Unsupervised Audio-Visual Lecture Segmentation
Official repository for our paper, "Unsupervised Audio-Visual Lecture Segmentation", WACV 2023.
Unsupervised Audio-Visual Lecture Segmentation
Darshan Singh S, Anchit Gupta, C. V. Jawahar, Makarand Tapaswi
IIIT Hyderabad
AVLectures
As a part of this work we introduce, AVLectures, a large-scale educational audio-visual lectures dataset to facilitate research in the domain of lecture video understanding. The dataset comprises of 86 courses with over 2,350 lectures for a total duration of 2,200 hours. Each course in our dataset consists of video lectures, corresponding transcripts, OCR outputs for frames, and optionally lecture notes, slides, and other metadata making our dataset a rich multi-modality resource.
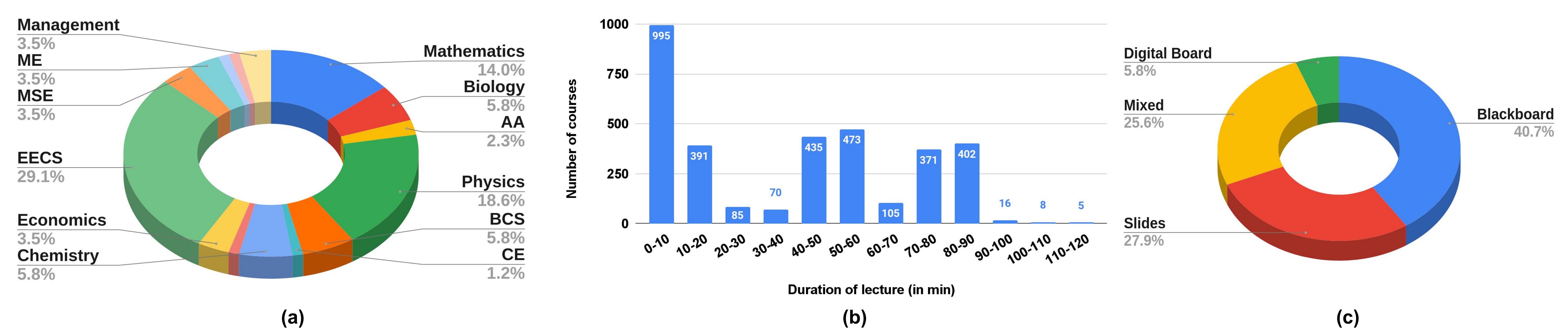
Courses span a broad range of subjects, including Mathematics, Physics, EECS, and Economics (see Fig. a). While the average duration of a lecture in the dataset is about 55 minutes, Fig. b shows a significant variation in the duration. We broadly categorize lectures based on their presentation modes into four types: (i) Blackboard, (ii) Slides, (iii) Digital Board, and (iv) Mixed, a combination of blackboard and slides (Fig. c shows the distribution of
presentation modes in our dataset).
Among the 86 courses in AVLectures, a significant subset of 15 courses also have temporal segmentation boundaries. We refer to this subset as the Courses with Segmentation (CwS) and the remainder 71 courses as the Courses without Segmentation (CwoS).
Download instructions and the dataset format
Each course is provided as a tar file so the user can download any course of interest or download the entire dataset at once.
To untar a course execute the following: tar xvzf <courseID.tar.gz>
Courses with Segmentation (CwS)
After extracting the directory structure of a CwS course would be as follows:
--mitxyz
---metadata/
---OCR/
---subtitles/
---videos/
---segmentation/
------segments_stats.pkl
------segments_ts.txt
------subtitles/
------videos/videos/: Contains originally downloaded lectures of that particular course.subtitles/: Contains corresponding subtitle files (.srt) for each of the video lectures invideos/. The names of the corresponding subtitle file and video file match.OCR/: Contains OCR of frames of the video lectures at a rate of 10 per second using Google Cloud OCR API. The no. of folders in this directory is equal to the no. of video lectures. The folders are named after the video lectures. Each file inside these folders is a.jsonfile and is named as follows:<frame_no>_<int_frame_rate>_<dec_frame_rate>_<timestamp>.json. For example:13500_29_97_450.jsonimplies that this OCR is of the 13500th frame of the video lecture whose frame rate is 29.97 fps (the timestamp can be calculated directly just by using these two i.e, frame no. and frame rate).segmentation/segments_ts.txt: This text file has the segmentation information of that particular course. Each line will be of the following form:
<clip_name>@@<segment_start_timestamp(in seconds)>@@<segment_end_timestamp(in seconds)>@@<lecture_name>where @@ is the delimiter.
segmentation/segements_stats.pkl: This pickle file has the complete segmentation information of that course in an OrderedDict. For each lecture of that course, this file provides the following details: start timestamp, end timestamp, no. of segments, and the total duration of the lecture.segentation/videos/:Contains the processed video lectures. We remove the intro, outro and optionally merge segments.segmentation/subtitles/:Contains the corresponding subtitle files (.srt) for each video lecture insegmentation/videos/.metadata/: Contains the optional data of the course, such as lecture notes, lecture slides, assignments, etc.
Courses without Segmentation (CwoS)
--mitxyz
---metadata/
---OCR/
---subtitles/
---videos/
------subtitles/
------videos/Temporal Segmentation
This code is inspired by https://github.com/antoine77340/howto100m .
Requirements
- Python 3
- PyTorch (>= 1.0)
- gensim
There are three stages to perform lecture segmentation:
- Extracting features from pretrained models. Please use this wonderful repo to extract the lecture features - https://github.com/antoine77340/video_feature_extractor/tree/master
The extracted features will be uploaded here (dataset_v1_leclist.pkl and dataset_v1_helper.pkl).
- Once the features are extracted, we can train our joint embedding model on CwoS. Please go to
code/lecture_aware_embds. You can execute the following command to train the model:
python train.py --num_thread_reader=8 --epochs=50 --batch_size=32 --n_pair=64 --embd_dim=4096 --checkpoint_dir=data/ckpt/ --avlectures=1 --we_dim=768 --BERT --avlectures_train_path='data/dataset_v1_leclist.pkl' --avlectures_helper_path='data/dataset_v1_helper.pkl' --save_every=10 --feature_dim=6144 --ocr=1 --ocr_dim=2048Optionally, you can also finetune the model on CwS as follows:
python train.py --num_thread_reader=8 --epochs=50 --batch_size=32 --embd_dim=4096 --checkpoint_dir=data/ckpt/ft/ --pretrain_path=data/ckpt/e50.pth --avlectures=1 --we_dim=768 --BERT --avlectures_train_path='data/seg_10s15s_2d3dOCRBERT.pkl' --save_every=10 --feature_dim=6144 --ocr=1 --ocr_dim=2048Next, we can extract the learned lecture-aware features of CwS from the checkpoint of our trained model as follows:
python extract_feats.py --we_dim=768 --BERT --eval_avlectures=1 --num_thread_reader=8 --embd_dim=4096 --pretrain_path=data/ckpt/e50.pth --avlectures_val_path='data/seg_10s15s_2d3dOCRBERT.pkl' --feature_dim=6144 --ocr=1 --ocr_dim=2048 --batch_size_val=1- Once the features are extracted, we can perform clustering using TW-FINCH as follows. (Please go to
code/TW_FINCH). Just executepython main.py. This will create a pickle file that will have the clusters. You can use this Google Drive folder to evaluate the quality of the generated cluster. Specifically, check out theEcls_Ecal.ipynbcolab notebook for evaluation.
Citation
If you find our dataset/code useful, feel free to leave a star, and please cite our paper as follows:
@InProceedings{S._2023_WACV,
author = {S., Darshan Singh and Gupta, Anchit and Jawahar, C. V. and Tapaswi, Makarand},
title = {Unsupervised Audio-Visual Lecture Segmentation},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)},
month = {January},
year = {2023},
pages = {5232-5241}
}Contact
Darshan Singh S (darshan.singh@research.iiit.ac.in)
Anchit Gupta (anchit.gupta@research.iiit.ac.in)




