aiide facilitates the creation of reinforcement learning (RL)-type environments for large language models (LLMs). It allows you to define and manage live data structures (components) that collectively form the environment (ENV). The LLM can interact with and modify these components by using user provided tools. After each action, along with the tool response, aiide adds the latest snapshot/state of all ENV components and removes all older ENV snapshots from the LLM's memory.
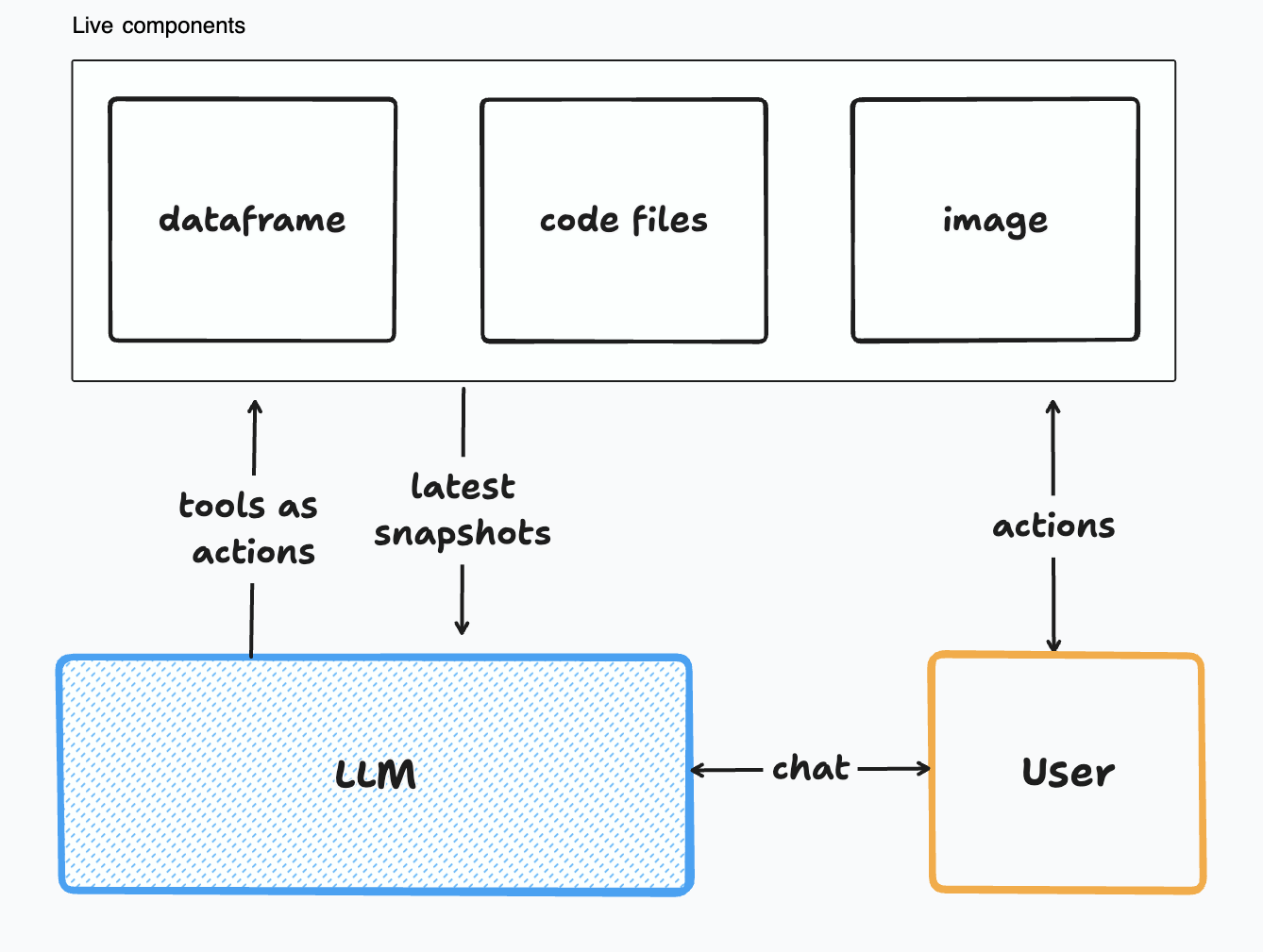
ENV states are made available to the LLM in the following way:
Tutorial
Let's build a simple form filling agent. We have a pandas dataframe with field names and we want the LLM to ask the user for answers to a couple of questions at a time and populate the said dataframe.
Here
- The environment is the dataframe
- We need a single tool that enables the LLM to add or edit values for any of the fields
- The library will automatically provide the latest snapshot of the dataframe to the LLM.(aiide will automatically remove older snapshots of the dataframe from the LLM memory to avoid confusing it and saving tokens)
-
Install the package
pip install aiide -
Let's start with defining a simple chat agent
# Import the AIIDE class
from aiide import AIIDE
# Import helper classes for defining functions for the LLM
from aiide.tools import TOOL_DEF, INT, FLOAT, STR, BOOL, LIST, DICT
import pandas as pd
# Define a class and inherit the AIIDE class
class FormFillingAgent(AIIDE):
def __init__(self):
# Let's define a dummy dataframe with fields and value as the columns
self.df = pd.DataFrame({
"Field":["name","age","gender","email","city","job","married"],
"Value":["Not yet assigned" for i in range(7)]
})
# Here we only have one component and providing it as the element for the reserved ENV array
self.ENV =[self.df.to_markdown(index=False)]
# use setup to define the system message, type of model, temperature etc
self.setup(messages=[{"role":"system","content":"You are a helpful assistant. Fill the form table attached by asking the user to answer a couple of fields from the table at a time."}],model="gpt-3.5-turbo",temperature=0.2)Set your openai key as
OPENAI_API_KEYenviroment variable or pass it in setup as api_key
-
Let's define the tool. We have to define the tool as a class inside our
FormFillingAgentclassclass FormFillingAgent(AIIDE): def __init__(self): ... class Tool: def __init__(self): # we can access the FormFillingAgent instance through .parent self.parent.df # We now have to define the function definition and assign it to the reserved self.tool_def variable self.tool_def = TOOL_DEF( name = "add_or_modify_form_values", description = "tool to add or modify field values", properties = [ STR( name = "field_name", enums=self.parent.df["Field"].values.tolist() ), STR( name = "value" ) ] ) # Main function of the tool is called when the tool is invoked by the agent def main(self, field_name,value): # let's set the value in the master dataframe self.parent.df.loc[self.parent.df['Field'] == field_name, 'Value'] = value # Update the ENV self.parent.ENV[0] = self.parent.df.to_markdown(index=False) # response to the agent return "Added value '"+str(value) + " to Field '"+field_name+"'"
> `TOOL_DEF` is a helper proxy for the JSON-SCHEMA of OpenAI function calling. You can directly add the json or even use your own pydantic model's `model_json()`. `TOOL_DEF` and associated `tools.*` would make the code less verbose and have the advantage of intellisense.
Checkout <br/>**[aiide's tool use tutorial](https://github.com/Anilturaga/aiide/blob/main/assets/tool_definitions.md)**
3. That's it. We can now start using the agent
`chat` is the function you invoke to start streaming agent response
```python
# create the agent instance
agent = FormFillingAgent()
while True:
# get the user message
user_query = input("User: ")
# you can enable and disable tools as you wish with the tools array
for each in agent.chat(user_query, tools=["add_or_modify_form_values"]):
# if the agent is reponding in text
if each["type"] == "text":
print(each["delta"],end="")
# is the agent is calling a tool
if each["type"] == "tool":
print("TOOL CALL:",each["name"],each["arguments"])
# the tool's response to the agent
if each["type"] == "tool_response":
print("TOOL RESPONSE",each["response"])
# for debugging, let's print the table after every turn
print(agent.df)- What if you want to take user's consent everytime before filling the table? it's incredibly simple!
You simply add a consent bool variable in the Tool class and update it in the chat loop as needed.
Here is the updated code:
# edit the tool to reject is the user rejects
class FormFillingAgent(AIIDE):
def __init__(self):
... previous code
class Tool:
def __init__(self):
# User consent bool
self.user_consent = False
... previous code
def main(self, field_name,value):
if self.user_consent == False:
return "User has rejected the insert, please try again"
# let's set the value in the master dataframe
self.parent.df.loc[self.parent.df['Field'] == field_name, 'Value'] = value
# Update the ENV
self.parent.ENV[0] = self.parent.df.to_markdown(index=False)
# response to the agent
return "Added value '"+str(value) + " to Field '"+field_name+"'"
agent = FormFillingAgent()
while True:
user_query = input("User: ")
for each in agent.chat(user_query, tools=["add_or_modify_form_values"]):
if each["type"] == "text":
print(each["delta"],end="")
if each["type"] == "tool":
print("TOOL CALL:",each["name"],each["arguments"])
# ask for user consent
user_consent = input("do you approve the above tool call?(y/n)")
if user_consent == 'y:
# you can access the tool instance like so
agent.Tool.user_consent = True
else:
agent.Tool.user_consent = False
if each["type"] == "tool_response":
print("TOOL RESPONSE",each["response"])
- Bonus!
You can use completions and stop sequences in the
chatfunction's arguments to implement prompting techniques such as ReAct, CoT etc!
For Example:from aiide import AIIDE import json from aiide.tools import *
class Agent(AIIDE): def init(self): self.outer_var = 15 self.setup( messages=[{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."}], temperature=0.0, )
agent = Agent() poems = [] for each in agent.chat( "Write 2 poems but end each poem with '---'", completion="1.", stop_words=["---"] ): print(each["delta"], end="") poems.append(each["content"]) print("\n\nSecond generation\n\n") for each in agent.chat(completion="---\n2. "): print(each["delta"], end="") poems.append(each["content"]) print("\n",poems)
### Reserved variables
Here is a non-exhaustive list of helper variables available across aiide agents and tools.