Handling image upload isn't a trivial task. Currently I have to implement such feature in a React Native app. Users can upload images to a feed controlled by a backend. Image uploading is data and network intensive, and you need to handle it gracefully to make it scalable and reduce stress on the server.
Eventually we decide to use Firebase Storage to handle heavy image uploading, the app then just submits the image URL to the backend server.
Firebase Storage is designed specifically for scale, security, and network resiliency:
- Scale: every file uploaded is backed by Google Cloud Storage, which scales to petabytes.
- Security: files can be secured to specific users or sets of users using Storage Security Rules.
- Network resiliency: uploads and downloads are automatically retried in the case of poor network connections, so you don’t have to keep track of network status.
At first, I thought I hit a dead end because I saw this quote from Firebase Blog:
React Native does not support the File and Blob types, so Firebase Storage uploads will not work in this environment. File downloads do work however.Luckily, I found a module that had File and Blob types support in React Native: https://github.com/wkh237/react-native-fetch-blob
Some features stand out and it sounds promising:
- Transfer data directly from/to storage without BASE64 bridging.
- File API supports normal files, Asset files, and CameraRoll files.
- Native-to-native file manipulation API, reduce JS bridging performance loss.
- File stream support for dealing with large file (Blob type).
- Blob, File, XMLHttpRequest polyfills that make browser-based library available in React Native (experimental).
So, let's build an App that can choose some photos on device and upload to
Firebase Storage with firebase and react-native-fetch-blob modules
This is how the app looks like after we finish:

Let's follow the steps below to implement it!
1. Init a demo project:
$ react-native init FirebaseStorageDemo2. Install necessary modules:
$ yarn add firebase react-native-fetch-blob react-native-image-picker
$ RNFB_ANDROID_PERMISSIONS=true react-native linkThe extra react-native-image-picker is for image picking.
3. Add permissions for Android:
to AndroidManifest.xml
...
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" android:required="false"/>
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera.autofocus" android:required="false"/>
...4. Configure Firebase Storage:
First we need to create an images folder in the root Storage:
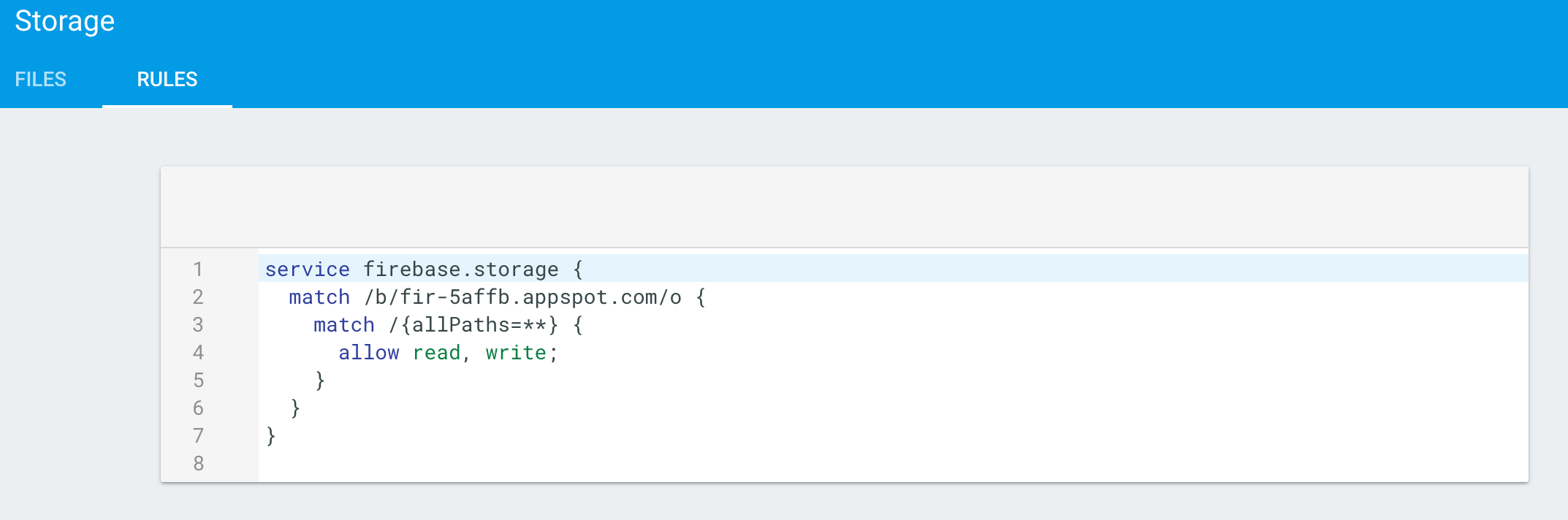
By default Firebase forbids read or write to the Storage folder. We need to open up permission rules.
For this demo app, I will just open up both read and write for the images
folder. In real situation, you probably want to tighten the permissions.
5. Initialize Firebase based on your config:
const config = {
apiKey: "<YOUR-API-KEY>",
authDomain: "<APP-NAME>.firebaseio.com",
storageBucket: "<APP-NAME>.appspot.com",
}
firebase.initializeApp(config)6. Enable Blob and XMLHttpRequest polyfills:
const Blob = RNFetchBlob.polyfill.Blob
window.XMLHttpRequest = RNFetchBlob.polyfill.XMLHttpRequest
window.Blob = Blob7. Implement uploadImage function:
const uploadImage = (uri, mime = 'application/octet-stream') => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const uploadUri = Platform.OS === 'ios' ? uri.replace('file://', '') : uri
const sessionId = new Date().getTime()
let uploadBlob = null
const imageRef = storage.ref('images').child(`${sessionId}`)
fs.readFile(uploadUri, 'base64')
.then((data) => {
return Blob.build(data, { type: `${mime};BASE64` })
})
.then((blob) => {
uploadBlob = blob
return imageRef.put(blob, { contentType: mime })
})
.then(() => {
uploadBlob.close()
return imageRef.getDownloadURL()
})
.then((url) => {
resolve(url)
})
.catch((error) => {
reject(error)
})
})
}Basically it uses Firebase SDK to create a reference to the Storage folder, then write the binary data from the selected image to it.
For Blob type, I find it most stable to encode the binary data with Base64
first. I hope it will get more stable in future release of react-native-fetch-blob