Django Realtime Playground
This is a set of experiments with various modern realtime libraries and asynchronous servers/frameworks together with Django. Personally I suggest using Centrifugo to add real-time on your Django site as most of solutions here is just a showcase
Includes:
- Django application - simple chat for authenticated users - every user can write messages, every user can remove any message.
- A set of async servers which run on different port and listen to connections from chat application.
At this moment there are some possible implementations of chat's realtime part using one of javascript libraries and one of async backend server:
- Node.js server + Socket.IO library
- Node.js server + Sock.js lib
- Python Tornado + Socket.IO
- Python Tornado + Sock.js
- Python Cyclone + jQuery Eventsource lib
Install and run
1) Clone this repo:
git clone https://github.com/FZambia/django-realtime-playground.git django-realtime-playground/
cd django-realtime-playground2) I suppose that you are familiar with virtualenv. Let's run our Django application:
pip install -r django/requirements.txt
cd django
# for django < 1.7
python manage.py syncdb
# for django >= 1.7 use migrate command
# python manage.py migrateCreate new superuser and run server:
python manage.py createsuperuser
python manage.py runserverGo to http://localhost:8000 and make sure that everything works.
3) As you can see after successful login into Django site - you can choose one of options how chat will work. Choose one.
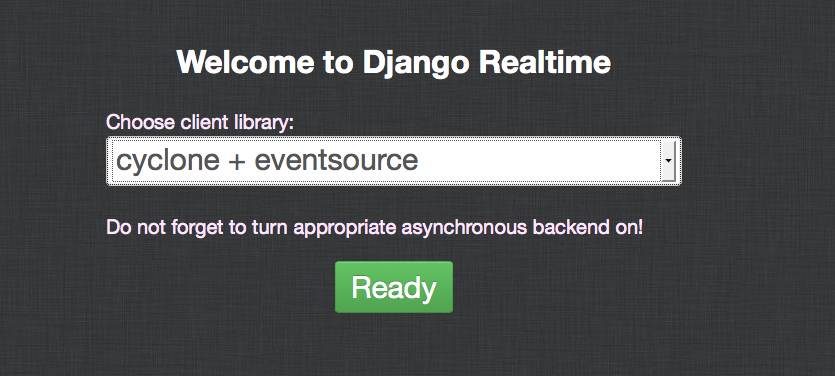
But before you click 'READY' button you must run appropriate async server. Look at folders - they named exactly as options. Now I should tell you how to run each of those servers.
-
Node.js + Socket.IO. To run this you should have Node installed.
cd node-socketio npm install node server.jsNow you have node server on port 8001.
-
Node.js + Sock.js. Same as Node + Socket.IO.
-
Tornado + Socket.IO
cd tornado-sockeio pip install -r requirements.txt python server.py -
Tornado + Sock.js. Same as Tornado + Socket.IO
-
Cyclone + Eventsource.
cd cyclone-eventsource pip install -r requirements.txt bash server.sh
4) After running appropriate async server you can click on button 'READY' and proceed to chat. Chat behaviour is the same for any of options selectedв
By default every async server will run on port 8001, but you can easily change it in code. But do not forget to change ASYNC_BACKEND_URL in Django's settings.py
How it works.
We can not allow bidirectional communication between client and async server because of authorization. So every event you create goes to Django. Then Django makes POST request to async server which broadcasts those event to all connected clients.