Quick reference
- Forked from : Julio Gutierrez
- Maintained by : 6jarjar6
- Where to get help: Github discussions
Supported tags
- edge (updated weekly)
- latest (updated monthly)
- YYYY-mm-dd (created monthly)
Quick reference (cont.)
- Where to file issues: Github issues
- Supported architecture: (more info) amd64, arm64
- Published image artifact details: DockerHub, Github packages
- Continuous integration: Github actions
- Source: Github
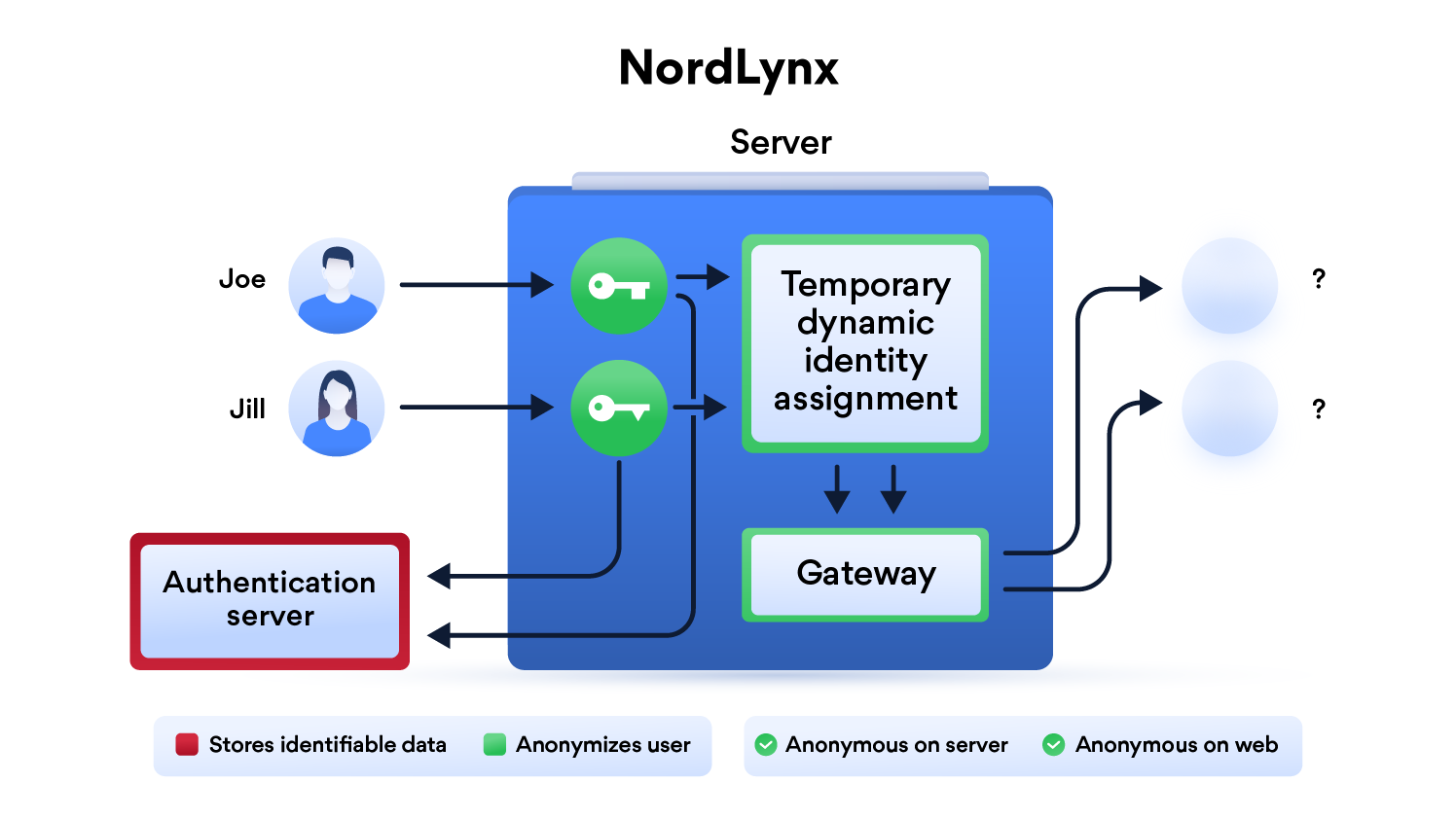
What is NordLynx?
NordLynx is a technology built around the WireGuard® VPN protocol. It lets you experience WireGuard’s speed benefits without compromising your privacy. You can find more information about NordLynx in this blog post.
What is WireGuard?
WireGuard® is an extremely simple yet fast and modern VPN that utilizes state-of-the-art cryptography. It aims to be faster, simpler, leaner, and more useful than IPsec, while avoiding the massive headache. It intends to be considerably more performant than OpenVPN. WireGuard is designed as a general purpose VPN for running on embedded interfaces and super computers alike, fit for many different circumstances. Initially released for the Linux kernel, it is now cross-platform (Windows, macOS, BSD, iOS, Android) and widely deployable. It is currently under heavy development, but already it might be regarded as the most secure, easiest to use, and simplest VPN solution in the industry.
Road warriors, roaming and returning home
If you plan to use Wireguard both remotely and locally, say on your mobile phone, you will need to consider routing. Most firewalls will not route ports forwarded on your WAN interface correctly to the LAN out of the box. This means that when you return home, even though you can see the Wireguard server, the return packets will probably get lost.
This is not a Wireguard specific issue and the two generally accepted solutions are NAT reflection (setting your edge router/firewall up in such a way as it translates internal packets correctly) or split horizon DNS (setting your internal DNS to return the private rather than public IP when connecting locally).
Both of these approaches have positives and negatives however their setup is out of scope for this document as everyone's network layout and equipment will be different.
Usage
Here are some example snippets to help you get started creating a container.
docker-compose (recommended, click here for more info)
---
version: "3"
services:
nordlynx:
image: ghcr.io/bubuntux/nordlynx
cap_add:
- NET_ADMIN #required
environment:
- PRIVATE_KEY=xxxxxxxxx #requireddocker-compose (using secret)
version: "3.9"
services:
nordlynx:
image: ghcr.io/bubuntux/nordlynx
cap_add:
- NET_ADMIN #required
environment:
- PRIVATE_KEY_FILE=/run/secrets/privatekey
secrets:
- privatekey
secrets:
privatekey:
file: ./privatekey.txtdocker cli (click here for more info)
docker run -d \
--cap-add=NET_ADMIN #required \
-e PRIVATE_KEY=xxxxxxxxx #required \
ghcr.io/6jarjar6/nordlynxReview the wiki for more practical usages and host specific instructions.
Module
Wireguard module is required, please install it manually if need it.
Environment
| Variable | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
PRIVATE_KEY |
[Required] | See How To Get Your PRIVATE_KEY or these instructions. |
PRIVATE_KEY_FILE |
File from which to get PASS, if using docker secrets this should be set to /run/secrets/ |
|
LISTEN_PORT |
51820 | A 16-bit port for listening. |
INTERFACE |
eth0 | The network interface to use inside the container. |
ADDRESS |
10.5.0.2/32 | A comma-separated list of IP (v4 or v6) addresses (optionally with CIDR masks) to be assigned to the interface. |
DNS |
103.86.96.100 103.86.99.100 |
A comma-separated list of IP (v4 or v6) addresses to be set as the interface's DNS servers, or non-IP hostnames to be set as the interface's DNS search domains. |
TABLE |
Controls the routing table to which routes are added. There are two special values: off disables the creation of routes altogether, and auto (suggested for most users) adds routes to the default table and enables special handling of default routes. |
|
ALLOWED_IPS |
0.0.0.0/0 | A comma-separated list of IP (v4 or v6) addresses with CIDR masks from which incoming traffic for this peer is allowed and to which outgoing traffic for this peer is directed. For Synology, read this. |
PERSISTENT_KEEP_ALIVE |
25 | A second interval, between 1 and 65535 inclusive, of how often to send an authenticated empty packet to the peer for the purpose of keeping a stateful firewall or NAT mapping valid persistently. |
PRE_UP/POST_UPPRE_DOWN/POST_DOWN |
Script snippets which will be executed by bash before/after setting up/tearing down the interface, most commonly used to configure custom DNS options or firewall rules. The special string %i is expanded to INTERFACE. For Synology, read this. |
|
QUERY |
Query for the api nordvpn (see https://sleeplessbeastie.eu/2019/02/18/how-to-use-public-nordvpn-api/) | |
COUNTRY_CODE |
Country code to filter server list. | |
PUBLIC_KEY |
Public key of the server to connect (auto select base on recommendation api). | |
END_POINT |
Ip address of the server to connect (auto select base on recommendation api). | |
ALLOW_LIST |
List of domains that are going to be accessible outside vpn (IE rarbg.to,yts.mx). | |
NET_LOCAL |
CIDR networks (IE 192.168.1.0/24), add a route to allows replies once the VPN is up. | |
NET6_LOCAL |
CIDR IPv6 networks (IE fe00:d34d:b33f::/64), add a route to allows replies once the VPN is up. | |
RECONNECT |
Time in seconds to re-establish the connection. | |
TZ |
UTC | Specify a timezone to use EG Europe/London. |
How To Get Your PRIVATE_KEY
To get your PRIVATE_KEY you will need to get an access token from the NordVPN website and then use the https://github.com/bubuntux/nordvpn container.
-
Log in to https://nordvpn.com/
-
On the left side, click on NordVPN
-
In the middle, under Manual setup, click on Set up NordVPN manually and go through the verification process
-
On the new page, in the middle, in the Access token box, click on Generate new token
-
In the Generate new token? pop-up box, select Set to expire in 30 days and click Generate token
-
In the Copy access token pop-up box, click the Copy linnk to copy your token
-
From your computer where Docker is installed, run the below command and replace
{{{TOKEN}}}with what you copied from step 6 above:docker run --rm --cap-add=NET_ADMIN -e TOKEN={{{TOKEN}}} ghcr.io/bubuntux/nordvpn:get_private_key -
Docker will do it's thing and spit out your
PRIVATE_KEY:user@hostname:~/docker> docker run --rm --cap-add=NET_ADMIN -e TOKEN=[redacted] ghcr.io/bubuntux/nordvpn:get_private_key Unable to find image 'ghcr.io/bubuntux/nordvpn:get_private_key' locally get_private_key: Pulling from bubuntux/nordvpn 06d39c85623a: Pull complete 3e1c241a05c8: Pull complete 0077b26e8dce: Pull complete Digest: sha256:0d91aabb4511d400b01e930654950729a4e859d3c250f61664662b0ed7027c56 Status: Downloaded newer image for ghcr.io/6jarjar6/nordvpn:get_private_key Waiting for daemon to start up... A new version of NordVPN is available! Please update the application. Welcome to NordVPN! You can now connect to VPN by using 'nordvpn connect'. A new version of NordVPN is available! Please update the application. Technology is already set to 'NORDLYNX'. A new version of NordVPN is available! Please update the application. Connecting to United States #5831 (us5831.nordvpn.com) You are connected to United States #5831 (us5831.nordvpn.com)! ############################################################ IP: 10.5.0.2/32 Private Key: [!!! THIS IS YOUR PRIVATE_KEY YOU NEED !!!] \(^O^)/############################################################ user@hostname:~/docker> -
Copy everything after
Privatey Key:(note the space after:) to the end of the line -- this is yourPRIVATE_KEY
Sysctl
| Option | Details |
|---|---|
net.ipv4.conf.all.src_valid_mark=1 |
May be required; depends on multiple factors. |
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1 |
Recommended when only using ipv4. |
Docker Compose Examples
nordlynx VPN container
This example will start a nordlynx VPN container on a legacy_p2p VPN server.
services:
nordlynx:
image: ghcr.io/6jarjar6/nordlynx
hostname: nordlynx
container_name: nordlynx
cap_add:
- NET_ADMIN # required
- SYS_MODULE # maybe
environment:
- PRIVATE_KEY=[redacted] # required
- QUERY=filters\[servers_groups\]\[identifier\]=legacy_p2p
- NET_LOCAL=192.168.0.0/16
- TZ=America/New_York
sysctls:
- net.ipv4.conf.all.src_valid_mark=1 # maybe
- net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter=2 # maybe; set reverse path filter to loose mode
- net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1 # disable ipv6; recommended if using ipv4 onlyPassing Another Container Through The nordlynx VPN Container
This example will create a Firefox container that routes traffic through the nordlynx VPN container.
Typically, when you do port forwarding for a container (for example, to access it from your computer's browser), you do it on the container.
When you pass a container's traffic through another container (the nordlynx VPN container in this case), both/all containers are in the same network. As such, you no longer do port forwarding on the container you want to access and, instead, do it on the nordlynx VPN container.
Additionally, you need to ensure the second container starts AFTER the nordlynx VPN container.
services:
nordlynx:
image: ghcr.io/6jarjar6/nordlynx
hostname: nordlynx
container_name: nordlynx
ports:
- "3000:3000" # port I want forwarded for the firefox container
- "3001:3001" # port I want forwarded for the firefox container
cap_add:
- NET_ADMIN # required
- SYS_MODULE # maybe
environment:
- PRIVATE_KEY=[redacted] # required
- QUERY=filters\[servers_groups\]\[identifier\]=legacy_p2p
- NET_LOCAL=192.168.0.0/16
- TZ=America/New_York
sysctls:
- net.ipv4.conf.all.src_valid_mark=1 # maybe
- net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter=2 # maybe; set reverse path filter to loose mode
- net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1 # disable ipv6; recommended if using ipv4 only
firefox:
image: lscr.io/linuxserver/firefox:latest
# hostname: firefox # won't work when you do network_mode
container_name: firefox
restart: unless-stopped
depends_on:
- nordlynx
network_mode: service:nordlynx
# ports: # won't work; you need to do this in the nordlynx VPN container
# - "3000:3000" # won't work; you need to do this in the nordlynx VPN container
# - "3001:3001" # won't work; you need to do this in the nordlynx VPN container
volumes:
- /path/to/config:/config
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=1000
- TZ=America/New_York
security_opt:
- seccomp:unconfined
shm_size: "1gb"