
scikit-rmt: Random Matrix Theory Python package
Random Matrix Theory, or RMT, is the field of Statistics that analyses matrices that their entries are random variables.
This package offers classes, methods and functions to give support to RMT in Python. Includes a wide range of utils to work with different random matrix ensembles, random matrix spectral laws and estimation of covariance matrices. See documentation or visit the https://github.com/AlejandroSantorum/scikit-rmt of the project for further information on the features included in the package.
Documentation
The documentation is available at https://scikit-rmt.readthedocs.io/en/latest/, which includes detailed information of the different modules, classes and methods of the package, along with several examples showing different funcionalities.
Installation
Using a virtual environment is recommended to minimize the chance of conflicts. However, the global installation should work properly as well.
Local installation using venv (recommended)
Navigate to your project directory.
cd MyProjectCreate a virtual environment (you can change the name "env").
python3 -m venv envActivate the environment "env".
source env/bin/activateInstall using pip.
pip install scikit-rmtYou may need to use pip3.
pip3 install scikit-rmtGlobal installation
Just install it using pip or pip3.
pip install scikit-rmtRequirements
scikit-rmt depends on the following packages:
- numpy - The fundamental package for scientific computing with Python
- matplotlib - Plotting with Python
- scipy - Scientific computation in Python
Check the pinned versions in the requirements.txt file.
Main features
scikit-rmt provides support to analyze, study and simulate Random Matrix Theory properties and results:
- Sampling of the following random matrix ensembles:
- Gaussian Ensemble (GOE, GUE and GSE; for beta=1, 2 and 4 respectively): class
GaussianEnsemble. - Wishart Ensemble (WRE, WCE and WQE; for beta=1, 2 and 4 respectively): class
WishartEnsemble. - Manova Ensemble (MRE, MCE and MQE; for beta=1, 2 and 4 respectively): class
ManovaEnsemble. - Circular Ensemble (COE, CUE, CSE; for beta=1, 2 and 4 respectively): class
CircularEnsemble.
- Gaussian Ensemble (GOE, GUE and GSE; for beta=1, 2 and 4 respectively): class
- Eigenvalue computation for the previous ensembles using the class method
eigvals. - Computation of the joint eigenvalue probability density function given the random matrix eigenvalues, using the class method
joint_eigval_pdf. - Computation of the empirical spectral histogram by executing the class method
eigval_hist. - Plotting of the empirical spectral histogram using the class method
plot_eigval_hist. - Computation and plotting of the following spectral laws (
spectral_lawsub-module), including the calculation and plotting of the corresponding probability density functions (PDFs) and cumulative distribution functions (CDFs):- Wigner Semicircle law: describes the limiting distribution of the eigenvalues of Wigner matrices (in particular, random matrices from the Gaussian Ensemble). Implemented by class
WignerSemicircleDistribution. - Tracy-Widom law: describes the limiting distribution of the largest eigenvalue of Wigner matrices (in particular, random matrices from the Gaussian Ensemble). Implemented by class
TracyWidomDistribution. - Marchenko-Pastur law: describes the limiting distribution of the eigenvalues of Wishart matrices (random matrices from the Wishart Ensemble). Implemented by class
MarchenkoPasturDistribution. - Manova Spectrum law: introduced and proved by K. W. Wachter (1980), it describes the limiting distribution of the eigenvalues of Manova matrices (random matrices from the Manova Ensemble). Implemented by class
ManovaSpectrumDistribution.
- Wigner Semicircle law: describes the limiting distribution of the eigenvalues of Wigner matrices (in particular, random matrices from the Gaussian Ensemble). Implemented by class
- Covariance matrix estimation using different matrix smoothing and estimation methods (
covariancemodule).- Estimation of sample covariance matrix using
sample_estimatorfunction. - Finite-sample Optimal (FSOpt) estimator by
fsopt_estimatorfunction. - Empirical Bayesian estimator by
empirical_bayesian_estimatorfunction. Haff in "Estimation of a covariance matrix under Stein’s loss" (1985). - Minimax estimator by
minimax_estimatorfunction - Linear shrinkage estimator by
linear_shrinkage_estimatorfunction. Ledoit and Wolf in "A well-conditioned estimator for large-dimensional covariance matrices" (2004). - Analytical shrinkage estimator by
analytical_shrinkage_estimatorfunction. Ledoit and Wolf in "Analytical nonlinear shrinkage of large-dimensional covariance matrices" (2020).
- Estimation of sample covariance matrix using
A brief tutorial
First of all, several random matrix ensembles can be sampled: Gaussian Ensembles, Wishart Ensembles, Manova Ensembles and Circular Ensembles. As an example, the following code shows how to sample a Gaussian Orthogonal Ensemble (GOE) random matrix.
from skrmt.ensemble.gaussian_ensemble import GaussianEnsemble
# sampling a GOE (beta=1) matrix of size 3x3
goe = GaussianEnsemble(beta=1, n=3)
print(goe.matrix)[[ 0.34574696 -0.10802385 0.38245343]
[-0.10802385 -0.60113963 0.28624612]
[ 0.38245343 0.28624612 -0.96503739]]Its spectral density can be easily plotted:
# sampling a GOE matrix of size 1000x1000
goe = GaussianEnsemble(beta=1, n=1000)
# plotting its spectral distribution in the interval (-2,2)
goe.plot_eigval_hist(bins=80, interval=(-2,2), density=True)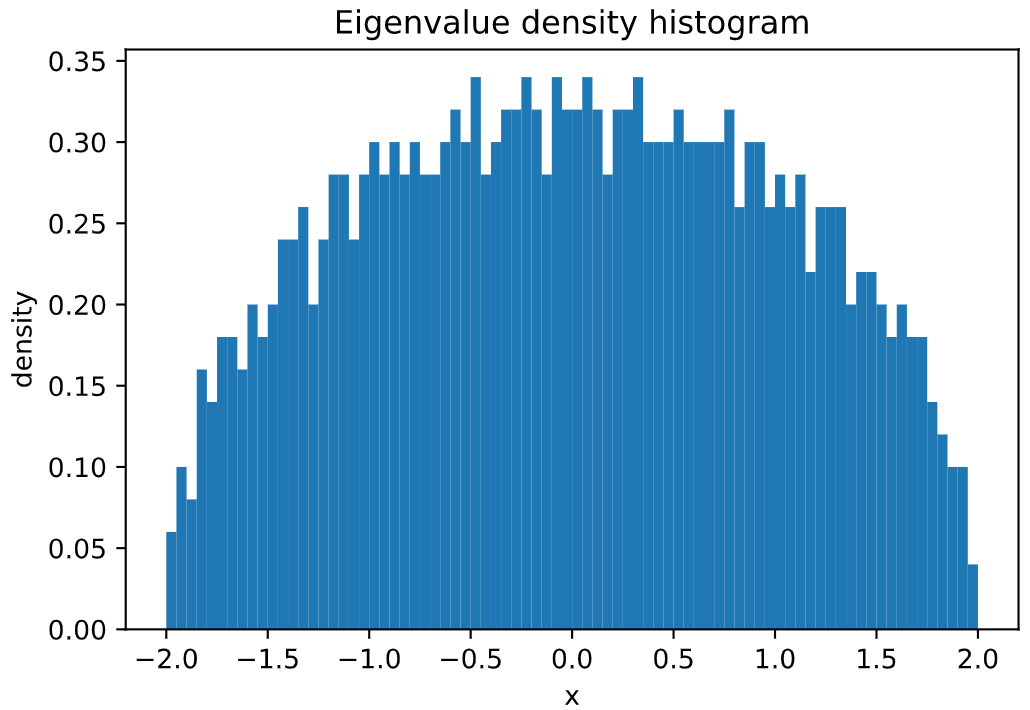
If we sample a non-symmetric/non-hermitian random matrix, its eigenvalues do not need to be real, so a 2D complex histogram has been implemented in order to study spectral density of these type of random matrices. It would be the case, for example, of Circular Symplectic Ensemble (CSE).
from skrmt.ensemble.circular_ensemble import CircularEnsemble
# sampling a CSE (beta=4) matrix of size 2000x2000
cse = CircularEnsemble(beta=4, n=1000)
cse.plot_eigval_hist(bins=80)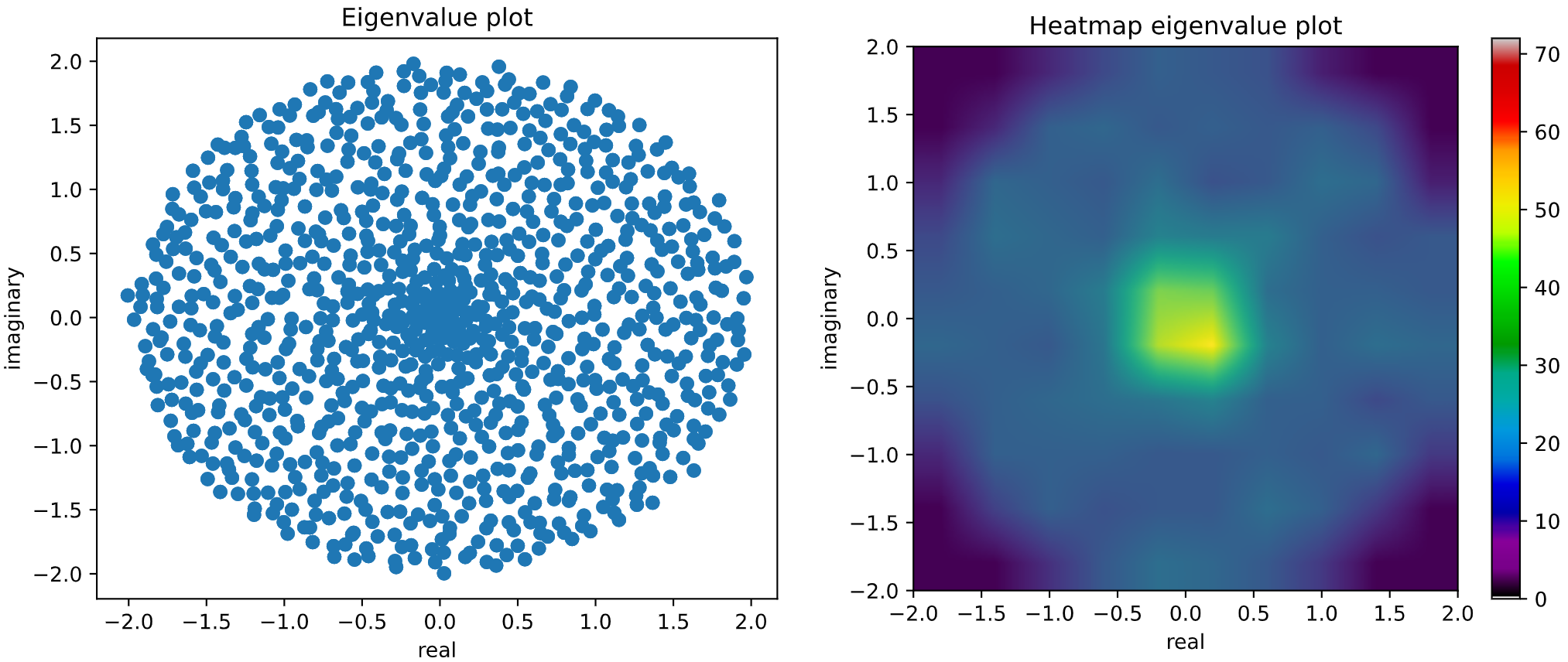
We can boost histogram representation using the results described by A. Edelman and I. Dumitriu
in Matrix Models for Beta Ensembles and by J. Albrecht, C. Chan, and A. Edelman in
Sturm Sequences and Random Eigenvalue Distributions (check references). Sampling certain
random matrices (Gaussian Ensemble and Wishart Ensemble matrices) in its tridiagonal form
we can speed up histogramming procedure. The following graphical simulation using GOE matrices
tries to illustrate it.
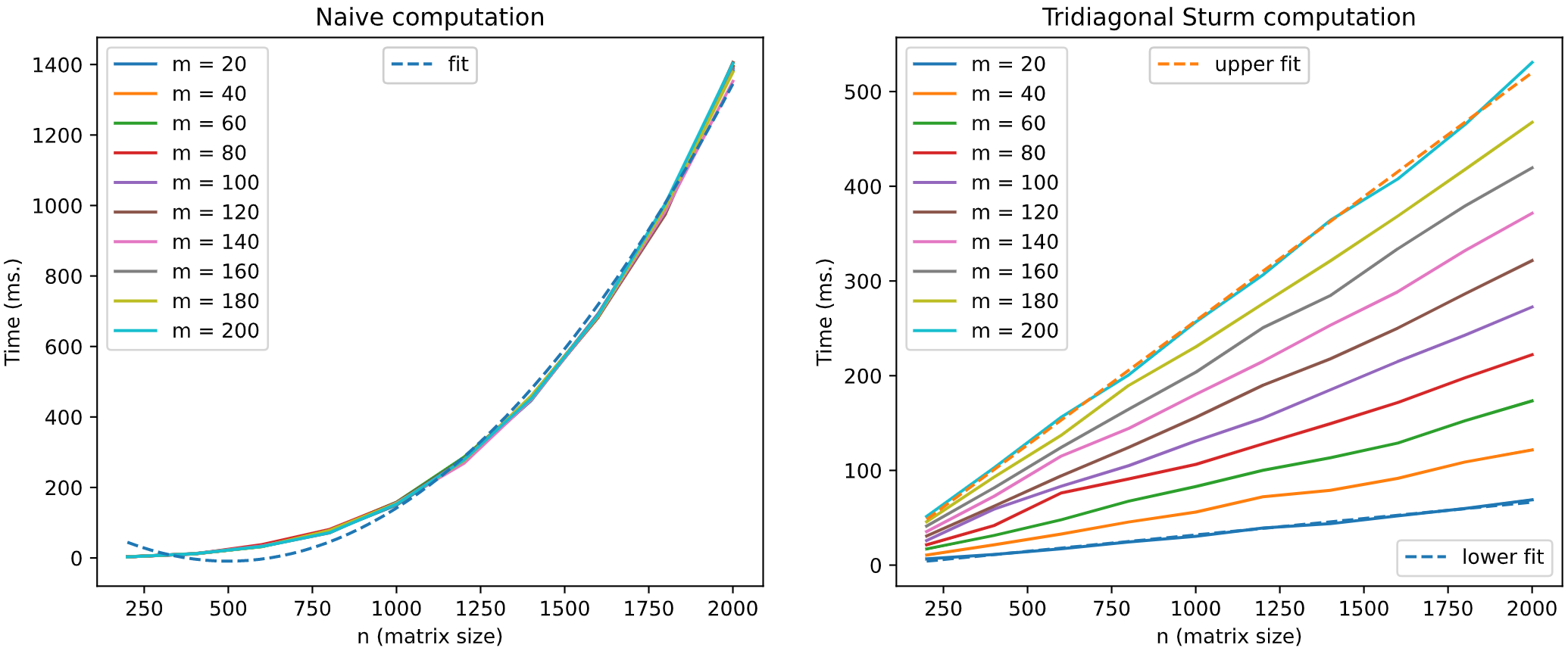
On the other hand, for all the supported ensembles, the joint eigenvalue probability density function can be computed by using the class method joint_eigval_pdf(eigvals=None). By default, the method computes the joint eigenvalue PDF of the eigenvalues of the sampled random matrix. However, the method can be called using a pre-computed array of eigenvalues, and the joint eigenvalue PDF of these eigenvalues is returned. AS an example, we can simulate sampling and histogramming many eigenvalues of GOE random matrices of size 2x2, as well as illustrating the joint eigenvalue PDF for GOE matrices 2x2. This simulation is shown in the figure below.
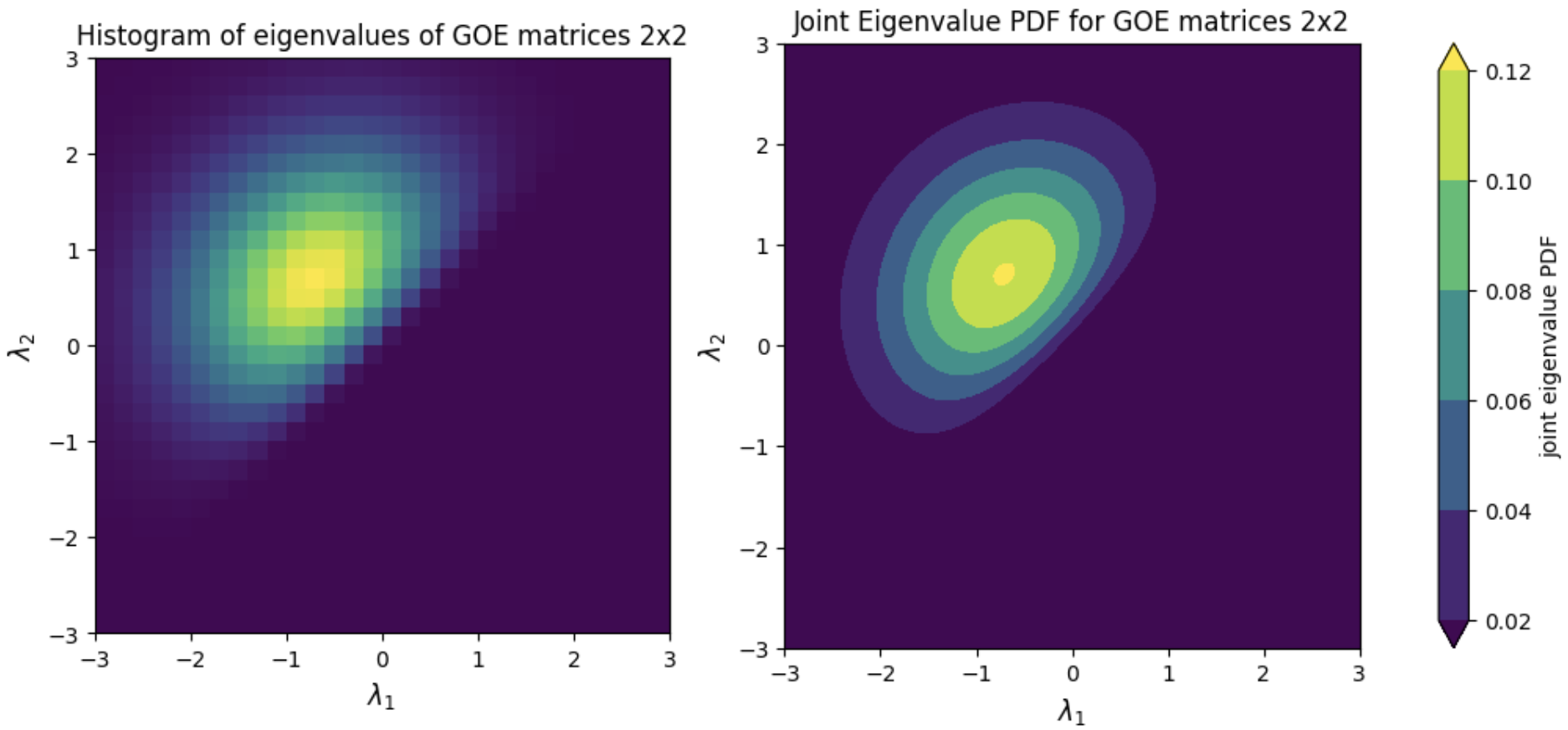
In addition, several spectral laws can be analyzed using this library, such as Wigner's Semicircle Law,
Marchenko-Pastur Law and Tracy-Widom Law. The analytical probability density function can also be plotted
by using the plot_law_pdf=True argument.
Plot of Wigner's Semicircle Law, sampling 100000 independent eigenvalues of a GOE matrix:
from skrmt.ensemble.spectral_law import WignerSemicircleDistribution
wsd = WignerSemicircleDistribution(beta=1)
wsd.plot_empirical_pdf(sample_size=100000, bins=80, density=True)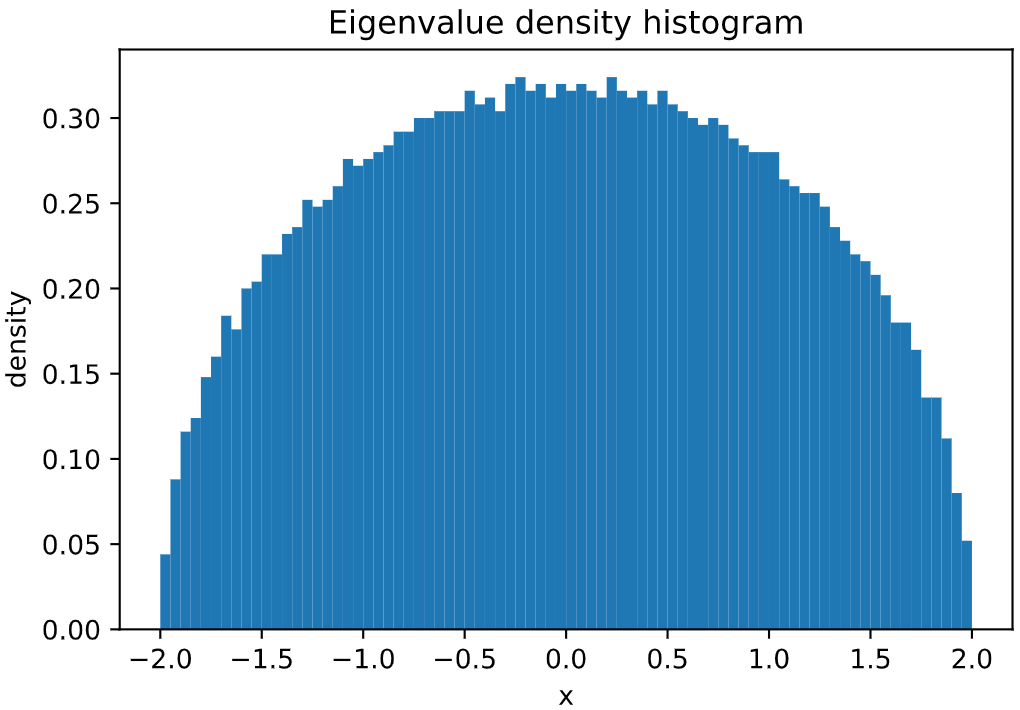
from skrmt.ensemble.spectral_law import WignerSemicircleDistribution
wsd = WignerSemicircleDistribution(beta=1)
wsd.plot_empirical_pdf(sample_size=100000, bins=80, density=True, plot_law_pdf=True)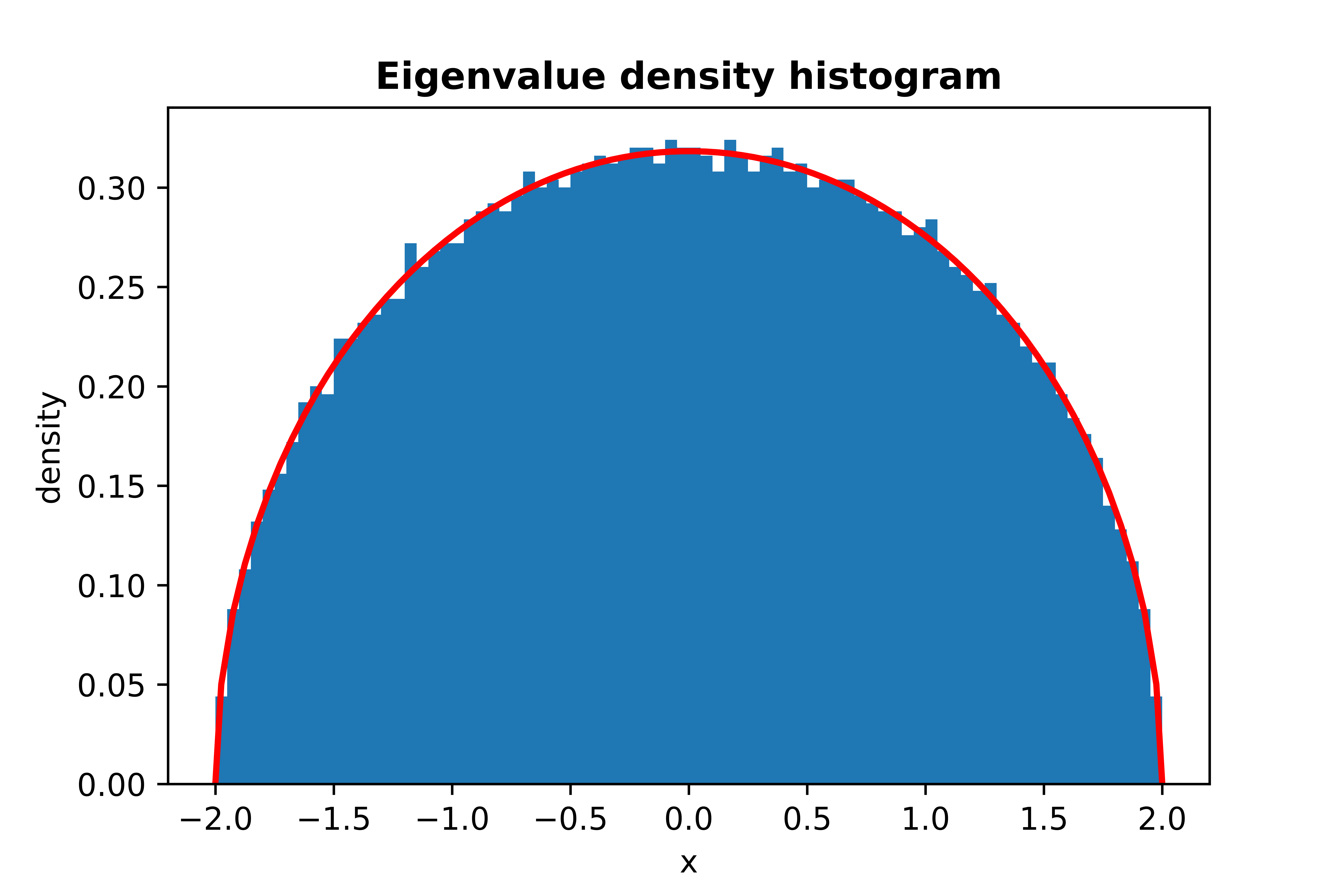
Plot of Marchenko-Pastur Law, sampling 100000 independent eigenvalues of a WRE matrix:
from skrmt.ensemble.spectral_law import MarchenkoPasturDistribution
mpd = MarchenkoPasturDistribution(beta=1, ratio=1/3)
mpd.plot_empirical_pdf(sample_size=100000, bins=80, density=True)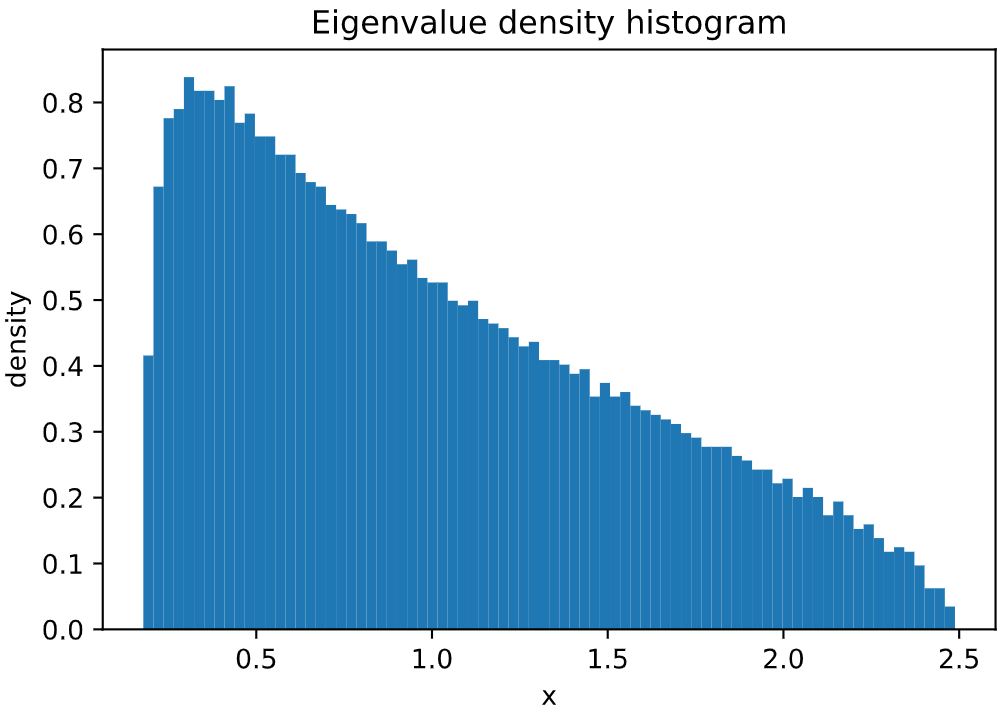
from skrmt.ensemble.spectral_law import MarchenkoPasturDistribution
mpd = MarchenkoPasturDistribution(beta=1, ratio=1/3)
mpd.plot_empirical_pdf(sample_size=100000, bins=80, density=True, plot_law_pdf=True)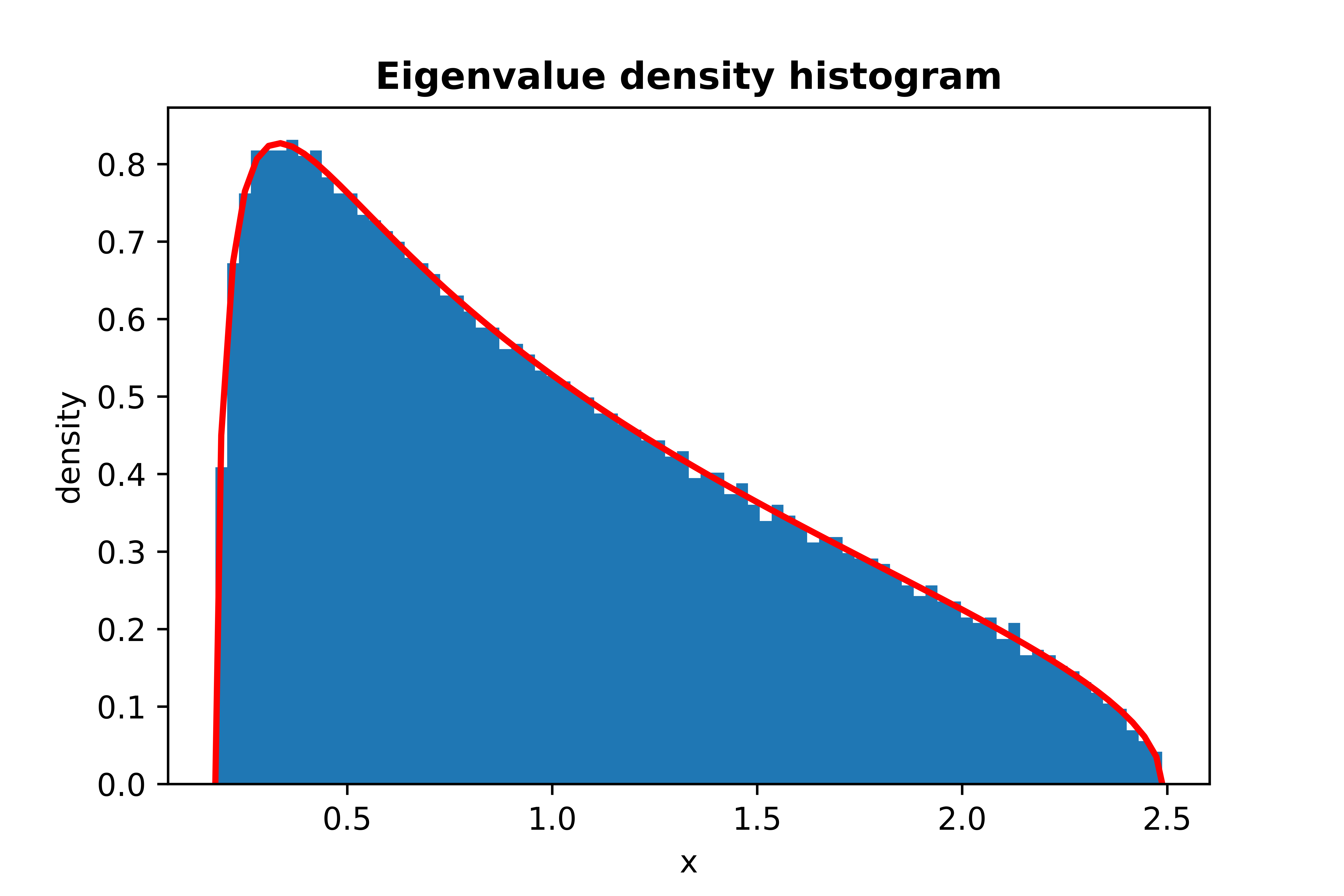
Plot of Tracy-Widom Law, sampling 30000 maximum eigenvalues of GOE matrices:
from skrmt.ensemble.spectral_law import TracyWidomDistribution
twd = TracyWidomDistribution(beta=1)
twd.plot_empirical_pdf(sample_size=30000, bins=80, density=True)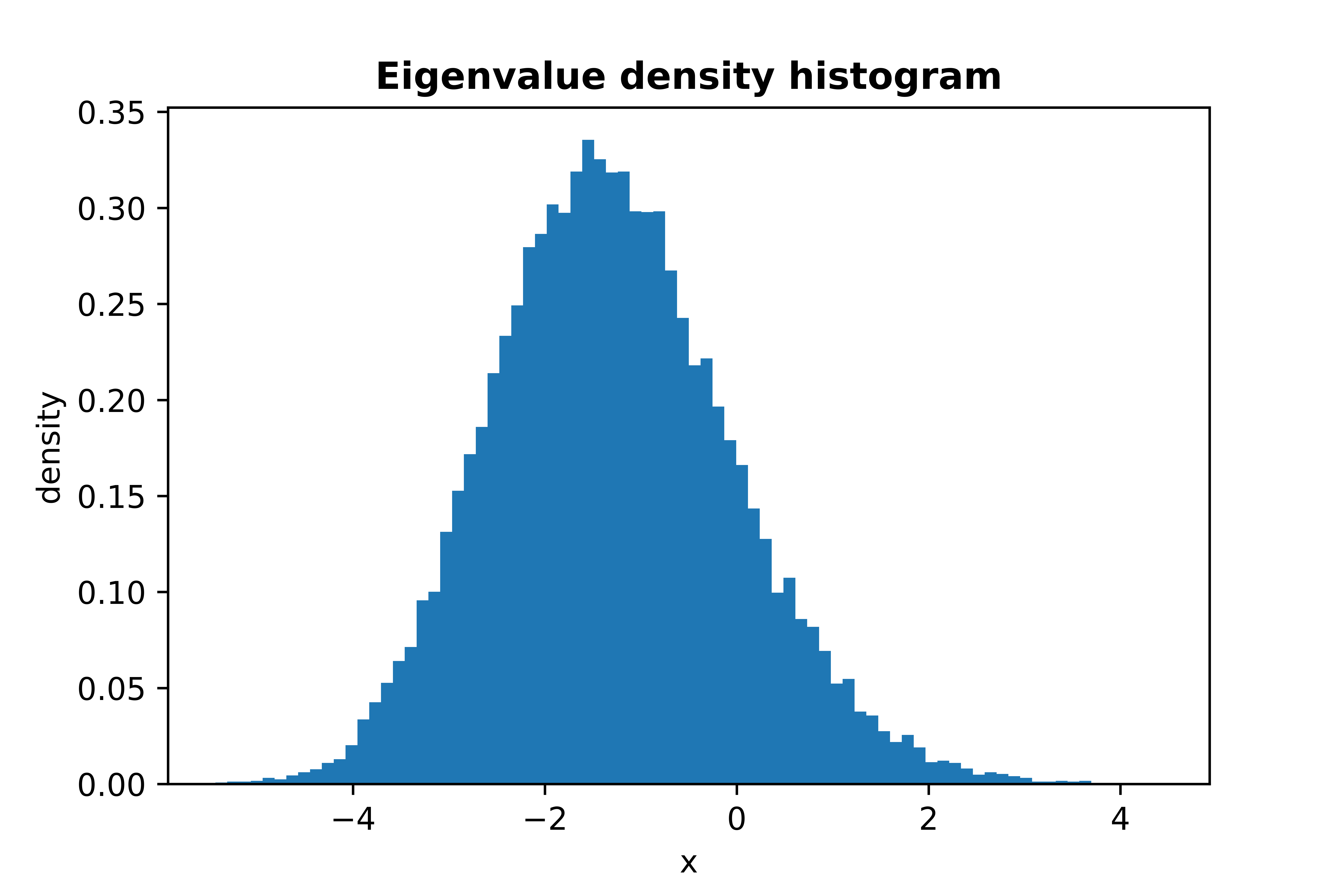
from skrmt.ensemble.spectral_law import TracyWidomDistribution
twd = TracyWidomDistribution(beta=1)
twd.plot_empirical_pdf(sample_size=30000, bins=80, density=True, plot_law_pdf=True)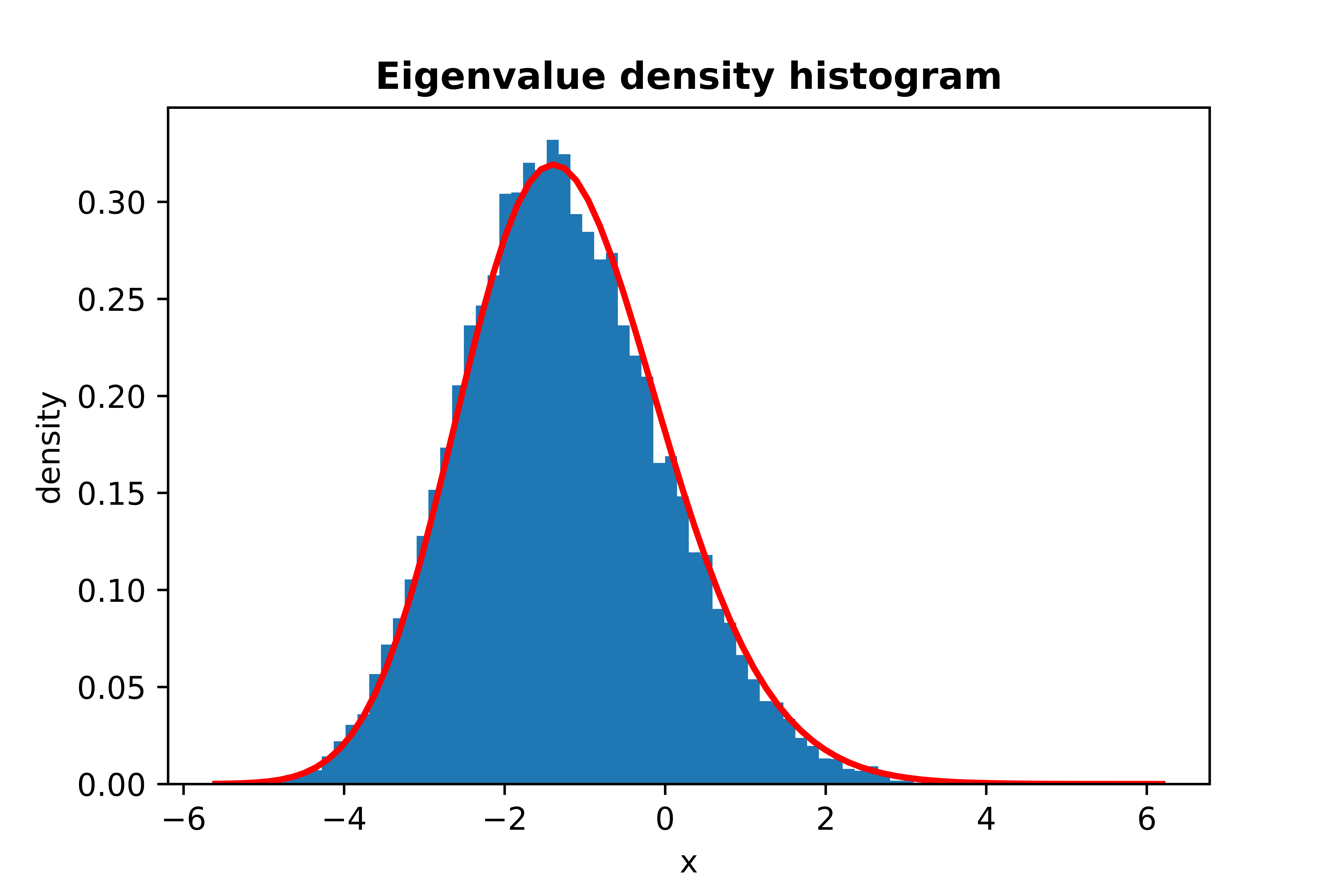
The proposed package scikit-rmt also provides support for computing and analyzing the probability density function (PDF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the main random matrix ensembles. In particular, the following classes are implemented in the ensemble.spectral_law module:
WignerSemicircleDistributioninskrmt.ensemble.spectral_law.MarchenkoPasturDistributioninskrmt.ensemble.spectral_law.TracyWidomDistributioninskrmt.ensemble.spectral_law.ManovaSpectrumDistributioninskrmt.ensemble.spectral_law.
For example, WignerSemicircleDistribution can be used to plot the Wigner's Semicircle Law PDF:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skrmt.ensemble.spectral_law import WignerSemicircleDistribution
x1 = np.linspace(-5, 5, num=1000)
x2 = np.linspace(-10, 10, num=2000)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12,4))
for sigma in [0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0]:
wsd = WignerSemicircleDistribution(beta=1, center=0.0, sigma=sigma)
y1 = wsd.pdf(x1)
y2 = wsd.pdf(x2)
ax1.plot(x1, y1, label=f"$\sigma$ = {sigma} (R = ${wsd.radius}$)")
ax2.plot(x2, y2, label=f"$\sigma$ = {sigma} (R = ${wsd.radius}$)")
ax1.legend()
ax1.set_xlabel("x", fontweight="bold")
ax1.set_xticks([-5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
ax1.set_ylabel("density", fontweight="bold")
ax2.legend()
ax2.set_xlabel("x", fontweight="bold")
ax2.set_xticks([-10, -8, -6, -4, -2, 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
ax2.set_ylabel("density", fontweight="bold")
fig.suptitle("Wigner Semicircle probability density function (PDF)", fontweight="bold")
plt.show()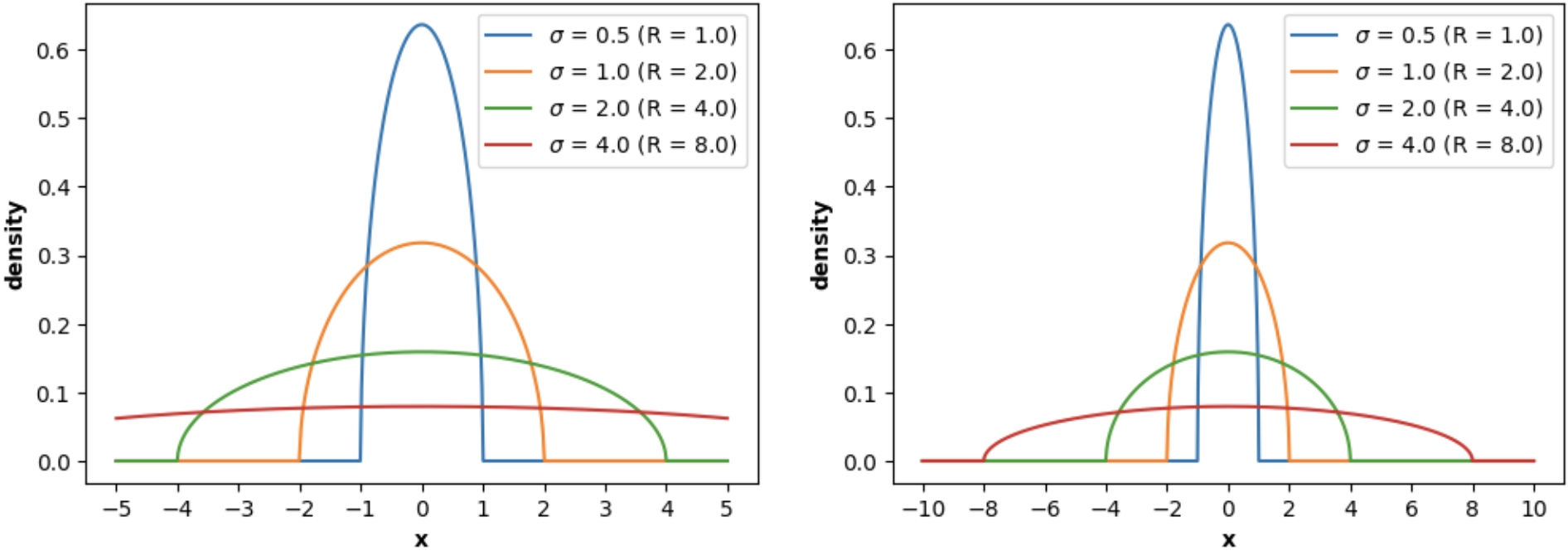
Similarly, MarchenkoPasturDistribution can be used to plot the Marchenko-Pastur Law PDF:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skrmt.ensemble.spectral_law import MarchenkoPasturDistribution
x1 = np.linspace(0, 4, num=1000)
x2 = np.linspace(0, 5, num=2000)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12,4))
for ratio in [0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 1.0, 1.4]:
mpl = MarchenkoPasturDistribution(beta=1, ratio=ratio, sigma=1.0)
y1 = mpl.pdf(x1)
y2 = mpl.pdf(x2)
ax1.plot(x1, y1, label=f"$\lambda$ = {ratio} ")
ax2.plot(x2, y2, label=f"$\lambda$ = {ratio} ")
ax1.legend()
ax1.set_ylim(0, 1.4)
ax1.set_xlabel("x", fontweight="bold")
ax1.set_ylabel("density", fontweight="bold")
ax2.legend()
ax2.set_ylim(0, 1.4)
ax2.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax2.set_xlabel("x", fontweight="bold")
ax2.set_ylabel("density", fontweight="bold")
fig.suptitle("Marchenko-Pastur probability density function (PDF)", fontweight="bold")
plt.show()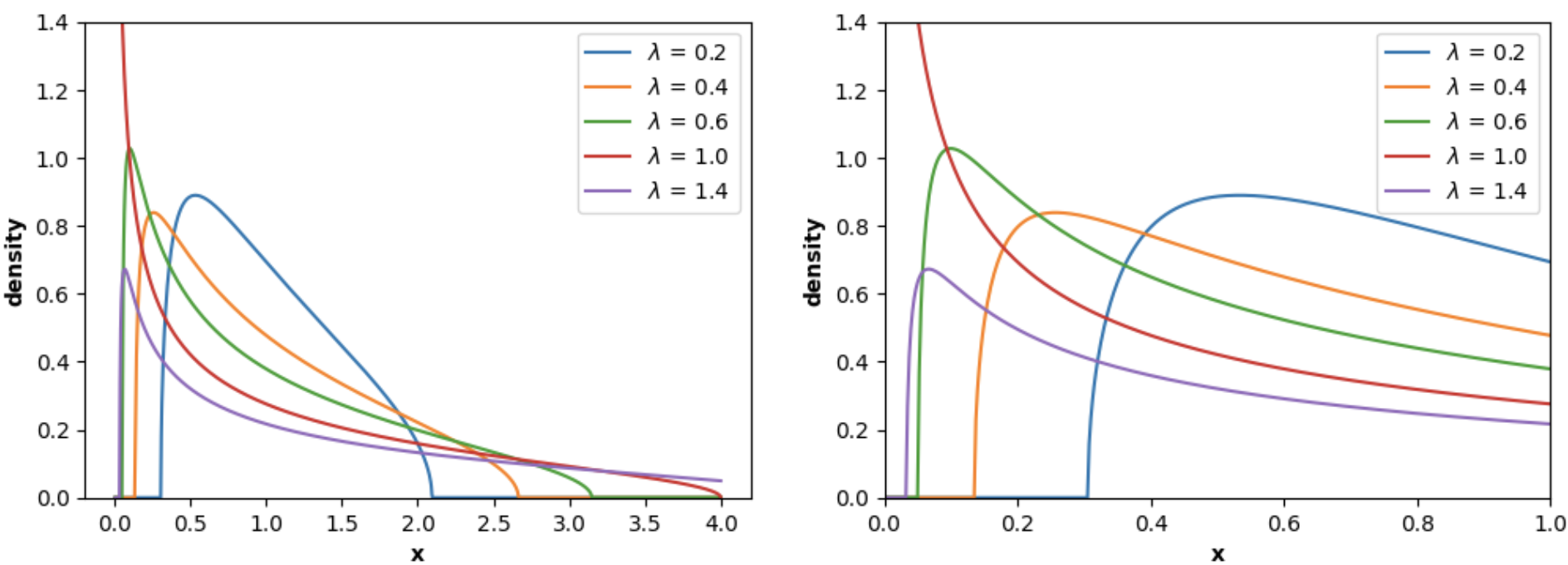
In the following example, we show how we can plot the PDF and CDF of the Tracy-Widom distribution using the class TracyWidomDistribution:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skrmt.ensemble.spectral_law import TracyWidomDistribution
x = np.linspace(-5, 2, num=1000)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12,4))
for beta in [1,2,4]:
twd = TracyWidomDistribution(beta=beta)
y_pdf = twd.pdf(x)
y_cdf = twd.cdf(x)
ax1.plot(x, y_pdf, label=f"$\\beta$ = {beta}")
ax2.plot(x, y_cdf, label=f"$\\beta$ = {beta}")
ax1.legend()
ax1.set_xlabel("x", fontweight="bold")
ax1.set_ylabel("density", fontweight="bold")
ax1.set_title("Probability density function")
ax2.legend()
ax2.set_xlabel("x", fontweight="bold")
ax2.set_ylabel("distribution", fontweight="bold")
ax2.set_title("Cumulative distribution function")
fig.suptitle("Tracy Widom Law", fontweight="bold")
plt.show()
The other module of this library implements several covariance matrix estimators:
- Sample estimator.
- Finite-sample optimal estimator (FSOpt estimator).
- Non-linear shrinkage analytical estimator (Ledoit & Wolf, 2020).
- Linear shrinkage estimator (Ledoit & Wolf, 2004).
- Empirical Bayesian estimator (Haff, 1980).
- Minimax estimator (Stain, 1982).
For certain problems, sample covariance matrix is not the best estimation for the population covariance matrix.
The following code illustrates the usage of the estimators.
from skrmt.covariance import analytical_shrinkage_estimator
# load dataset with your own/favorite function (such as pandas.read_csv)
X = load_dataset('dataset_file.data')
# get estimation
Sigma = analytical_shrinkage_estimator(X)
# ... Do something with Sigma. For example, PCA.For more information or insight about the usage of the library, you can visit the official documentation https://scikit-rmt.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ or the directory notebooks, that contains several Python notebooks with tutorials and plenty of examples.
License
The package is licensed under the BSD 3-Clause License. A copy of the license can be found along with the code.
Main references
-
James Albrecht, Cy Chan, and Alan Edelman, "Sturm Sequences and Random Eigenvalue Distributions", Foundations of Computational Mathematics, vol. 9 iss. 4 (2009), pp 461-483. [pdf] [doi]
-
Ioana Dumitriu and Alan Edelman, "Matrix Models for Beta Ensembles", Journal of Mathematical Physics, vol. 43 no. 11 (2002), pp. 5830-5547 arXiv:math-ph/0206043
-
Rowan Killip and Rostyslav Kozhan, "Matrix Models and Eigenvalue Statistics for Truncations of Classical Ensembles of Random Unitary Matrices", Communications in Mathematical Physics, vol. 349 (2017) pp. 991-1027. arxiv.org/pdf/1501.05160.pdf
-
Olivier Ledoit and Michael Wolf, "Analytical Nonlinear Shrinkage of Large-dimensional Covariance Matrices", Annals of Statistics, vol. 48, no. 5 (2020) pp. 3043–3065. [pdf]
-
Olivier Ledoit and Michael Wolf, "A Well-conditioned Estimator for Large-dimensional Covariance Matrices", Journal of Multivariate Analysis, vol. 88 (2004) pp. 365–411. [pdf]
Attribution
This project has been developed by Alejandro Santorum Varela (2021) as part of the final degree project in Computer Science (Autonomous University of Madrid), supervised by Alberto Suárez González.
If you happen to use scikit-rmt in your work or research, please cite its GitHub repository:
A. Santorum, "scikit-rmt", https://github.com/AlejandroSantorum/scikit-rmt, 2021. GitHub repository.
The corresponding BibTex entry is
@misc{Santorum2021,
author = {A. Santorum},
title = {scikit-rmt},
year = {2021},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/AlejandroSantorum/scikit-rmt}},
note = {GitHub repository}
}

