ESP8266 WiFi Library for Arduino
ESP8266 library for Arduino that facilitates the implementation of WiFi communication via user sketches.
ESP8266 is a very powerful and 802.11b/g/n protocol based low cost WiFi module. It is contained with a sufficient size of EEPROM and a 32-bit MPU necessary to TCP/IP protocol stack built-in. You can easily build a WiFi device with a serial communication from physical computing boards such as Arduino and Raspberry Pi.

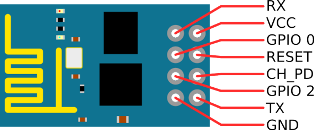
ESP8266 WiFi Library for Arduino provides a function for easily WiFi communication using ESP8266 from your sketch via the serial on such as Arduino UNO, Leonardo and MEGA.
Also this library has a debug output facility can monitor the transmitted and received data.
Expamle the sketch
This exmaple sketch sends HTTP1.1 request to url of www.google.co.jp via TCP port 80 and it receives a response.
The first step is join to a WiFi access point, and establish TCP connection with HTTP server. After that, send HTTP request and receive the response from the server. The series of steps will be used ESP8266 class methods.
Actual wiring diagram of this example is the below. In this example, Software Serial is used to output of the response. you connect serial port of your PC to the D8 and D9 by the USB-Serial module such as FT232.
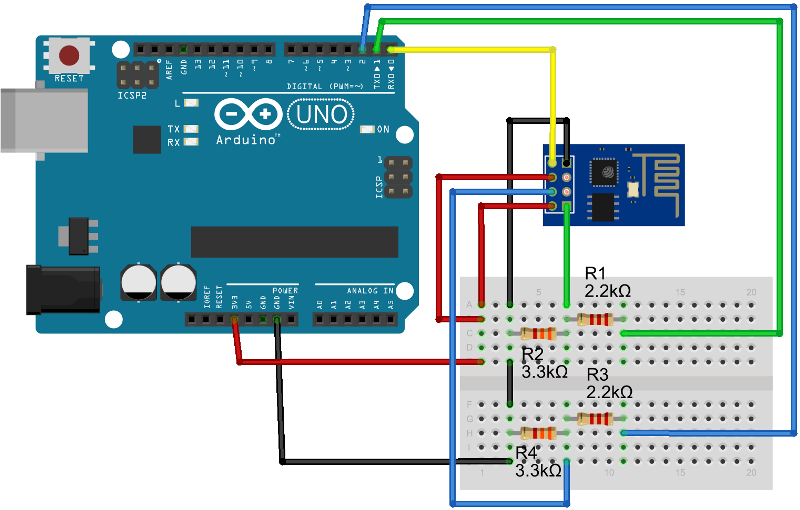 Note: This example uses an 8-pin and 9-pin of Arduino for the received data output to the serial. This signal is different from the serial wiring for ESP8266.
Note: This example uses an 8-pin and 9-pin of Arduino for the received data output to the serial. This signal is different from the serial wiring for ESP8266.
#include "Arduino.h"
#include "ESP8266.h"
#include "SoftwareSerial.h"
SoftwareSerial ConsoleOut(8, 9);
#define SSID "MySSID"
#define PWD "MyPassword"
void setup() {
char *ipAddress, ap[31];
WiFi.reset(WIFI_RESET_HARD);
WiFi.begin(9600);
if (WiFi.join(SSID, PWD) == WIFI_ERR_OK) {
ipAddress = WiFi.ip(WIFI_MODE_STA);
ConsoleOut.print(F("\n\rIP address:"));
ConsoleOut.print(ipAddress);
ConsoleOut.print(':');
if (WiFi.isConnect(ap))
ConsoleOut.println(ap);
else
ConsoleOut.println(F("not found"));
} else
while (1);
}
void loop() {
if (WiFi.connect((char *)"www.google.co.jp", 80) == WIFI_ERR_CONNECT) {
if (WiFi.send((const uint8_t *)"GET / HTTP/1.1\r\n\r\n") == WIFI_ERR_OK) {
int16_t c;
uint16_t len = WiFi.listen(10000UL);
while (len)
if ((c = WiFi.read()) > 0) {
ConsoleOut.write((char)c);
len--;
}
} else
ConsoleOut.println(F("Send fail"));
WiFi.close();
} else
ConsoleOut.println(F("TCP connect fail"));
WiFi.disconnect();
while (1);
}Installation on your arduino IDE
Download a zip file of the ESP8266 library code from Download ZIP and you can import a .zip library in accordance with here methods to your arduino IDE.
How to use ESP8266 WiFi Library for Arduino
ESP8266 Firmware version
Required firmware version. Conformed firmware and the flash writer program could get from the forum of Espressif.
AT version:0.22.0.0
SDK version:1.0.0Summary
ESP8266 class instance can be referred with the WiFi variable from your sketch by including a ESP8266.h header file.
#include "ESP8266.h"ESP8266 class has the following functions for controlling the ESP8266 module.
WiFi.reset // Hardware or software reset for HSP8266 module.
WiFi.begin // Begin WIFI connection and transmission.
WiFi.end // End WIFI connection.
WiFi.config // Configure connection mode and multi connection.
WiFi.join // Connect to the WiFi access point for the station.
WiFi.disconnect // Disconnect from the WiFi access point.
WiFi.isConnect // Inquire the connection establishment status with specified the access point.
WiFi.ip // Get IP address and report resulted IP address string.
WiFi.status // Inquire the current WiFi connection status.
WiFi.setup // Setup access connection topology.
WiFi.connect // Start the IP connection for client side.
WiFi.server // Start the IP connection for server side with passive SYN.
WiFi.close // Close the IP connection.
WiFi.send // Sending data along with making a connection establishment.
WiFi.receive // Start listening, and then stores the received data to the buffer.
WiFi.listen // Starts the listening, and returns data length necessary for receiving.
WiFi.available // Get the number of bytes available for reading from ESP8266.
WiFi.read // Return a character that was received from ESP8266.