Lighthouse Bot (deprecated)
Update: LighthouseBot has been deprecated and we now recommend using the official Lighthouse CI project to automate running Lighthouse for every commit, view the changes, and prevent regressions
Historical README below
This repo contained the frontend and backend for running Lighthouse in CI and integration with Github Pull Requests. An example web service is hosted for demo purposes.
Auditing GitHub Pull Requests
Please note: This drop in service is considered Beta. There are no SLAs or uptime guarantees. If you're interested in running your own CI server in a Docker container, check out Running your own CI server.
Lighthouse can be setup as part of your CI on Travis only. As new pull requests come in, the Lighthouse Bot tests the changes and reports back the new score.

To audit pull requests, do the following:
1. Initial setup
Add the lighthousebot to your repo
First, add lighthousebot as a collaborator on your repo. Lighthouse CI uses an OAuth token scoped to the repo permission in order to update the status of your PRs and post comments on the issue as the little Lighthouse icon.
* Until Lighthousebot accepts your invitation to collaborate, which is currently a lengthy manual process, it does not have permission to update the status of your PRs. However, it will post a comment on your PR.
Get an API Key
Request an API Key. API keys will eventually be enforced and are necessary so we can contact you when there are changes to the CI system.
Once you have a key, update Travis settings by adding an LIGHTHOUSE_API_KEY environment variables with your key:

The lighthousebot script will include your key in requests made to the CI server.
2. Deploy the PR
We recommend deploying your PR to a real staging server instead of running a local server on Travis. A staging environment will produce realistic performance numbers that are more representative of your production setup. The Lighthouse report will be more accurate.
In .travis.yml, add an after_success that deploys the PR's changes to a staging server.
after_success:
- ./deploy.sh # TODO(you): deploy the PR changes to your staging server.Since every hosting environment has different deployment setups, the implementation of deploy.sh is left to the reader.
Tip: Using Google App Engine? Check out
deploy_pr_gae.shwhich shows how to install the GAE SDK and deploy PR changes programmatically.
3. Call lighthousebot
Install the script:
npm i --save-dev https://github.com/GoogleChromeLabs/lighthousebotAdd an NPM script to your package.json:
"scripts": {
"lh": "lighthousebot"
}Next, in .travis.yml call npm run lh as the last step in after_success:
install:
- npm install # make sure to install the deps when Travis runs.
after_success:
- ./deploy.sh # TODO(you): deploy the PR changes to your staging server.
- npm run lh -- https://staging.example.comWhen Lighthouse is done auditing the URL, the bot will post a comment to the pull request containing the updated scores:

You can also opt-out of the comment by using the --no-comment flag.
Failing a PR when it drops your Lighthouse score
Lighthouse CI can prevent PRs from being merged when one of the scores falls
below a specified value. Just include one or more of --pwa, --perf, --seo,
--a11y, or --bp:
after_success:
- ./deploy.sh # TODO(you): deploy the PR changes to your staging server.
- npm run lh -- --perf=96 --pwa=100 https://staging.example.com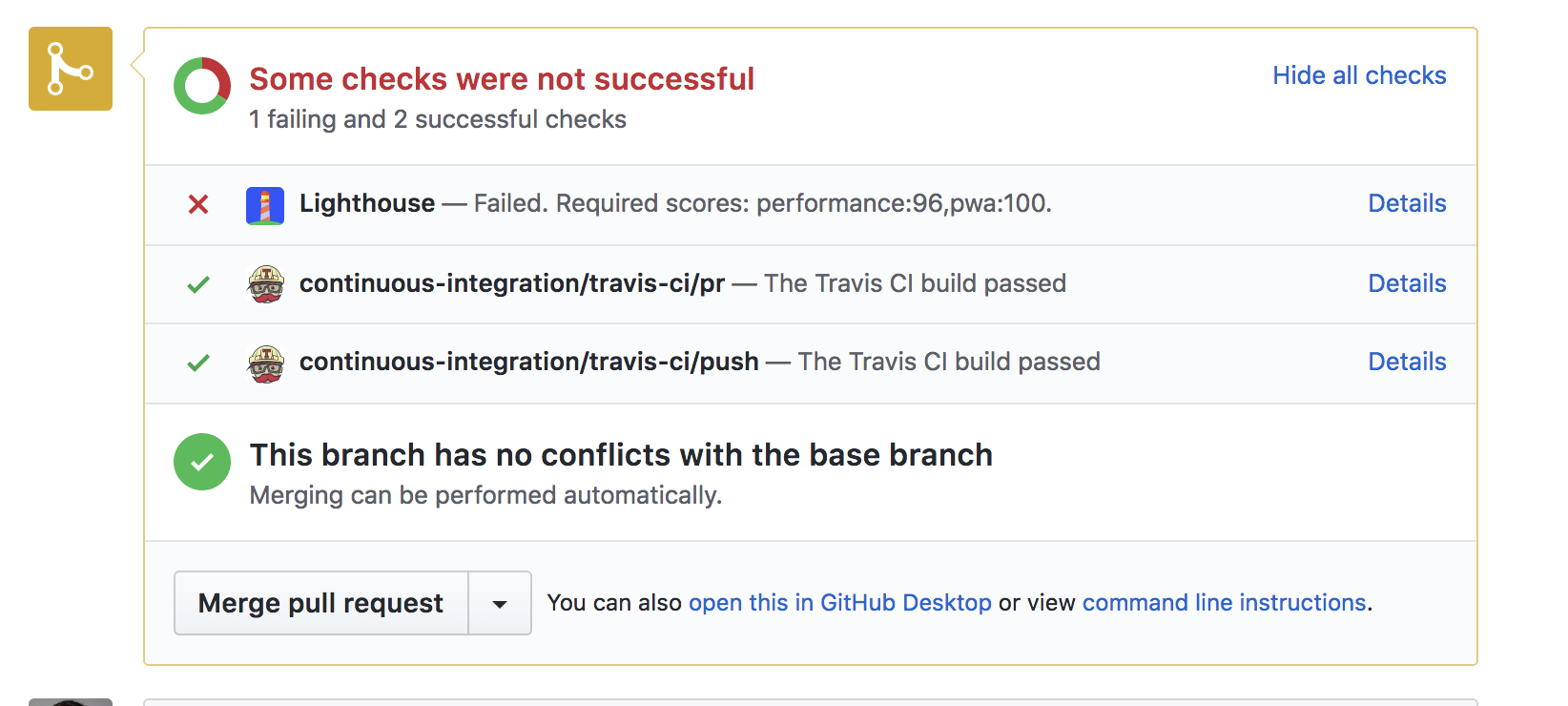
Options
$ lighthouse-ci -h
Usage:
runlighthouse.js [--perf,pwa,seo,a11y,bp=<score>] [--no-comment] [--runner=chrome,wpt] <url>
Options:
Minimum score values can be passed per category as a way to fail the PR if
the thresholds are not met. If you don't provide thresholds, the PR will
be mergeable no matter what the scores.
--pwa Minimum PWA score for the PR to be considered "passing". [Number]
--perf Minimum performance score for the PR to be considered "passing". [Number]
--seo Minimum seo score for the PR to be considered "passing". [Number]
--a11y Minimum accessibility score for the PR to be considered "passing". [Number]
--bp Minimum best practices score for the PR to be considered "passing". [Number]
--no-comment Doesn't post a comment to the PR issue summarizing the Lighthouse results. [Boolean]
--runner Selects Lighthouse running on Chrome or WebPageTest. [--runner=chrome,wpt]
--help Prints help.
Examples:
Runs Lighthouse and posts a summary of the results.
runlighthouse.js https://example.com
Fails the PR if the performance score drops below 93. Posts the summary comment.
runlighthouse.js --perf=93 https://example.com
Fails the PR if perf score drops below 93 or the PWA score drops below 100. Posts the summary comment.
runlighthouse.js --perf=93 --pwa=100 https://example.com
Runs Lighthouse on WebPageTest. Fails the PR if the perf score drops below 93.
runlighthouse.js --perf=93 --runner=wpt --no-comment https://example.comRunning on WebPageTest instead of Chrome
By default, lighthousebot runs your PRs through Lighthouse hosted in the cloud. As an alternative, you can test on real devices using the WebPageTest integration:
lighthousebot --perf=96 --runner=wpt https://staging.example.comAt the end of testing, your PR will be updated with a link to the WebPageTest results containing the Lighthouse report!
Running your own CI server
Want to setup your own Lighthouse instance in a Docker container?
The good news is Docker does most of the work for us! The bulk of getting started is in Development. That will take you through initial setup and show how to run the CI frontend.
For the backend, see builder/README.md for building and running the Docker container.
Other changes, to the "Development" section:
- Create a personal OAuth token in https://github.com/settings/tokens. Drop it in
frontend/.oauth_token. - Add a
LIGHTHOUSE_CI_HOSTenv variable to Travis settings that points to your own URL. The one where you deploy the Docker container.
Development
Initial setup:
- Ask an existing dev for the oauth2 token. If you need to regenerate one, see below.
- Create
frontend/.oauth_tokenand copy in the token value.
- Create
Run the dev server:
cd frontend
npm run startThis will start a web server and use the token in .oauth_token. The token is used to update PR status in Github.
In your test repo:
- Run
npm i --save-dev https://github.com/GoogleChromeLabs/lighthousebot - Follow the steps in Auditing Github Pull Requests for setting up your repo.
Notes:
- If you want to make changes to the builder, you'll need Docker and the GAE Node SDK.
- To make changes to the CI server, you'll probably want to run ngrok so you can test against a local server instead of deploying for each change. In Travis settings,
add a
LIGHTHOUSE_CI_HOSTenv variable that points to your ngrok instance.
Generating a new OAuth2 token
If you need to generate a new OAuth token:
- Sign in to the lighthousebot Github account. (Admins: the credentials are in the usual password tool).
- Visit personal access tokens: https://github.com/settings/tokens.
- Regenerate the token. Important: this invalidates the existing token so other developers will need to be informed.
- Update token in
frontend/.oauth_token.
Deploy
By default, these scripts deploy to Google App Engine Flexible containers (Node). If you're running your own CI server, use your own setup :)
Deploy the frontend:
npm run deploy YYYY-MM-DD frontendDeploy the CI builder backend:
npm run deploy YYYY-MM-DD builderSource & Components
This repo contains several different pieces for the Lighthouse Bot: a backend, frontend, and frontend UI.
UI Frontend
Quick way to try Lighthouse: https://lighthouse-ci.appspot.com/try
Relevant source:
frontend/public/- UI for https://lighthouse-ci.appspot.com/try.
Bot CI server (frontend)
Server that responds to requests from Travis.
REST endpoints:
https://lighthouse-ci.appspot.com/run_on_chromehttps://lighthouse-ci.appspot.com/run_on_wpt
Example
Note: lighthousebot does this for you.
POST https://lighthouse-ci.appspot.com/run_on_chrome
Content-Type: application/json
X-API-KEY: <YOUR_LIGHTHOUSE_API_KEY>
{
testUrl: "https://staging.example.com",
thresholds: {
pwa: 100,
perf: 96,
},
addComment: true,
repo: {
owner: "<REPO_OWNER>",
name: "<REPO_NAME>"
},
pr: {
number: <PR_NUMBER>,
sha: "<PR_SHA>"
}
}Relevant source:
frontend/server.js- server which accepts Github pull requests and updates the status of your PR.
CI backend (builder)
Server that runs Lighthouse against a URL, using Chrome.
REST endpoints:
https://lighthouse-ci.appspot.com/ci
Example
Note: lighthousebot does this for you.
curl -X POST \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "X-API-KEY: <YOUR_LIGHTHOUSE_API_KEY>" \
--data '{"output": "json", "url": "https://staging.example.com"}' \
https://builder-dot-lighthouse-ci.appspot.com/ciFAQ
Why not deployment events?
Github's Deployment API would be ideal, but it has some downsides:
- Github Deployments happen after a pull is merged. We want to support blocking PR merges based on a LH score.
- We want to be able to audit changes as they're add to the PR.
pull_request/pushevents are more appropriate for that.
Why not a Github Webhook?
The main downside of a Github webhook is that there's no way to include custom data in the payload Github sends to the webhook handler. For example, how would Lighthouse know what url to test? With a webhook, the user also has to setup it up and configure it properly.
Future work: Lighthouse Bot could define a file that developer includes in their
repo. The bot's endpoint could pull a .lighthouse_ci file that includes meta
data {minLighthouseScore: 96, testUrl: 'https://staging.example.com'}. However,
this requires work from the developer.