so this can be costly if there are a huge amount of stretched items that each contains a lot of content. Especially nested stretched masonry layouts should be avoided unless they are small/trivial. This can be ameliorated by the author by opting out from the stretching on most items though, e.g. specifyingjustify/align-items:startand then opting in for just a few items withjustify/align-self:stretchto let those items fill the masonry axis. Otherjustify/align-tracksvalues such ascenter,endand<content-distribution>(other thanstretch) shouldn't be a problem though since they just reposition the items which is fast. (This performance analysis is from a Gecko perspective, but I suspect there's some truth to it for other engines as well.)Graceful degradation
A Masonry design should degrade quite nicely in an UA that supports Grid layout but not Masonry layout if the
grid/grid-templateshorthands are avoided and the longhands are used instead. e.g.Here's a testcase to demonstrate. It gives you a three-column grid layout, but with "more gaps" than if the UA supported
masonry. (A video of the masonry layout for comparison.)