cv4pve-autosnap
Proxmox VE automatic snapshot tool
More information about cv4pve-autosnap
More information about Qemu guest agent
:star: We appreciate your star, it helps!
______ _ __
/ ____/___ __________(_)___ _ _____ _____/ /_
/ / / __ \/ ___/ ___/ / __ \ | / / _ \/ ___/ __/
/ /___/ /_/ / / (__ ) / / / / |/ / __(__ ) /_
\____/\____/_/ /____/_/_/ /_/|___/\___/____/\__/
Automatic snapshot VM/CT with retention (Made in Italy)
cv4pve-autosnap is a part of suite cv4pve.
For more information visit https://www.corsinvest.it/cv4pve
Usage:
cv4pve-autosnap [command] [options]
Options:
--api-token <api-token> Api token format 'USER@REALM!TOKENID=UUID'. Require Proxmox VE 6.2 or later
--username <username> User name <username>@<realm>
--password <password> The password. Specify 'file:path_file' to store password in file.
--validate-certificate Validate SSL Certificate Proxmox VE node.
--host <host> (REQUIRED) The host name host[:port],host1[:port],host2[:port]
--vmid <vmid> (REQUIRED) The id or name VM/CT comma separated (eg. 100,101,102,TestDebian)
-vmid,-name,-@node-???,-@tag-?? exclude from list (e.g. @all,-200,-TestUbuntu,-@tag-customer1)
range 100:107,-105,200:204
'@pool-???' for all VM/CT in specific pool (e.g. @pool-customer1),
'@tag-???' for all VM/CT in specific tags (e.g. @tag-customerA),
'@node-???' for all VM/CT in specific node (e.g. @node-pve1, @node-\$(hostname)),
'@all-???' for all VM/CT in specific host (e.g. @all-pve1, @all-\$(hostname)),
'@all' for all VM/CT in cluster
--timeout <timeout> Timeout operation in seconds [default: 30]
--timestamp-format <timestamp-format> Specify different timestamp format [default: yyMMddHHmmss]
--max-perc-storage <max-perc-storage> Max percentage storage [default: 95]
--version Show version information
-?, -h, --help Show help and usage information
Commands:
snap Will snap one time
clean Remove auto snapshots
status Get list of all auto snapshotsCopyright and License
Copyright: Corsinvest Srl For licensing details please visit LICENSE.md
Commercial Support
This software is part of a suite of tools called cv4pve-tools. If you want commercial support, visit the site
Tutorial
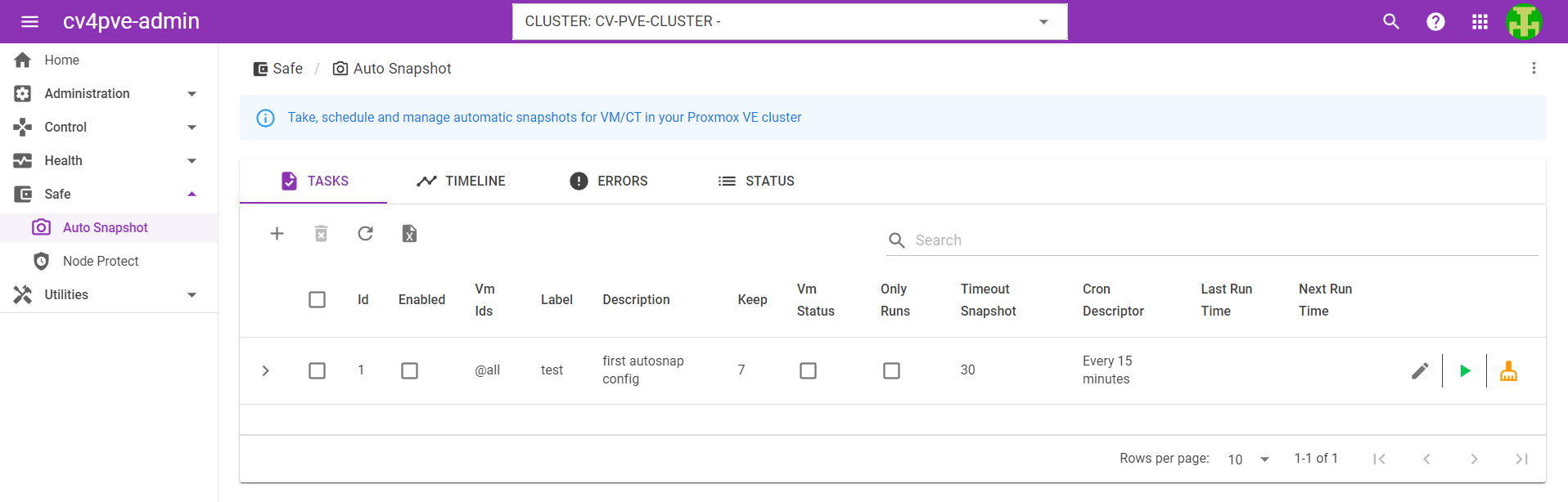
Web GUI Version in cv4pve-admin
Introduction
Automatic snapshot for Proxmox VE with retention.
In this version the tool works outside the Proxmox VE host using the API. The reasons are:
- if the host does not work the tool does not work
- using the API, future changes are guaranteed
- Root access is not required, a user is required to perform the operation
- use of standard https / https json technology
Main features
- Completely written in C#
- Use native Api REST Proxmox VE (library C#)
- Independent os (Windows, Linux, Macosx)
- Installation rapid, unzip file extract binary
- Not require installation in Proxmox VE
- Execute out side Proxmox VE
- For KVM and LXC
- Work for single node or cluster, automatically resolve VM/CT id/name
- Use id or name with --vmid parameter
- Can keep multiple snapshots --keep
- Clean all snapshots
- Multiple schedule VM/CT using --label (es. daily,monthly)
- Hook script
- Multiple VM/CT (100,102,ubuVm,debVm,pipperoVm,fagianoVm or all or pool) in a single execution
- Exclusion specific VM/CT using minus e.g --vmid=all,-100
- Exclusion template from snapshot
- Waiting for the snapshot process to finish
- Alerting in QEMU, agent not enabled.
- Save memory VM Qemu in snap using parameter --state.
- No stop on error
- Script hook for metrics
- Timeout remove/create snapshot in --timeout parameter specify in second
- Support multiple host for HA in --host parameter es. host[:port],host1[:port],host2[:port]
- Multiple output text,unicode,unicodeAlt,markdown,html
- Use Api token --api-token parameter
- Support range vmid 100:103,134,200:204,-102
- Support different timestamp format with parameter --timestamp-format
- Check the storage space used by the disks in the VM / CT is available by default (95%) parameter --max-perc-storage
- Execution with file parameter e.g. @FileParameter.parm
- Snapshots are removed with force parameter
- Decide only runs VM/CT
- Support Proxmox VE Tags in vmid
- Validate certificate SSL, default not validate
Permission
For execution is required permission: VM.Audit, VM.Snapshot, Datastore.Audit, Pool.Audit.
Api token
From version 6.2 of Proxmox VE is possible to use Api token. This feature permit execute Api without using user and password. If using Privilege Separation when create api token remember specify in permission.
Custom timestamp format
Timestamp format is based on C# date and time format string.
Configuration and use
E.g. install on linux 64
Download last package e.g. Debian cv4pve-autosnap-linux-x64.zip, on your os and install:
root@debian:~# unzip cv4pve-autosnap-linux-x64.zipThis tool need basically no configuration.
Snapshot a VM/CT one time
root@debian:~# cv4pve-autosnap --host=192.168.0.100 --username=root@pam --password=fagiano --vmid=111 snap --label=daily --keep=2This command snap VM 111.
root@debian:~# cv4pve-autosnap --host=192.168.0.100 --username=root@pam --password=fagiano --vmid="all,-111" snap --label=daily --keep=2
ACTION Snap
VMs: all,-111
Label: daily
Keep: 2
State: False
Timeout: 30000
Timestamp format: yyMMddHHmmss
Max % Storage : 95%
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Storage | Type | Valid | Used % | Max Disk (GB) | Disk (GB) |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
| cv-pve01/hddpool | zfspool | Ok | 58.2 | 1797 | 1046 |
| cv-pve01/nfs-arc | nfs | Ok | 21.1 | 3269 | 689 |
| cv-pve01/ssdpool | zfspool | Ok | 24.4 | 859 | 209 |
| cv-pve02/hddpool | zfspool | Ok | 71.7 | 1797 | 1288 |
| cv-pve02/nfs-arc | nfs | Ok | 21.1 | 3269 | 689 |
| cv-pve02/ssdpool | zfspool | Ok | 5.5 | 898 | 49 |
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
----- VM 103 Qemu -----
VM 103 consider enabling QEMU agent see https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Qemu-guest-agent
Create snapshot: autodaily211203164953
Remove snapshot: autodaily211202164953
VM execution 00:00:02.3060904
----- VM 105 Qemu -----
Create snapshot: autodaily211203164955
Remove snapshot: autodaily211202164955
....This command snap all VMs except 111.
The --keep tells that it should be kept 2 snapshots, if there are more than 2 snapshots, the 3 one will be erased (sorted by creation time). The --state save memory VM. The --timeout specify the timeout remove/creation snapshot.
When create a snapshot the software add "auto" prefix of the name the snapshot.
On the VM it is checked if "QEMU agent" is enabled, otherwise an alert is displayed.
Clean a VM/CT one time
root@debian:~# cv4pve-autosnap --host=192.168.0.100 --username=root@pam --password=fagiano --vmid=111 clean --label=4hours --keep=2
----- VM 100 QEMU -----
Remove snapshot: auto4hours190617080002
Remove snapshot: auto4hours190617120002
Remove snapshot: auto4hours190617160002
Remove snapshot: auto4hours190617200002Status snapshots
root@debian:~# cv4pve-autosnap --host=192.168.0.100 --username=root@pam --password=fagiano --vmid=100 status
┌──────┬─────┬───────────────────┬──────────────────────────────┬──────────────────────────────┬─────────────────┬─────┐
│ NODE │ VM │ TIME │ PARENT │ NAME │ DESCRIPTION │ RAM │
├──────┼─────┼───────────────────┼──────────────────────────────┼──────────────────────────────┼─────────────────┼─────┤
│ pve1 │ 100 │ 19/08/28 09:21:35 │ no-parent │ auto4hours190828112133 │ cv4pve-autosnap │ │
│ pve1 │ 100 │ 19/08/28 12:23:09 │ auto4hours190828112133 │ auto4hours190828142307 │ cv4pve-autosnap │ │
│ pve1 │ 100 │ 19/08/29 06:50:23 │ auto4hours190828142307 │ auto4hours190829085021 │ cv4pve-autosnap │ │
│ pve1 │ 100 │ 19/08/29 07:32:15 │ auto4hours190829085021 │ auto4hours190829093214 │ cv4pve-autosnap │ │
└──────┴─────┴───────────────────┴──────────────────────────────┴──────────────────────────────┴─────────────────┴─────┘Output type:
-o|--output Type output (default: text) Text,Json,JsonPretty
Execution with file parameter
Is possible execute with file parameter
root@debian:~# cv4pve-autosnap @FileParameter.parmFile FileParameter.parm
--host=192.168.0.100
--username=root@pam
--password=fagiano
--vmid=100
statusHook script
Before run hook script, program create environment variable:
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_PHASE
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_VMID
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_VMNAME
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_VMTYPE
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_LABEL
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_KEEP
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_SNAP_NAME
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_VMSTATE #1/0
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_DEBUG #1/0
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_DRY_RUN #1/0
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_DURATION
CV4PVE_AUTOSNAP_STATE #1/0See example hook file script-hook.bat, script-hook.sh
Some words about Snapshot consistency and what qemu-guest-agent can do for you
Bear in mind, that when taking a snapshot of a running VM, it's basically like if you have a server which gets pulled away from the Power. Often this is not cathastrophic as the next fsck will try to fix Filesystem Issues, but in the worst case this could leave you with a severely damaged Filesystem, or even worse, half written Inodes which were in-flight when the power failed lead to silent data corruption. To overcome these things, we have the qemu-guest-agent to improve the consistency of the Filesystem while taking a snapshot. It won't leave you a clean filesystem, but it sync()'s outstanding writes and halts all i/o until the snapshot is complete. Still, there might me issues on the Application layer. Databases processes might have unwritten data in memory, which is the most common case. Here you have the opportunity to do additional tuning, and use hooks to tell your vital processes things to do prio and post freezes.
First, you want to make sure that your guest has the qemu-guest-agent running and is working properly. Now we use custom hooks to tell your services with volatile data, to flush all unwritten data to disk. On debian based linux systems the hook file can be set in /etc/default/qemu-guest-agent and could simply contain this line:
DAEMON_ARGS="-F/etc/qemu/fsfreeze-hook"Create /etc/qemu/fsfreeze-hook and make ist look like:
#!/bin/sh
# This script is executed when a guest agent receives fsfreeze-freeze and
# fsfreeze-thaw command, if it is specified in --fsfreeze-hook (-F)
# option of qemu-ga or placed in default path (/etc/qemu/fsfreeze-hook).
# When the agent receives fsfreeze-freeze request, this script is issued with
# "freeze" argument before the filesystem is frozen. And for fsfreeze-thaw
# request, it is issued with "thaw" argument after filesystem is thawed.
LOGFILE=/var/log/qga-fsfreeze-hook.log
FSFREEZE_D=$(dirname -- "$0")/fsfreeze-hook.d
# Check whether file $1 is a backup or rpm-generated file and should be ignored
is_ignored_file() {
case "$1" in
*~ | *.bak | *.orig | *.rpmnew | *.rpmorig | *.rpmsave | *.sample | *.dpkg-old | *.dpkg-new | *.dpkg-tmp | *.dpkg-dist |
*.dpkg-bak | *.dpkg-backup | *.dpkg-remove)
return 0 ;;
esac
return 1
}
# Iterate executables in directory "fsfreeze-hook.d" with the specified args
[ ! -d "$FSFREEZE_D" ] && exit 0
for file in "$FSFREEZE_D"/* ; do
is_ignored_file "$file" && continue
[ -x "$file" ] || continue
printf "$(date): execute $file $@\n" >>$LOGFILE
"$file" "$@" >>$LOGFILE 2>&1
STATUS=$?
printf "$(date): $file finished with status=$STATUS\n" >>$LOGFILE
done
exit 0For testing purposes place this into /etc/qemu/fsfreeze-hook.d/10-info:
#!/bin/bash
dt=$(date +%s)
case "$1" in
freeze)
echo "frozen on $dt" | tee >(cat >/tmp/fsfreeze)
;;
thaw)
echo "thawed on $dt" | tee >(cat >>/tmp/fsfreeze)
;;
esac
Now you can place files for different Services in /etc/qemu/fsfreeze-hook.d/ that tell those services what to to prior and post snapshots. A very common example is mysql. Create a file /etc/qemu/fsfreeze-hook.d/20-mysql containing
#!/bin/sh
# Flush MySQL tables to the disk before the filesystem is frozen.
# At the same time, this keeps a read lock in order to avoid write accesses
# from the other clients until the filesystem is thawed.
MYSQL="/usr/bin/mysql"
MYSQL_OPTS="-uroot"
MYSQL_PWD="mypassword"
FIFO=/var/run/mysql-flush.fifo
# Check mysql is installed and the server running
[ -x "$MYSQL" ] && "$MYSQL" $MYSQL_OPTS < /dev/null || exit 0
flush_and_wait() {
printf "FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCK \\G\n"
trap 'printf "$(date): $0 is killed\n">&2' HUP INT QUIT ALRM TERM
read < $FIFO
printf "UNLOCK TABLES \\G\n"
rm -f $FIFO
}
case "$1" in
freeze)
mkfifo $FIFO || exit 1
flush_and_wait | "$MYSQL" $MYSQL_OPTS &
# wait until every block is flushed
while [ "$(echo 'SHOW STATUS LIKE "Key_blocks_not_flushed"' |\
"$MYSQL" $MYSQL_OPTS | tail -1 | cut -f 2)" -gt 0 ]; do
sleep 1
done
# for InnoDB, wait until every log is flushed
INNODB_STATUS=$(mktemp /tmp/mysql-flush.XXXXXX)
[ $? -ne 0 ] && exit 2
trap "rm -f $INNODB_STATUS; exit 1" HUP INT QUIT ALRM TERM
while :; do
printf "SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS \\G" |\
"$MYSQL" $MYSQL_OPTS > $INNODB_STATUS
LOG_CURRENT=$(grep 'Log sequence number' $INNODB_STATUS |\
tr -s ' ' | cut -d' ' -f4)
LOG_FLUSHED=$(grep 'Log flushed up to' $INNODB_STATUS |\
tr -s ' ' | cut -d' ' -f5)
[ "$LOG_CURRENT" = "$LOG_FLUSHED" ] && break
sleep 1
done
rm -f $INNODB_STATUS
;;
thaw)
[ ! -p $FIFO ] && exit 1
echo > $FIFO
;;
*)
exit 1
;;
esac