GMM-Demux
GMM-Demux is a Gaussian-Mixture-Model-based software for processing sample barcoding data (cell hashing and MULTI-seq).
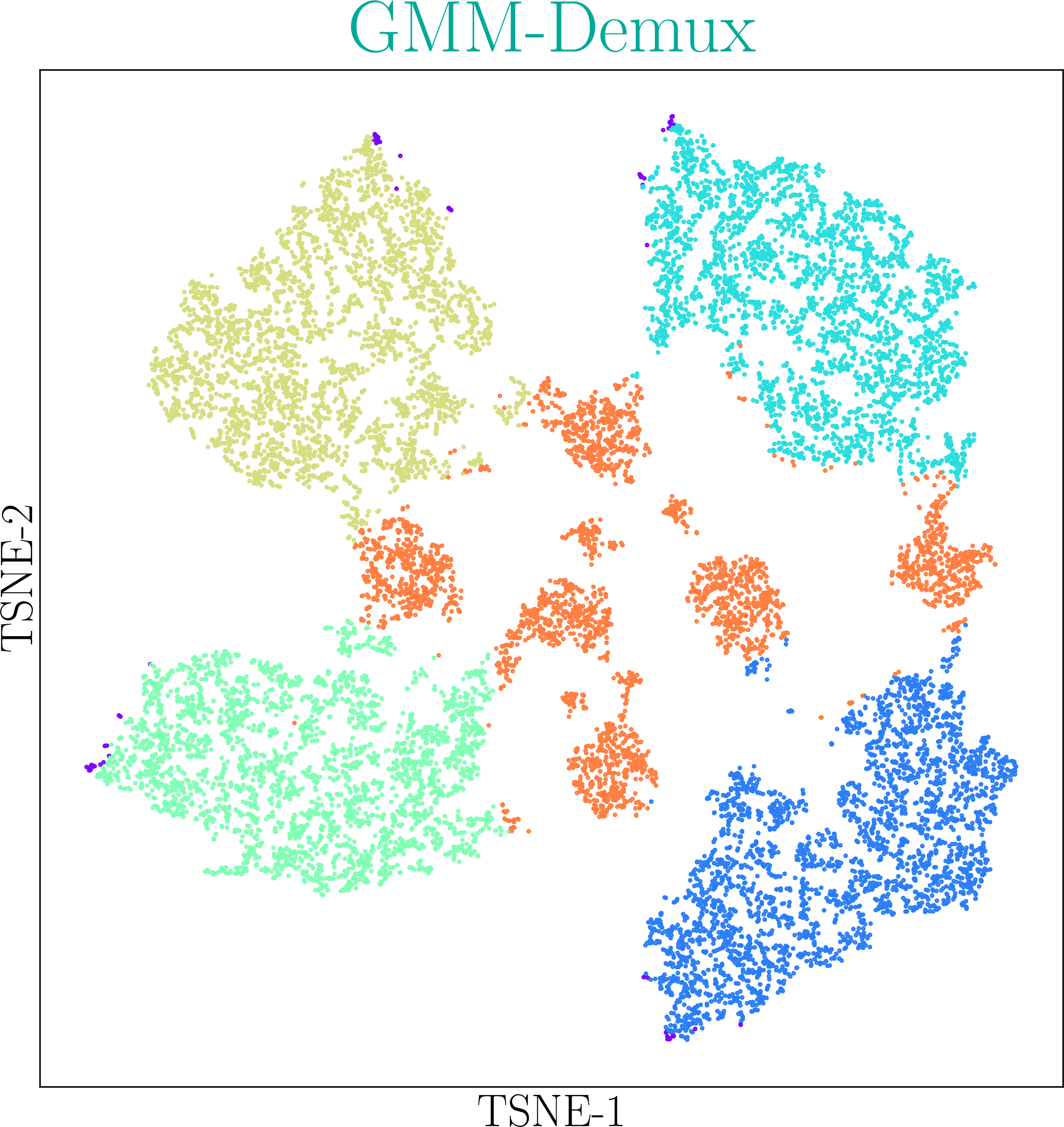
GMM-Demux identifies Multi-Sample Multiplets (MSMs) in a sample barcoding dataset. Below shows an example distribution of MSMs in a PBMC scRNA-seq dataset. Orange dots in the scatter plot are MSMs.

Description
GMM-Demux removes Multi-Sample-Multiplets (MSMs) in a cell hashing dataset and estimates the percentages of Same-Sample-Multiplets (SSMs) and singlets in the remaining dataset. GMM-Demux also verifies if a putative cell type exists, or is it merely an artifact induced by multiplets.
Multiplet-induced fake cell types are called "phony cell types".
Examples of phony cell types in a PBMC CITE-seq dataset is provided in the figure below:

In the above figure, both the CD3+CD19+ and the CD4+CD8+ cell types are multiplet-induced fake cell types.
Phony type clusters have large percentages of MSMs, as above figure shows. Both phony type clusters have large MSM percentages.
Percentages of MSMs are used as key features by GMM-Demux to classify GEM clusters.
Terminology
-
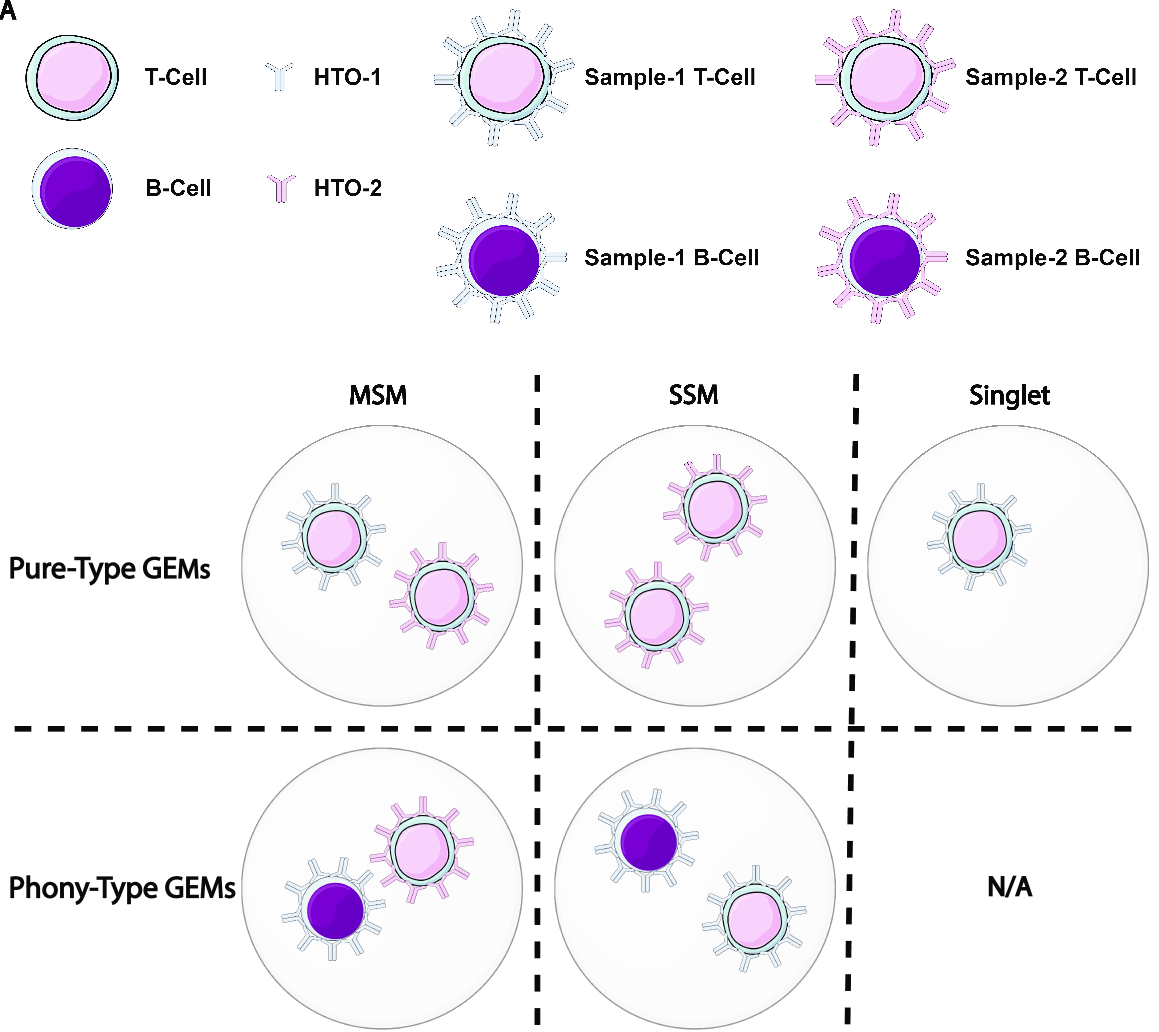
Singlet: A droplet that contains a single cell.
-
MSM: Multi-Sample Multiplet. A MSM is a multiplet that contains cells from different samples in sample barcoding. MSMs can be identified by GMM-Demux.
-
SSM: Same-Sample Multiplet. A SSM is a multiplet that contains cells from a single sample in sample barcoding. SSMs cannot be separated from singlets by sample barcoding.
-
SSD: Same-Sample Droplet. SSD is a combined category of both SSMs and singlets.
-
Pure type: a pure type cell type is a real cell type that exist in the tissue.
-
Phony type: a phony type cell type is an artificial cell type that is an artifact produced by multiplets.
-
Mixture type: a mixture type cell type is a cluster of droplets in which there exist a non-trivial fraction of phony type droplets.
An illustration of the above terminologies in a PBMC dataset is provided in the figure below:
Features
- Remove cell-hashing-identifiable multiplets (i.e., MSMs) from the dataset.
- Estimate the fraction of cell-hashing-unidentifiable multiplets (SSMs) in the remaining dataset (the RSSM percentage).
- Test if a putative cell type is a pure (real) cell type or is it a phony (fake) cell type.
Example Dataset
- An example cell hashing dataset is provided in the example_input folder. It contains the per-drop HTO count matrix of a 4-sample cell hashing library prep. The input folder has the same file format with the CellRanger v3 output.
Authors
Hongyi Xin, Qi Yan, Yale Jiang, Jiadi Luo, Carla Erb, Richard Duerr, Kong Chen and Wei Chen
Maintainer
Hongyi Xin
Requirement
GMM-Demux requires python3 (>3.5).
Install
GMM-Demux can be directly installed from PyPi. Or it can be built and installed locally.
Install GMM-Demux from PyPi.
pip3 install --user GMM_DemuxIn some OS, the pip3 is linked to pip by default. For these OS, the installation command is simply:
pip install --user GMM_DemuxCheck if pip3 is linked to pip with pip -V.
If one chooses to install GMM-Demux from PyPi, it is unnecessary to download GMM-Demux from github. However, we still recommend downloading the example dataset to try out GMM-Demux.
Install GMM-Demux locally using setuptools and pip3.
You may choose to install GMM-Demux locally after cloning the github repository. However, this is for advanced users only and support is not gauranteed. The command is provided below:
cd <GMM-Demux dir>
python3 setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
pip3 install --user . Post installation processes
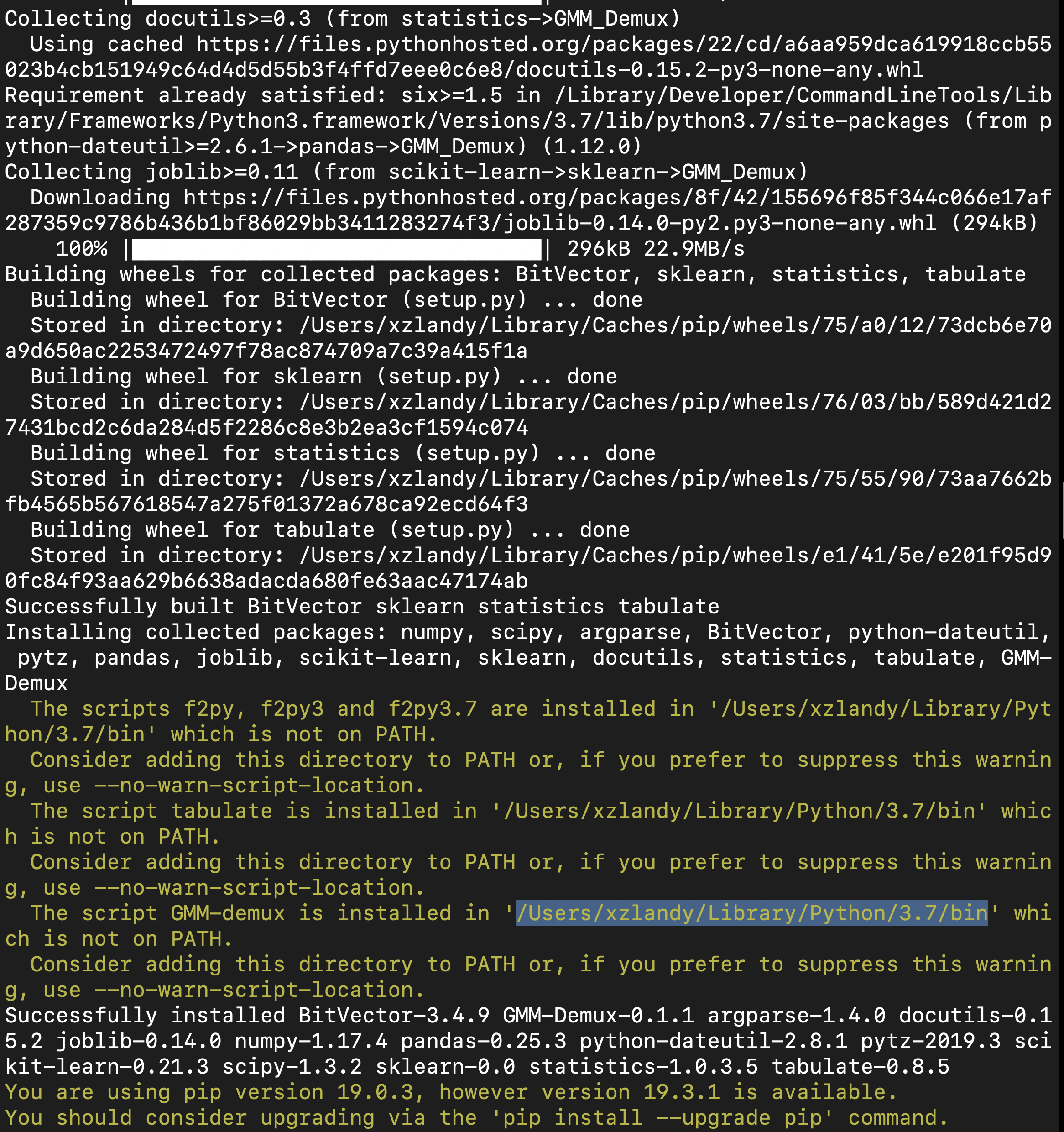
If this is the first time you install a python3 software through pip, make sure you add the pip binary folder to your PATH variable.
Typically, the pip binary folder is located at ~/.local/bin.
The pip binary folder might locate at a different location if the user uses virtual enviroment. Pay attention to the pip installation output.
Here is an example installation output. The path of the pip binary folder is highlighted:
To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATHTo permenantly add the pip library folder to your PATH variable, append the following line to your .bashrc file (assuming bash is the default shell).
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATHContent
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the GMM_Demux folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the example_cell_types folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the example_hto.csv file.
Usage
Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the GMM-demux command.
GMM-demux <cell_hashing_path> <HTO_names><HTO_names> is a list of sample tags (HTOs) separated by ',' without whitespace.
For example, there are four sample barcoding tags in the example cell hashing dataset.
They are HTO_1, HTO_2, HTO_3, HTO_4. The <HTO_names> variable therefore is HTO_1,HTO_2,_HTO_3,HTO_4.
The non-MSM droplets (SSDs) of the dataset are stored in the GMM_Demux_mtx folder under the current directory by default.
The output path can also be specified through the -o flag.
Example Command
An example cell hashing data is provided in the example_input folder.
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4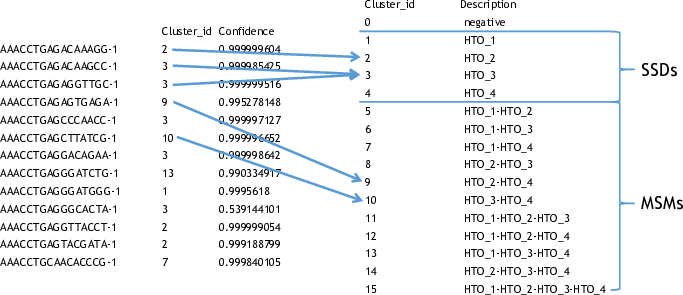 ## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
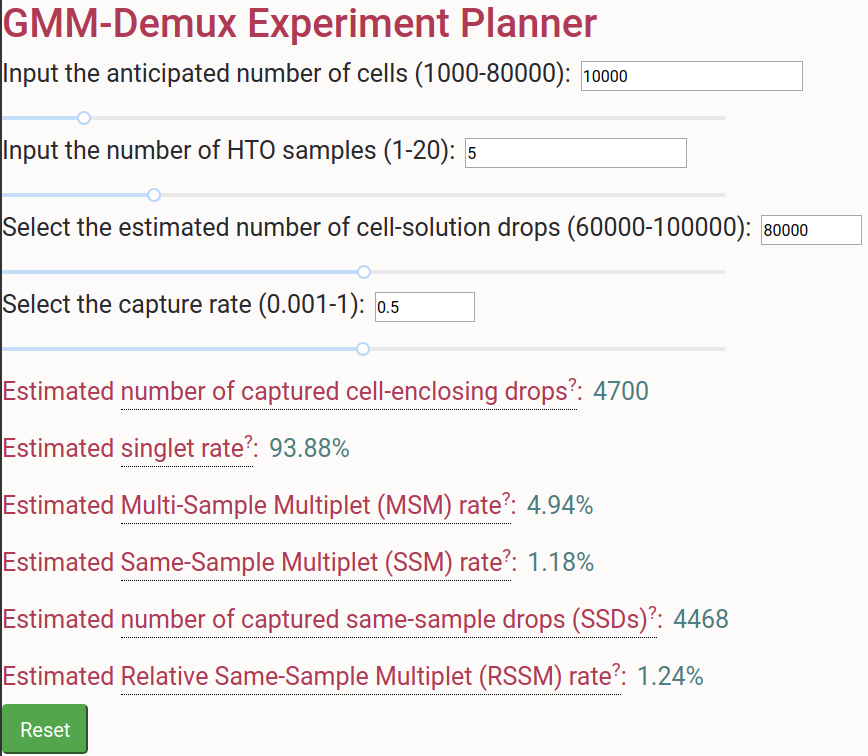
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[
## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[ ](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!