# Harden Windows Security | A New Threat to Malware ## Harden Windows Safely, Securely, Only With Official Microsoft Methods
Hardening Categories ![]() How To Use
How To Use ![]() Features
Features ![]() Related
Related ![]() Trust
Trust ![]() Support
Support ![]() Security Recommendations
Security Recommendations ![]() Resources
Resources ![]() License
License ![]() Wiki
Wiki ![]() Basic FAQs
Basic FAQs ![]() Roadmap
Roadmap

[!IMPORTANT]\ Click/Tap on Each of the Items Below to Access Them on This GitHub Repository
App Control for Business Resources
The WDACConfig Module for App Control for Business
Read the Rationale Behind This GitHub Repository

[!NOTE]\ Windows by default is secure and safe, this repository does not imply nor claim otherwise. Just like anything, you have to use it wisely and don't compromise yourself with reckless behavior and bad user configuration; Nothing is foolproof. This repository only uses the tools and features that have already been implemented by Microsoft in Windows OS to fine-tune it towards the highest security and locked-down state, using well-documented, supported, recommended and official methods. Continue reading for comprehensive info.
How To Use
 Start The Harden Windows Security Using GUI (Graphical User Interface)
Start The Harden Windows Security Using GUI (Graphical User Interface)
(irm 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/HotCakeX/Harden-Windows-Security/main/Harden-Windows-Security.ps1')+'P'|iex Install the Harden Windows Security Module from PowerShell Gallery
Install the Harden Windows Security Module from PowerShell Gallery
Check the documentation and How to use
Click/Tap here for commands ```powershell Install-Module -Name 'Harden-Windows-Security-Module' -Force ```
```powershell Protect-WindowsSecurity -GUI ``` ```powershell Confirm-SystemCompliance ``` ```powershell Unprotect-WindowsSecurity ```

Requirements 
![]() PowerShell (latest version), Install it from 🛍️ Microsoft Store or using Winget:
PowerShell (latest version), Install it from 🛍️ Microsoft Store or using Winget: Winget install Microsoft.PowerShell
![]() Any device that meets the Windows 11 hardware and Virtualization Based Security requirements.
Any device that meets the Windows 11 hardware and Virtualization Based Security requirements.
![]() Virtualization technology and Secure Boot enabled in your UEFI settings. Official guide - How to enable Secure Boot on: HP - Lenovo - Dell.
Virtualization technology and Secure Boot enabled in your UEFI settings. Official guide - How to enable Secure Boot on: HP - Lenovo - Dell.
![]() No 3rd party AV installed.
No 3rd party AV installed.
![]() Latest available version of Windows installed.
Latest available version of Windows installed.
[!TIP]\ Restart your device after applying the hardening measures.

Features 
![]() Everything always stays up-to-date with the newest proactive security measures that are industry standards and scalable.
Everything always stays up-to-date with the newest proactive security measures that are industry standards and scalable.
![]() Everything is in clear text, nothing hidden, no 3rd party executable or pre-compiled binary is involved.
Everything is in clear text, nothing hidden, no 3rd party executable or pre-compiled binary is involved.
![]() No Windows functionality is removed/disabled against Microsoft's recommendations.
No Windows functionality is removed/disabled against Microsoft's recommendations.
![]() All of the links and sources are from official Microsoft websites, straight from the source. No bias, No FUD, No misinformation and definitely No old obsolete methods. That's why there are no links to 3rd party news websites, forums, made up blogs/articles, and such.
All of the links and sources are from official Microsoft websites, straight from the source. No bias, No FUD, No misinformation and definitely No old obsolete methods. That's why there are no links to 3rd party news websites, forums, made up blogs/articles, and such.
With the following exceptions
| Link Count| Link | Reason | |:----:|:-----------------------------:|:----------------------------------------------------------:| | 1 | Intel website | i7 13700k product page | | 1 | state.gov | List of State Sponsors of Terrorism | | 1 | orpa.princeton.edu | OFAC Sanctioned Countries | | 2 | Wikipedia | TLS - providing additional information | | 1 | UK Cyber Security Centre | TLS - providing additional information | | 1 | Security.Stackexchange Q&A | TLS - providing additional information | | 1 | browserleaks.com/tls | TLS - Browser test | | 1 | clienttest.ssllabs.com | TLS - Browser test | | 1 | scanigma.com/knowledge-base | TLS - providing additional information | | 1 | cloudflare.com/ssl/reference/ | TLS - providing additional information | | 1 | github.com/ssllabs/research/ | TLS - providing additional information | | 1 | Wayback Machine | Providing additional information about Edge Browser |![]() The module primarily uses Group policies, the Microsoft recommended way of configuring Windows. It also uses PowerShell cmdlets where Group Policies aren't available, and finally uses a few registry keys to configure security measures that can neither be configured using Group Policies nor PowerShell cmdlets. This is why the module doesn't break anything or cause unwanted behavior.
The module primarily uses Group policies, the Microsoft recommended way of configuring Windows. It also uses PowerShell cmdlets where Group Policies aren't available, and finally uses a few registry keys to configure security measures that can neither be configured using Group Policies nor PowerShell cmdlets. This is why the module doesn't break anything or cause unwanted behavior.
![]() This Readme page lists all of the security measures applied by the module.
This Readme page lists all of the security measures applied by the module.
![]() When a hardening measure is no longer necessary because it's applied by default by Microsoft on new builds of Windows, it will also be removed from the module in order to prevent any problems and because it won't be necessary anymore.
When a hardening measure is no longer necessary because it's applied by default by Microsoft on new builds of Windows, it will also be removed from the module in order to prevent any problems and because it won't be necessary anymore.
![]() The module can be run infinite number of times, it's made in a way that it won't make any duplicate changes.
The module can be run infinite number of times, it's made in a way that it won't make any duplicate changes.
![]() Applying these hardening measures makes your PC compliant with Microsoft Security Baselines and Secured-core PC specifications (provided that you use modern hardware that supports the latest Windows security features) - See what makes a Secured-core PC - Check Device Guard category for more info
Applying these hardening measures makes your PC compliant with Microsoft Security Baselines and Secured-core PC specifications (provided that you use modern hardware that supports the latest Windows security features) - See what makes a Secured-core PC - Check Device Guard category for more info
Secured-core – recommended for the most sensitive systems and industries like financial, healthcare, and government agencies. Builds on the previous layers and leverages advanced processor capabilities to provide protection from firmware attacks.
![]() Since I originally created this repository for myself and people I care about, I always maintain it to the highest possible standard.
Since I originally created this repository for myself and people I care about, I always maintain it to the highest possible standard.
![]() If you have multiple accounts on your device, you only need to apply the hardening measures 1 time with Admin privileges, that will make system-wide changes. Then you can optionally run the module, without Admin privileges, for each standard user to apply the Non-Admin category.
If you have multiple accounts on your device, you only need to apply the hardening measures 1 time with Admin privileges, that will make system-wide changes. Then you can optionally run the module, without Admin privileges, for each standard user to apply the Non-Admin category.
[!WARNING]\ For your own security, exercise caution when considering any other 3rd-party tools, programs, or scripts claiming to harden or modify Windows OS in any way. Verify their legitimacy thoroughly before use and after each release. Avoid blind trust in 3rd party Internet sources. Additionally, if they don't adhere to the rules mentioned above, they can cause system damage, unknown issues, and bugs.
- Read the Trust section to see how you can 100% Trust this repository.
- How are Group Policies for this module created and maintained?

Hardening Categories
-
Commands that require Administrator Privileges (click/tap on each of these to see in-depth info)
- Microsoft Security Baselines
- Microsoft 365 Apps Security Baselines
- Microsoft Defender
- Attack surface reduction rules
- Bitlocker Settings
- Device Guard
- TLS Security
- Lock Screen
- UAC (User Account Control)
- Windows Firewall
- Optional Windows Features
- Windows Networking
- Miscellaneous Configurations
- Windows Update configurations
- Edge Browser configurations
- Certificate Checking Commands
- Country IP Blocking
- Downloads Defense Measures

-
Commands that don't require Administrator Privileges

Microsoft Security Baselines
![]() A security baseline is a group of Microsoft-recommended configuration settings that explains their security implications. These settings are based on feedback from Microsoft security engineering teams, product groups, partners, and customers.
A security baseline is a group of Microsoft-recommended configuration settings that explains their security implications. These settings are based on feedback from Microsoft security engineering teams, product groups, partners, and customers.
Continue reading in the official documentation
Optional Overrides for Microsoft Security Baselines
![]() Highly recommended to apply these overrides, the module will ask you whether you want to apply them or not. Use Optional Overrides when applying the hardening measures on Azure VMs.
Highly recommended to apply these overrides, the module will ask you whether you want to apply them or not. Use Optional Overrides when applying the hardening measures on Azure VMs.

Microsoft 365 Apps Security Baselines

![]() The security baseline for Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise is published twice a year, usually in June and December.
The security baseline for Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise is published twice a year, usually in June and December.
Microsoft Security Baselines Version Matrix

Microsoft Defender
-
 Extends the Cloud Security Scan time to the maximum amount of 60 seconds, by default it is 10 seconds. You need to be aware that this means actions like downloading and opening an unknown file will make Microsoft Defender send samples of it to the Cloud for more advanced analysis and it can take a maximum of 60 seconds from the time you try to open that unknown file to the time when it will be opened (if deemed safe).
Extends the Cloud Security Scan time to the maximum amount of 60 seconds, by default it is 10 seconds. You need to be aware that this means actions like downloading and opening an unknown file will make Microsoft Defender send samples of it to the Cloud for more advanced analysis and it can take a maximum of 60 seconds from the time you try to open that unknown file to the time when it will be opened (if deemed safe).  CSP
CSP- Here is an example of the notification you will see in Windows 11 if that happens.
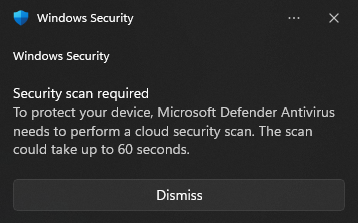
 Configures the Cloud Block/Protection Level to the maximum level of Zero Tolerance and Block At First Sight. No unknown file can run on your system without first being recognized by the Microsoft's Security Graph and other globally omniscient systems.
Configures the Cloud Block/Protection Level to the maximum level of Zero Tolerance and Block At First Sight. No unknown file can run on your system without first being recognized by the Microsoft's Security Graph and other globally omniscient systems.  CSP
CSP
 Configures the Microsoft Defender to send all samples automatically. Increasing protection by participating in the SpyNet / MAPS network.
Configures the Microsoft Defender to send all samples automatically. Increasing protection by participating in the SpyNet / MAPS network.  CSP
CSP
 Sets the SpyNet membership to Advanced, improving Cloud Protection.
Sets the SpyNet membership to Advanced, improving Cloud Protection.  CSP
CSP
 Enables file hash computation; designed to allow admins to force the anti-malware solution to "compute file hashes for every executable file that is scanned if it wasn't previously computed" to "improve blocking for custom indicators in Microsoft Defender Advanced Threat Protection (Microsoft Defender ATP).
Enables file hash computation; designed to allow admins to force the anti-malware solution to "compute file hashes for every executable file that is scanned if it wasn't previously computed" to "improve blocking for custom indicators in Microsoft Defender Advanced Threat Protection (Microsoft Defender ATP).  CSP
CSP
 Clears Quarantined items after 1 day instead of the default behavior of keeping them indefinitely.
Clears Quarantined items after 1 day instead of the default behavior of keeping them indefinitely.  CSP
CSP
 Allows Microsoft Defender to download security updates even on a metered connection.
Allows Microsoft Defender to download security updates even on a metered connection.  CSP
CSP
 Enables Microsoft Defender to scan mapped network drives during full scan.
Enables Microsoft Defender to scan mapped network drives during full scan.  CSP
CSP
 Enables Microsoft Defender to scan emails. The engine will parse the mailbox and mail files.
Enables Microsoft Defender to scan emails. The engine will parse the mailbox and mail files.  CSP
CSP
 Enables Microsoft Defender to scan Removable Drives.
Enables Microsoft Defender to scan Removable Drives.  CSP
CSP
 Enables Microsoft Defender to scan Reparse Points.
Enables Microsoft Defender to scan Reparse Points.  CSP
CSP
 Forces Microsoft Defender to scan network files.
Forces Microsoft Defender to scan network files.  CSP
CSP
-
 Sets the Signature Update Interval to every 3 hours instead of automatically.
Sets the Signature Update Interval to every 3 hours instead of automatically.  CSP
CSP-
Configure and validate Microsoft Defender Antivirus network connections
-
Security intelligence updates for Microsoft Defender Antivirus and other Microsoft antimalware
-
Paste the following PowerShell code to retrieve the latest available online versions of the Platform, Signatures, and Engine for Microsoft Defender
-
$X = irm "https://www.microsoft.com/security/encyclopedia/adlpackages.aspx?action=info" @{Engine = $X.versions.engine; Signatures = $X.versions.signatures.'#text'; Platform = $X.versions.platform} | ft -AutoSize
 Forces Microsoft Defender to check for new virus and spyware definitions before it runs a scan.
Forces Microsoft Defender to check for new virus and spyware definitions before it runs a scan.  CSP
CSP
 Makes Microsoft Defender run catch-up scans for scheduled quick scans. A computer can miss a scheduled scan, usually because the computer is off at the scheduled time, but now after the computer misses two scheduled quick scans, Microsoft Defender runs a catch-up scan the next time someone logs onto the computer.
Makes Microsoft Defender run catch-up scans for scheduled quick scans. A computer can miss a scheduled scan, usually because the computer is off at the scheduled time, but now after the computer misses two scheduled quick scans, Microsoft Defender runs a catch-up scan the next time someone logs onto the computer.  CSP
CSP
 Enables scanning of restore points
Enables scanning of restore points  CSP
CSP
 Makes sure Async Inspection for Network protection of Microsoft Defender is turned on - Network protection now has a performance optimization that allows Block mode to start asynchronously inspecting long connections after they're validated and allowed by SmartScreen, which might provide a potential reduction in the cost that inspection has on bandwidth and can also help with app compatibility problems.
Makes sure Async Inspection for Network protection of Microsoft Defender is turned on - Network protection now has a performance optimization that allows Block mode to start asynchronously inspecting long connections after they're validated and allowed by SmartScreen, which might provide a potential reduction in the cost that inspection has on bandwidth and can also help with app compatibility problems.  CSP
CSP
-

 Enables Smart App Control (if it's in Evaluation mode): adds significant protection from new and emerging threats by blocking apps that are malicious or untrusted. Smart App Control also helps to block potentially unwanted apps, which are apps that may cause your device to run slowly, display unexpected ads, offer extra software you didn't want, or do other things you don't expect.
Enables Smart App Control (if it's in Evaluation mode): adds significant protection from new and emerging threats by blocking apps that are malicious or untrusted. Smart App Control also helps to block potentially unwanted apps, which are apps that may cause your device to run slowly, display unexpected ads, offer extra software you didn't want, or do other things you don't expect.-
Smart App Control is User-Mode (and enforces Kernel-Mode) App Control for Business, more info in the Wiki. You can see its status in System Information and enable it manually from Microsoft Defender app's GUI. It is very important for Windows and Windows Defender intelligence updates to be always up-to-date in order for Smart App Control to work properly as it relies on live intelligence and definition data from the cloud and other sources to make a Smart decision about programs and files it encounters.
-
Smart App Control uses ISG (Intelligent Security Graph). The ISG isn't a "list" of apps. Rather, it uses the same vast security intelligence and machine learning analytics that power Microsoft Defender SmartScreen and Microsoft Defender Antivirus to help classify applications as having "known good", "known bad", or "unknown" reputation. This cloud-based AI is based on trillions of signals collected from Windows endpoints and other data sources and processed every 24 hours. As a result, the decision from the cloud can change.
-
Smart App Control can block a program entirely from running or only some parts of it in which case your app or program will continue working just fine most of the time. It's improved a lot since it was introduced, and it continues doing so. Consider turning it on after clean installing a new OS and fully updating it.
-
Smart App Control enforces the Microsoft Recommended Driver Block rules and the Microsoft Recommended Block Rules
-
Once you turn Smart App Control off, it can't be turned on without resetting or reinstalling Windows.
-

 Enables "Send optional diagnostic data" because it is required for Smart App Control to operate when it's in evaluation mode or turned on, and for communication with Intelligent Security Graph (ISG). This setting will be automatically applied if Smart App Control is already turned on or you choose to turn it on.
Enables "Send optional diagnostic data" because it is required for Smart App Control to operate when it's in evaluation mode or turned on, and for communication with Intelligent Security Graph (ISG). This setting will be automatically applied if Smart App Control is already turned on or you choose to turn it on.  CSP
CSP
-
 Enables Controlled Folder Access. It helps protect your valuable data from malicious apps and threats, such as ransomware. Controlled folder access protects your data by checking apps against a list of known, trusted apps. Due to the recent wave of global ransomware attacks, it is important to use this feature to protect your valuables files, specially OneDrive folders.
Enables Controlled Folder Access. It helps protect your valuable data from malicious apps and threats, such as ransomware. Controlled folder access protects your data by checking apps against a list of known, trusted apps. Due to the recent wave of global ransomware attacks, it is important to use this feature to protect your valuables files, specially OneDrive folders.  CSP
CSP-
If it blocks a program from accessing one of your folders it protects, and you absolutely trust that program, then you can add it to exclusion list using Microsoft Defender GUI or PowerShell. you can also query the list of allowed apps using PowerShell (commands below). with these commands, you can backup your personalized list of allowed apps, that are relevant to your system, and restore them in case you clean install your Windows.
-
 The root of the OneDrive folders of all the user accounts will be added to the protected folders list of Controlled Folder Access, to provide Ransomware protection for the entire OneDrive folder.
The root of the OneDrive folders of all the user accounts will be added to the protected folders list of Controlled Folder Access, to provide Ransomware protection for the entire OneDrive folder.  CSP
CSP -
# Add multiple programs to the exclusion list of Controlled Folder Access Add-MpPreference -ControlledFolderAccessAllowedApplications 'C:\Program Files\App\app.exe','C:\Program Files\App2\app2.exe' -
# Get the list of all allowed apps (Get-MpPreference).ControlledFolderAccessAllowedApplications
-
-
 Enables Mandatory ASLR, It might cause compatibility issues only for some poorly-made 3rd party programs, specially portable ones.
Enables Mandatory ASLR, It might cause compatibility issues only for some poorly-made 3rd party programs, specially portable ones.  CSP
CSP-
Automatically detects and excludes the Git executables of GitHub Desktop and Git (Standalone version) from mandatory ASLR if they are installed on the system. More info here
-
You can add Mandatory ASLR override for a trusted program using the PowerShell command below or in the Program Settings section of Exploit Protection in Microsoft Defender app.
Set-ProcessMitigation -Name "C:\TrustedApp.exe" -Disable ForceRelocateImages
-
-
 Applies Exploit Protections/Process Mitigations from this list to the following programs:
Applies Exploit Protections/Process Mitigations from this list to the following programs:  CSP
CSP-
All channels of Microsoft Edge browser
-
Quick Assist app
-
Some System processes
-
Microsoft 365 apps
-
More apps and processes will be added to the list over time once they are properly validated to be fully compatible.
-
Exploit Protection configurations are also accessible in XML format within this repository. When implementing exploit protections using an XML file, the existing exploit mitigations will seamlessly integrate rather than being overwritten. Should there be pre-existing exploit protections applied to an executable on the system, and the XML file specifies different mitigations for the same executable, these protections will be merged and applied collectively.
-
 Turns on Data Execution Prevention (DEP) for all applications, including 32-bit programs. By default, the output of
Turns on Data Execution Prevention (DEP) for all applications, including 32-bit programs. By default, the output of BCDEdit /enum "{current}"(in PowerShell) for the NX bit isOptInbut this module sets it toAlwaysOn
 Check for the latest virus and spyware security intelligence on startup.
Check for the latest virus and spyware security intelligence on startup.  CSP
CSP
 Specifies the maximum depth to scan archive files to the maximum possible value of
Specifies the maximum depth to scan archive files to the maximum possible value of 4,294,967,295 CSP
CSP
 Defines the maximum size of downloaded files and attachments to be scanned and set it to the maximum possible value of
Defines the maximum size of downloaded files and attachments to be scanned and set it to the maximum possible value of 10,000,000 KBor10 GB. the default is20480 KBor~20MB CSP
CSP
 Enables the Enhanced Phishing Protection service.
Enables the Enhanced Phishing Protection service.  CSP
CSP
 Enables notifying user of malicious and phishing scenarios in Microsoft Defender Enhanced Phishing Protection.
Enables notifying user of malicious and phishing scenarios in Microsoft Defender Enhanced Phishing Protection.  CSP
CSP
 Enables the feature in Enhanced Phishing Protection in Microsoft Defender SmartScreen that warns users if they reuse their work or school password.
Enables the feature in Enhanced Phishing Protection in Microsoft Defender SmartScreen that warns users if they reuse their work or school password.  CSP
CSP
 Enables warning users if they type their work or school passwords in unsafe apps.
Enables warning users if they type their work or school passwords in unsafe apps.  CSP
CSP
 Enables automatic data collection (formerly known as Capture Threat Window) of Enhanced Phishing Protection in Microsoft Defender SmartScreen for security analysis from a suspicious website or app.
Enables automatic data collection (formerly known as Capture Threat Window) of Enhanced Phishing Protection in Microsoft Defender SmartScreen for security analysis from a suspicious website or app.  CSP
CSP

 Creates scheduled task for fast weekly Microsoft recommended driver block list update.. You won't see this prompt if the task already exists and is enabled or running.
Creates scheduled task for fast weekly Microsoft recommended driver block list update.. You won't see this prompt if the task already exists and is enabled or running.

 Set Microsoft Defender engine and platform update channel to beta.
Set Microsoft Defender engine and platform update channel to beta.  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP
 Defines the number of days before spyware security intelligence is considered out of date to 2. The default is 7.
Defines the number of days before spyware security intelligence is considered out of date to 2. The default is 7.  CSP
CSP
 Defines the number of days before virus security intelligence is considered out of date to 2. The default is 7.
Defines the number of days before virus security intelligence is considered out of date to 2. The default is 7.  CSP
CSP
 Sets the default action for Severe and High threat levels to Remove, for Medium and Low threat levels to Quarantine.
Sets the default action for Severe and High threat levels to Remove, for Medium and Low threat levels to Quarantine.  CSP
CSP
 Configures real-time protection and Security Intelligence Updates to be enabled during OOBE.
Configures real-time protection and Security Intelligence Updates to be enabled during OOBE.  CSP
CSP
 Enables a network protection setting that blocks malicious network traffic instead of displaying a warning.
Enables a network protection setting that blocks malicious network traffic instead of displaying a warning.  CSP
CSP
 Configures the Brute-Force Protection to use cloud aggregation to block IP addresses that are over 99% likely malicious
Configures the Brute-Force Protection to use cloud aggregation to block IP addresses that are over 99% likely malicious  CSP
CSP
 Configures the Brute-Force Protection to detect and block attempts to forcibly sign in and initiate sessions
Configures the Brute-Force Protection to detect and block attempts to forcibly sign in and initiate sessions  CSP
CSP
 Sets the internal feature logic to determine blocking time for the Brute-Force Protections
Sets the internal feature logic to determine blocking time for the Brute-Force Protections  CSP
CSP
 Configures the Remote Encryption Protection to use cloud intel and context, and block when confidence level is above 90%.
Configures the Remote Encryption Protection to use cloud intel and context, and block when confidence level is above 90%.  CSP
CSP
 Configures the Remote Encryption Protection to detect and block attempts to replace local files with encrypted versions from another device
Configures the Remote Encryption Protection to detect and block attempts to replace local files with encrypted versions from another device  CSP
CSP
 Sets the internal feature logic to determine blocking time for the Remote Encryption Protection
Sets the internal feature logic to determine blocking time for the Remote Encryption Protection  CSP
CSP
 Extends the brute-force protection coverage in the Microsoft Defender Antivirus to block local network addresses.
Extends the brute-force protection coverage in the Microsoft Defender Antivirus to block local network addresses.  CSP
CSP
 Enables ECS Configurations in the Microsoft Defender. They improve product health and security by automatically fixing any possible issues/bugs that may arise, in a timely manner.
Enables ECS Configurations in the Microsoft Defender. They improve product health and security by automatically fixing any possible issues/bugs that may arise, in a timely manner.
 Enables Network Protection to be configured into block or audit mode on Windows Server.
Enables Network Protection to be configured into block or audit mode on Windows Server.  CSP
CSP
[!TIP]\ Performance analyzer for Microsoft Defender Antivirus

Attack surface reduction rules
![]() Attack surface reduction rules target certain software behaviors, such as:
Attack surface reduction rules target certain software behaviors, such as: ![]() CSP
CSP
- Launching executable files and scripts that attempt to download or run files
- Running obfuscated or otherwise suspicious scripts
- Performing behaviors that apps don't usually initiate during normal day-to-day work
Such software behaviors are sometimes seen in legitimate applications. However, these behaviors are often considered risky because they are commonly abused by attackers through malware. Attack surface reduction rules can constrain software-based risky behaviors and help keep your organization safe.
Reducing your attack surface means protecting your devices and network, which leaves attackers with fewer ways to perform attacks. Configuring attack surface reduction rules in Windows can help!
[!TIP]\ all 19 available Attack Surface Reduction rules shown in the official chart will be enabled. The Harden Windows Security application also allows you to individually configure each Attack Surface Reduction rule.

Bitlocker Settings
-

 The module sets up and configures Bitlocker using official documentation, with the most secure configuration and military grade encryption algorithm, XTS-AES-256, to protect the confidentiality and integrity of all information at rest.
The module sets up and configures Bitlocker using official documentation, with the most secure configuration and military grade encryption algorithm, XTS-AES-256, to protect the confidentiality and integrity of all information at rest.  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP-
It offers 2 security levels for OS drive encryption: Enhanced and Normal.
-
In Normal security level, the OS drive is encrypted with TPM and Startup PIN. This provides very high security for your data, specially with a PIN that's long, complicated (uppercase and lowercase letters, symbols, numbers, spaces) and isn't the same as your Windows Hello PIN.
-
In Enhanced security level, the OS drive is encrypted with TPM and Startup PIN and Startup key. This provides the highest level of protection by offering Multifactor Authentication. You will need to enter your PIN and also plug in a flash drive, containing a special BitLocker key, into your device in order to unlock it. Continue reading more about it here.
-
Once the OS drive is encrypted, for every other non-OS drive, there will be prompts for confirmation before encrypting it. The encryption will use the same algorithm as the OS drive and uses Auto-unlock key protector. Removable flash drives are skipped.
-
The recovery information of all of the drives are saved in a single well-formatted text file in the root of the OS drive
C:\BitLocker-Recovery-Info-All-Drives.txt. It's very important to keep it in a safe and reachable place as soon as possible, e.g., in OneDrive's Personal Vault which requires additional authentication to access. See here and here for more info. You can use it to unlock your drives if you ever forget your PIN, lose your Startup key (USB Flash Drive) or TPM no longer has the correct authorization (E.g., after a firmware change). -
TPM has special anti-hammering logic which prevents malicious user from guessing the authorization data indefinitely. Microsoft defines that maximum number of failed attempts in Windows is 32 and every single failed attempt is forgotten after 2 hours. This means that every continuous two hours of powered on (and successfully booted) operation without an event which increases the counter will cause the counter to decrease by 1. You can view all the details using this PowerShell command:
Get-TPM. -
Check out Lock Screen category for more info about the recovery password and the 2nd anti-hammering mechanism.
-
BitLocker will bring you a real security against the theft of your device if you strictly abide by the following basic rules:
-
As soon as you have finished working, either Hibernate or shut Windows down and allow for every shadow of information to disappear from RAM within 2 minutes. This practice is recommended in High-Risk Environments.
-
Do not mix 3rd party encryption software and tools with Bitlocker. Bitlocker creates a secure end-to-end encrypted ecosystem for your device and its peripherals, this secure ecosystem is backed by things such as software, Virtualization Technology, TPM 2.0 and UEFI firmware, Bitlocker protects your data and entire device against real-life attacks and threats. You can encrypt your external SSDs and flash drives with Bitlocker too.
-
-
[!IMPORTANT]\ AMD Zen 2 and 3 CPUs have a vulnerability in them, if you use one of them, make sure your Bitlocker Startup PIN is at least 16 characters long (max is 20).
-
 Enables or disables DMA protection from Bitlocker Countermeasures based on the status of Kernel DMA protection. Kernel DMA Protection is not compatible with other BitLocker DMA attacks countermeasures. It is recommended to disable the BitLocker DMA attacks countermeasures if the system supports Kernel DMA Protection (this module does that exactly). Kernel DMA Protection provides higher security bar for the system over the BitLocker DMA attack countermeasures, while maintaining usability of external peripherals. you can check the status of Kernel DMA protection using this official guide.
Enables or disables DMA protection from Bitlocker Countermeasures based on the status of Kernel DMA protection. Kernel DMA Protection is not compatible with other BitLocker DMA attacks countermeasures. It is recommended to disable the BitLocker DMA attacks countermeasures if the system supports Kernel DMA Protection (this module does that exactly). Kernel DMA Protection provides higher security bar for the system over the BitLocker DMA attack countermeasures, while maintaining usability of external peripherals. you can check the status of Kernel DMA protection using this official guide.  CSP
CSP- Kernel DMA Protection (Memory Access Protection) for OEMs page shows the requirements for Kernel DMA Protection. for Intel CPUs, support for requirements such as VT-X and VT-D can be found in each CPU's respective product page. e.g. Intel i7 13700K
 Disallows standard (non-Administrator) users from changing the Bitlocker Startup PIN or password
Disallows standard (non-Administrator) users from changing the Bitlocker Startup PIN or password  CSP
CSP
-
 (Only on Physical machines) Enables Hibernate and adds Hibernate to Start menu's power options.
(Only on Physical machines) Enables Hibernate and adds Hibernate to Start menu's power options.  CSP
CSP- Devices that support Modern Standby have the most security because (S1-S3) power states which belong to the legacy sleep modes are not available. In Modern Standby, security components remain vigilant and the OS stays protected. Applying Microsoft Security Baselines also automatically disables the legacy (S1-S3) sleep states.
 Enables network connectivity in standby on modern standby-capable systems. This ensures security updates for Microsoft Defender and Windows will be installed automatically.
Enables network connectivity in standby on modern standby-capable systems. This ensures security updates for Microsoft Defender and Windows will be installed automatically.  CSP
CSP
Refer to this official documentation about the countermeasures of Bitlocker

Device Guard

-
 Secure boot (without requiring DMA protection) for Virtualization-Based Security
Secure boot (without requiring DMA protection) for Virtualization-Based Security  CSP
CSP-
This is in accordance with Microsoft's recommendation. This option provides Secure Boot with as much protection as is supported by a given computer’s hardware. A computer with input/output memory management units (IOMMUs) will have Secure Boot with DMA protection. A computer without IOMMUs will simply have Secure Boot enabled.
-
Secure boot has 2 parts, part 1 is enforced using the Group Policy by this module, but for part 2, you need to enable Secure Boot in your UEFI firmware settings if it's not enabled by default (which is the case on older hardware).
-
 Virtualization-based protection of Code Integrity + UEFI Lock
Virtualization-based protection of Code Integrity + UEFI Lock  CSP
CSP
 Local Security Authority (LSA) process Protection + UEFI Lock
Local Security Authority (LSA) process Protection + UEFI Lock  CSP
CSP
 Enables Machine Identity Isolation Configuration in Enforcement mode.
Enables Machine Identity Isolation Configuration in Enforcement mode.
-

 Enables Virtualization-based Security and Memory Integrity in Mandatory mode.
Enables Virtualization-based Security and Memory Integrity in Mandatory mode.- Special care should be used before enabling this mode, since, in case of any failure of the virtualization modules, the system will refuse to boot.
[!TIP]\ Most of the Device Guard and Virtualization-Based Security features are Automatically enabled by default on capable and modern hardware. The rest of them will be enabled and configured to the most secure state after you apply the Microsoft Security Baselines and the Harden Windows Security policies.
[!IMPORTANT]\ About UEFI Lock
UEFI locked security measures are rooted in Proof of Physical Presence and they can't be disabled by modifying Group Policy, registry keys or other Administrative tasks. The only way to disable UEFI locked security measures is to have physical access to the computer, reboot and access the UEFI settings, supply the credentials to access the UEFI, turn off Secure Boot, reboot the system and then you will be able to disable those security measures with Administrator privileges.
[!NOTE]\ Device Protection in Windows Security Gives You One of These 4 Hardware Scores
- Standard hardware security not supported
- This means that your device does not meet at least one of the requirements of Standard Hardware Security.
- Your device meets the requirements for Standard Hardware Security.
- Your device meets the requirements for Enhanced Hardware Security
- Your device has all Secured-core PC features enabled

TLS Security
Changes made by this category only affect things that use Schannel SSP: that includes IIS web server, built-in inbox Windows apps and some other programs supplied by Microsoft, including Windows network communications, but not 3rd party software that use portable stacks like Java, nodejs, python or php.
If you want to read more: Demystifying Schannel
[!NOTE]\ This category checks whether Battle.net client is installed on the system and if it is then includes
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHAas an additional cipher suite in the policy due to a known issue. The way Battle.net client is detected is by checking the presence ofBattle.net.exeorBattle.net Launcher.exeinC:\Program Files (x86)\Battle.net\folder.
 Disables TLS 1 and TLS 1.1 security protocols that only exist for backward compatibility. All modern software should and do use
Disables TLS 1 and TLS 1.1 security protocols that only exist for backward compatibility. All modern software should and do use TLS 1.2andTLS 1.3. CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP
 Disables MD5 Hashing Algorithm that is only available for backward compatibility
Disables MD5 Hashing Algorithm that is only available for backward compatibility
 Disables the following weak ciphers that are only available for backward compatibility:
Disables the following weak ciphers that are only available for backward compatibility: "DES 56-bit","RC2 40-bit","RC2 56-bit","RC2 128-bit","RC4 40-bit","RC4 56-bit","RC4 64-bit","RC4 128-bit","3DES 168-bit (Triple DES 168)"
 Configures the TLS to only use the following secure cipher suites and in this exact order:
Configures the TLS to only use the following secure cipher suites and in this exact order:  CSP
CSP
TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 Configures TLS ECC Curves to use the following prioritized Curves order:
Configures TLS ECC Curves to use the following prioritized Curves order:  CSP
CSP
nistP521
curve25519
NistP384
NistP256- By default, in Windows, the order is this:
curve25519
NistP256
NistP384
Lock Screen
 Automatically locks device after X seconds of inactivity (just like mobile phones), which is set to 120 seconds (2 minutes) in this module, you can change that to any value you like.
Automatically locks device after X seconds of inactivity (just like mobile phones), which is set to 120 seconds (2 minutes) in this module, you can change that to any value you like.  CSP
CSP
-

 Requires CTRL+ALT+DEL on the lock screen, kernel protected set of key strokes. The reason and logic behind it is:
Requires CTRL+ALT+DEL on the lock screen, kernel protected set of key strokes. The reason and logic behind it is:  CSP
CSP- A malicious user might install malware that looks like the standard sign-in dialog box for the Windows operating system and capture a user's password. The attacker can then sign into the compromised account with whatever level of user rights that user has.
-
 Enables a security anti-hammering feature that sets a threshold of 5 for the number of failed sign-in attempts that causes the device to be locked by using BitLocker. Sign-in attempts include Windows password or Windows Hello authentication methods. This threshold means, if the specified maximum number of failed sign-in attempts is exceeded, the device will invalidate the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) protector and any other protector except the 48-digit recovery password, and then reboot. During Device Lockout mode, the computer or device only boots into the touch-enabled Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) until an authorized user enters the recovery password to restore full access.
Enables a security anti-hammering feature that sets a threshold of 5 for the number of failed sign-in attempts that causes the device to be locked by using BitLocker. Sign-in attempts include Windows password or Windows Hello authentication methods. This threshold means, if the specified maximum number of failed sign-in attempts is exceeded, the device will invalidate the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) protector and any other protector except the 48-digit recovery password, and then reboot. During Device Lockout mode, the computer or device only boots into the touch-enabled Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) until an authorized user enters the recovery password to restore full access.- This module (in the Bitlocker category) automatically saves the 48-digit recovery password of each drive in itself, the location of it will also be visible on the PowerShell console when you run it. It is very important to keep it in a safe and reachable place, e.g. in OneDrive's Personal Vault which requires authentication to access. See Here and Here for more info about OneDrive's Personal Vault
 Configures account lockout policy: Account lockout threshold, Sets the number of allowed failed sign-in attempts to 5. In combination with other policies in this category, this means every 5 failed sign-in attempts will need a full day to pass before 5 more attempts can be made, otherwise Bitlocker will engage, system will be restarted and 48-digit Bitlocker code will be asked. This policy greatly prevents brute force attempts.
Configures account lockout policy: Account lockout threshold, Sets the number of allowed failed sign-in attempts to 5. In combination with other policies in this category, this means every 5 failed sign-in attempts will need a full day to pass before 5 more attempts can be made, otherwise Bitlocker will engage, system will be restarted and 48-digit Bitlocker code will be asked. This policy greatly prevents brute force attempts.  CSP
CSP
 Configures account lockout policy: Sets Account lockout duration to 1440 minutes or 1 day. In combination with other policies in this category, this means every 5 failed sign-in attempts will need a full day to pass before 5 more attempts can be made, otherwise Bitlocker will engage, system will be restarted and 48-digit Bitlocker code will be asked.
Configures account lockout policy: Sets Account lockout duration to 1440 minutes or 1 day. In combination with other policies in this category, this means every 5 failed sign-in attempts will need a full day to pass before 5 more attempts can be made, otherwise Bitlocker will engage, system will be restarted and 48-digit Bitlocker code will be asked.  CSP
CSP
 Configures account lockout policy: Sets Reset account lockout counter to 1440 minutes or 1 day. In combination with other policies in this category, this means every 5 failed sign-in attempts will need a full day to pass before 5 more attempts can be made, otherwise Bitlocker will engage, system will be restarted and 48-digit Bitlocker code will be asked.
Configures account lockout policy: Sets Reset account lockout counter to 1440 minutes or 1 day. In combination with other policies in this category, this means every 5 failed sign-in attempts will need a full day to pass before 5 more attempts can be made, otherwise Bitlocker will engage, system will be restarted and 48-digit Bitlocker code will be asked.  CSP
CSP
 Hides email address of the Microsoft account on lock screen, if your device is in a trusted place like at home then this isn't necessary.
Hides email address of the Microsoft account on lock screen, if your device is in a trusted place like at home then this isn't necessary.
-
 Don't display username at sign-in; If a user signs in as Other user, the full name of the user isn't displayed during sign-in. In the same context, if users type their email address and password at the sign-in screen and press Enter, the displayed text "Other user" remains unchanged, and is no longer replaced by the user's first and last name, as in previous versions of Windows 10. Additionally, if users enter their domain user name and password and click Submit, their full name isn't shown until the Start screen displays.
Don't display username at sign-in; If a user signs in as Other user, the full name of the user isn't displayed during sign-in. In the same context, if users type their email address and password at the sign-in screen and press Enter, the displayed text "Other user" remains unchanged, and is no longer replaced by the user's first and last name, as in previous versions of Windows 10. Additionally, if users enter their domain user name and password and click Submit, their full name isn't shown until the Start screen displays.  CSP
CSP- Useful If you have devices that store sensitive data, with monitors displayed in unsecured locations, or if you have devices with sensitive data that are remotely accessed, revealing logged on user's full names or domain account names
-

 Don't display last signed-in; This security policy setting determines whether the name of the last user to sign in to the device is displayed on the Secure Desktop. If this policy is enabled, the full name of the last user to successfully sign in isn't displayed on the Secure Desktop, nor is the user's sign-in tile displayed. Additionally, if the Switch user feature is used, the full name and sign-in tile aren't displayed. The sign-in screen requests both Username + Windows Hello credentials.
Don't display last signed-in; This security policy setting determines whether the name of the last user to sign in to the device is displayed on the Secure Desktop. If this policy is enabled, the full name of the last user to successfully sign in isn't displayed on the Secure Desktop, nor is the user's sign-in tile displayed. Additionally, if the Switch user feature is used, the full name and sign-in tile aren't displayed. The sign-in screen requests both Username + Windows Hello credentials.  CSP
CSP-
This feature can be useful to enable if you live in High-Risk Environments and you don't want anyone to get any information about your accounts when you aren't logged-in.
-
This policy will prevent you from using "Forgot my PIN" feature in lock screen or logon screen. If you forget your PIN, you won't be able to recover it.
-
If you use Windows Hello Face or Fingerprint, you can easily login using those credential providers without the need to supply username first.
-
 Don't Display Network Selection UI on Lock Screen (like WIFI Icon); This setting allows you to control whether anyone can interact with available networks UI on the logon screen. Once enabled, the device's network connectivity state cannot be changed without signing into Windows. Suitable for High-Risk Environments.
Don't Display Network Selection UI on Lock Screen (like WIFI Icon); This setting allows you to control whether anyone can interact with available networks UI on the logon screen. Once enabled, the device's network connectivity state cannot be changed without signing into Windows. Suitable for High-Risk Environments.  CSP
CSP
-
 Applies the following PIN Complexity rules to Windows Hello
Applies the following PIN Complexity rules to Windows Hello  CSP. Please note that, by default, any character can be set as a PIN. However, the following policies ensure that certain characters are always included as a minimum requirement.
CSP. Please note that, by default, any character can be set as a PIN. However, the following policies ensure that certain characters are always included as a minimum requirement.-
Expires every 180 days (default behavior is to never expire)
 CSP
CSP- Setting an expiration date ensures that, in the event of theft, a threat actor cannot indefinitely attempt to guess the PIN. After 180 days, the PIN expires, rendering it unusable even if guessed correctly. To reset the PIN, authentication via a Microsoft account or EntraID—likely inaccessible to the attacker—will be required. Combined with anti-hammering and BitLocker policies, this expiration guarantees that a threat actor cannot endlessly persist in guessing the PIN.
-
History of the 1 most recent selected PIN is preserved to prevent the user from reusing it
 CSP
CSP

User Account Control
-
 Prompt for elevation of privilege on secure desktop for all binaries in Administrator accounts, which presents the sign-in UI and restricts functionality and access to the system until the sign-in requirements are satisfied. The secure desktop's primary difference from the user desktop is that only trusted processes running as SYSTEM are allowed to run here (that is, nothing is running at the user's privilege level). The path to get to the secure desktop from the user desktop must also be trusted through the entire chain.
Prompt for elevation of privilege on secure desktop for all binaries in Administrator accounts, which presents the sign-in UI and restricts functionality and access to the system until the sign-in requirements are satisfied. The secure desktop's primary difference from the user desktop is that only trusted processes running as SYSTEM are allowed to run here (that is, nothing is running at the user's privilege level). The path to get to the secure desktop from the user desktop must also be trusted through the entire chain.  CSP
CSP-
Default Behavior: Prompt for consent for non-Windows binaries: When an operation for a non-Microsoft application requires elevation of privilege, the user is prompted on the secure desktop to select either Permit or Deny. If the user selects Permit, the operation continues with the user's highest available privilege.
-
Harden Windows Security Behavior: When an operation requires elevation of privilege, the user is prompted on the secure desktop to select either Permit or Deny. If the user selects Permit, the operation continues with the user's highest available privilege.
-

 Only elevate executables that are signed and validated by enforcing cryptographic signatures on any interactive application that requests elevation of privilege. One of the Potential impacts of it is that it can prevent certain poorly designed programs from prompting for UAC.
Only elevate executables that are signed and validated by enforcing cryptographic signatures on any interactive application that requests elevation of privilege. One of the Potential impacts of it is that it can prevent certain poorly designed programs from prompting for UAC.  CSP
CSP
-

 Hides the entry points for Fast User Switching.
Hides the entry points for Fast User Switching.  CSP
CSP- This policy will prevent you from using "Forgot my PIN" feature in lock screen or logon screen. If you forget your PIN, you won't be able to recover it.
 Sets the behavior of the elevation prompt for Standard users to Prompt for Credentials on the Secure Desktop.
Sets the behavior of the elevation prompt for Standard users to Prompt for Credentials on the Secure Desktop.  CSP
CSP
 Configures the type of Admin Approval Mode to be Admin Approval Mode with enhanced privilege protection.
Configures the type of Admin Approval Mode to be Admin Approval Mode with enhanced privilege protection.

Windows Firewall
 Sets the Network Location of all connections to Public; Public network means less trust to other network devices.
Sets the Network Location of all connections to Public; Public network means less trust to other network devices.
 Sets inbound and outbound default actions for Domain Firewall Profile to Block; because this module is Not intended to be used on devices that are part of a domain or controlled by an Active Directory Domain Controller, since they will have their own policies and policy management systems in place.
Sets inbound and outbound default actions for Domain Firewall Profile to Block; because this module is Not intended to be used on devices that are part of a domain or controlled by an Active Directory Domain Controller, since they will have their own policies and policy management systems in place.  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP
 Enables Windows Firewall logging for Domain, Private and Public profiles, sets the log file size for each of them to the max
Enables Windows Firewall logging for Domain, Private and Public profiles, sets the log file size for each of them to the max 32.767 MB. Defines separate log files for each of the firewall profiles. Logs only dropped packets for Private and Public profiles, Logs both dropped and successful packets for Domain profile. CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP
 Disables Multicast DNS (mDNS) UDP-in Firewall Rules for all 3 Firewall profiles, This might interfere with Miracast screen sharing, which relies on the Public profile, and homes where the Private profile is not selected, but it does add an extra measure of security in public places, like a coffee shop.
Disables Multicast DNS (mDNS) UDP-in Firewall Rules for all 3 Firewall profiles, This might interfere with Miracast screen sharing, which relies on the Public profile, and homes where the Private profile is not selected, but it does add an extra measure of security in public places, like a coffee shop.
- The domain name
.localwhich is used in mDNS (Multicast DNS) is a special-use domain name reserved by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) so that it may not be installed as a top-level domain in the Domain Name System (DNS) of the Internet.
- The domain name

Optional Windows Features

-
 The module disables the following rarely used features in Windows optional features (Control Panel):
The module disables the following rarely used features in Windows optional features (Control Panel):-
PowerShell v2: because it's old and doesn't support AMSI.
-
Work Folders client: not used when your computer is not part of a domain or enterprise network.
-
Internet Printing Client: used in combination with IIS web server, old feature, can be disabled without causing problems further down the road.
-
Windows Media Player (legacy): isn't needed anymore, Windows 11 has a modern media player app.
-
Microsoft Defender Application Guard, it's deprecated. Learn more about Microsoft Edge Security Features here.
-
-
 Uninstalls these optional features (Windows Settings -> Apps -> Optional Features):
Uninstalls these optional features (Windows Settings -> Apps -> Optional Features):-
Notepad (system): legacy Notepad program. Windows 11 has multi-tabbed modern Notepad app.
-
VBSCRIPT: a legacy deprecated scripting engine component, Microsoft does not recommend using this component unless and until it is really required.
-
Internet Explorer mode for Edge browser: It's only used by a few possible organizations that have very old internal websites.
-
WMIC: Old and deprecated, not secure and is in Microsoft recommended block rules.
-
WordPad: Old and deprecated. None of the new features of Word documents are supported in it. Recommended to use Word Online, Notepad or M365 Word.
-
PowerShell ISE: Old PowerShell environment that doesn't support versions above 5.1. Highly recommended to use Visual Studio Code for PowerShell usage and learning. You can even replicate the ISE experience in Visual Studio Code. You can access Visual Studio Code online in your browser without the need to install anything.
-
Steps Recorder: it's deprecated.
-
-
 Enables these optional features (Control Panel):
Enables these optional features (Control Panel):-
Windows Sandbox: install, test and use programs in a disposable virtual operation system, completely separate from your main OS
-
Hyper-V: a great hybrid hypervisor (Type 1 and Type 2) to run virtual machines on. check out this Hyper-V Wiki page
-

Windows Networking

 Disables NetBIOS over TCP/IP on all network interfaces.
Disables NetBIOS over TCP/IP on all network interfaces.
 Disables Smart Multi-Homed Name Resolution because it uses NetBIOS and LLMNR, protocols that shouldn't be used anymore.
Disables Smart Multi-Homed Name Resolution because it uses NetBIOS and LLMNR, protocols that shouldn't be used anymore.  CSP
CSP
 Disables LMHOSTS lookup protocol on all network adapters, legacy feature that's not used anymore.
Disables LMHOSTS lookup protocol on all network adapters, legacy feature that's not used anymore.
 Disables Printing over HTTP because HTTP is not encrypted and it's an old feature that's not used anymore.
Disables Printing over HTTP because HTTP is not encrypted and it's an old feature that's not used anymore.  CSP
CSP
 Clears all the entries in Remotely accessible registry paths.
Clears all the entries in Remotely accessible registry paths.
 Clears all the entries in Remotely accessible registry paths and subpaths.
Clears all the entries in Remotely accessible registry paths and subpaths.
 Sets the minimum required SMB version for Client to
Sets the minimum required SMB version for Client to 3.1.1which is the latest available version at the moment and was introduced years ago with Windows 10.
 Sets the minimum required SMB version for Server to
Sets the minimum required SMB version for Server to 3.1.1which is the latest available version at the moment and was introduced years ago with Windows 10.

 Blocks NTLM completely for SMB.
Blocks NTLM completely for SMB.
 Requires encryption for SMB client/workstation.
Requires encryption for SMB client/workstation.
 Enables encryption for SMB Server. Its status can be checked using the following PowerShell command:
Enables encryption for SMB Server. Its status can be checked using the following PowerShell command: (get-SmbServerConfiguration).EncryptData. If the returned value is$Truethen SMB Encryption is turned on.
 Enables QUIC for SMB Client.
Enables QUIC for SMB Client.
 Enables QUIC for SMB Server.
Enables QUIC for SMB Server.
 Configures the Cipher Suites from the default value of
Configures the Cipher Suites from the default value of AES_128_GCM,AES_128_CCM,AES_256_GCM,AES_256_CCMtoAES_256_GCM,AES_256_CCM,AES_128_GCM,AES_128_CCMfor the SMB Client. CSP
CSP
 Configures the Cipher Suites from the default value of
Configures the Cipher Suites from the default value of AES_128_GCM,AES_128_CCM,AES_256_GCM,AES_256_CCMtoAES_256_GCM,AES_256_CCM,AES_128_GCM,AES_128_CCMfor the SMB Server. CSP
CSP

Miscellaneous Configurations
-
 Sets Early launch antimalware engine's status to
Sets Early launch antimalware engine's status to 8which is Good only. The default value is3, which allows good, unknown and 'bad but critical'. that is the default value, because setting it to8can prevent your computer from booting if the driver it relies on is critical but at the same time unknown or bad. CSP
CSP- By being launched first by the kernel, ELAM is ensured to be launched before any third-party software and is therefore able to detect malware in the boot process and prevent it from initializing. ELAM drivers must be specially signed by Microsoft to ensure they are started by the Windows kernel early in the boot process.
 Disables location services (Location, Windows Location Provider, Location Scripting) system wide. Websites and apps won't be able to use your precise location, however they will still be able to detect your location using your IP address.
Disables location services (Location, Windows Location Provider, Location Scripting) system wide. Websites and apps won't be able to use your precise location, however they will still be able to detect your location using your IP address.  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP
-
 Enables
Enables svchost.exemitigations. built-in system services hosted insvchost.exeprocesses will have stricter security policies enabled on them. These stricter security policies include a policy requiring all binaries loaded in these processes to be signed by Microsoft, and a policy disallowing dynamically generated code. CSP
CSP- Requires Business Windows licenses. e.g., Windows 11 pro for Workstations, Enterprise or Education.
 Turns on Enhanced mode search for Windows indexer. The default is classic mode.
Turns on Enhanced mode search for Windows indexer. The default is classic mode.  CSP
CSP
- This causes some UI elements in the search settings in Windows settings to become unavailable for Standard user accounts to view, because it will be a managed feature by an Administrator.
 Enables SMB/LDAP Signing
Enables SMB/LDAP Signing  CSP
CSP  CSP
CSP
 Enables Edge browser (stable/beta/dev channels) to download and install updates on any network, metered or not; because the updates are important and should not be suppressed.
Enables Edge browser (stable/beta/dev channels) to download and install updates on any network, metered or not; because the updates are important and should not be suppressed.
 Enables all Windows users to use Hyper-V and Windows Sandbox by adding all Windows users to the "Hyper-V Administrators" security group using its SID. By default, only Administrators can use Hyper-V or Windows Sandbox.
Enables all Windows users to use Hyper-V and Windows Sandbox by adding all Windows users to the "Hyper-V Administrators" security group using its SID. By default, only Administrators can use Hyper-V or Windows Sandbox.
-
 Creates custom views for Windows Event Viewer to help keep tabs on important security events:
Creates custom views for Windows Event Viewer to help keep tabs on important security events:-
Sudden Shut down events (due to power outage)
-
Checks to make sure Other Logon/Logoff Events Audit is active
 CSP
CSP -
Failed Login attempts via PIN at lock screen
- Error/Status code
0xC0000064indicates wrong PIN entered at lock screen
- Error/Status code
-
USB storage Connects & Disconnects (Flash drives, phones etc.)
 Enables WinVerifyTrust Signature Validation, a security feature related to WinVerifyTrust function that handles Windows Authenticode signature verification for portable executable (PE) files.
Enables WinVerifyTrust Signature Validation, a security feature related to WinVerifyTrust function that handles Windows Authenticode signature verification for portable executable (PE) files.
 Enables Command line process auditing.
Enables Command line process auditing.  CSP
CSP
 Enables the RPC Endpoint Mapper Client Authentication policy.
Enables the RPC Endpoint Mapper Client Authentication policy.  CSP
CSP
 Enables a policy that requests claims and compound authentication for Dynamic Access Control and Kerberos armoring.
Enables a policy that requests claims and compound authentication for Dynamic Access Control and Kerberos armoring.  CSP
CSP

 Enables Windows Protected Print.
Enables Windows Protected Print.  CSP
CSP
 Configures the SSH client's configurations to use the following secure MACs (Message Authentication Codes):
Configures the SSH client's configurations to use the following secure MACs (Message Authentication Codes): MACs hmac-sha2-512-etm@openssh.com,hmac-sha2-256-etm@openssh.com,umac-128-etm@openssh.com.

 Enables support for long paths.
Enables support for long paths.

 Force strong key protection for user keys stored on the computer. User is prompted when the key is first used.
Force strong key protection for user keys stored on the computer. User is prompted when the key is first used.

Windows Update Configurations
Windows updates are extremely important. They always should be installed as fast as possible to stay secure and if a reboot is required, it should be done immediately. Threat actors can weaponize publicly disclosed vulnerabilities the same day their POC (Proof-Of-Concept) is released..
In Windows by default, devices will scan daily, automatically download and install any applicable updates at a time optimized to reduce interference with usage, and then automatically try to restart when the end user is away.
The following policies the module configures make sure the default behavior explained above is tightly enforced.
 Enables Windows Update to download and install updates on any network, metered or not; because the updates are important and should not be suppressed, that's what bad actors would want.
Enables Windows Update to download and install updates on any network, metered or not; because the updates are important and should not be suppressed, that's what bad actors would want.  CSP
CSP
 Enables "Receive Updates for other Microsoft products" (such as PowerShell)
Enables "Receive Updates for other Microsoft products" (such as PowerShell)
 Enables "Notify me when a restart is required to finish updating".
Enables "Notify me when a restart is required to finish updating".  CSP
CSP
 Specifies the number of days before quality updates are installed on devices automatically to 1 day.
Specifies the number of days before quality updates are installed on devices automatically to 1 day.  CSP
CSP
 Specifies the number of days before feature updates are installed on devices automatically to 1 day.
Specifies the number of days before feature updates are installed on devices automatically to 1 day.  CSP
CSP
 Sets the number of grace period days before feature updates are installed on devices automatically to 1 day.
Sets the number of grace period days before feature updates are installed on devices automatically to 1 day.  CSP
CSP
 Sets the number of grace period days before quality updates are installed on devices automatically to 1 day.
Sets the number of grace period days before quality updates are installed on devices automatically to 1 day.  CSP
CSP
 Configures the automatic updates to happen every day, automatically be downloaded and installed, notify users for restart.
Configures the automatic updates to happen every day, automatically be downloaded and installed, notify users for restart.  CSP
CSP
 Enables features introduced via servicing that are off by default so that users will be able to get new features after having Windows Update settings managed by Group Policy as the result of running this category.
Enables features introduced via servicing that are off by default so that users will be able to get new features after having Windows Update settings managed by Group Policy as the result of running this category.  CSP
CSP

Edge Browser configurations
 Block 3rd party cookies - Recommendatory policy
Block 3rd party cookies - Recommendatory policy
 Sets the share additional operating system region setting to never - Recommendatory policy
Sets the share additional operating system region setting to never - Recommendatory policy
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA Reason: NO Perfect Forward Secrecy, CBC, SHA1
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA Reason: NO Perfect Forward Secrecy, CBC, SHA1
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 Reason: NO Perfect Forward Secrecy
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 Reason: NO Perfect Forward Secrecy
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA Reason: CBC, SHA1
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA Reason: CBC, SHA1Due to security reasons, many policies cannot be used when you are signed into Edge browser using personal Microsoft account. This module does not use any of those policies. When those policies are applied, they are ignored by the browser and edge://policy/ shows an error for them.
- You can view all of the policies being applied to your Edge browser by visiting this page:
edge://policy/ - You can find all of the available internal Edge pages in here:
edge://about/
- Useful links:

Certificate Checking Commands
![]() In this category, the module downloads and runs sigcheck64.exe from Sysinternals, then lists valid certificates not rooted to the Microsoft Certificate Trust List in the User and Machine certificate stores. Except for some possible Microsoft certificates, Windows insider builds certificates or certificates that have your own computer's name, which are perfectly safe and should not be deleted, All other certificates that will be listed should be treated as dangerous and removed from your system immediately.
In this category, the module downloads and runs sigcheck64.exe from Sysinternals, then lists valid certificates not rooted to the Microsoft Certificate Trust List in the User and Machine certificate stores. Except for some possible Microsoft certificates, Windows insider builds certificates or certificates that have your own computer's name, which are perfectly safe and should not be deleted, All other certificates that will be listed should be treated as dangerous and removed from your system immediately.

Country IP Blocking
![]() The module uses the newest range of
The module uses the newest range of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses of State Sponsors of Terrorism and OFAC Sanctioned Countries, directly from official IANA sources repository, then creates 2 rules (inbound and outbound) for each list in Windows firewall, completely blocking connections to and from those countries.
Once you have those Firewall rules added, you can use this method to see if any of the blocked connections were from/to those countries.
[!NOTE]\ Threat actors can use VPN, VPS etc. to mask their originating IP address and location. So don't take this category as the perfect solution for network protection.

Downloads Defense Measures 

![]() To combat the threat of more sophisticated malware, a preemptive measure is taken by creating and deploying a WDAC policy on the system. This policy blocks the execution of executables and other potentially harmful file types in the Downloads folder, using the WDACConfig module.
To combat the threat of more sophisticated malware, a preemptive measure is taken by creating and deploying a WDAC policy on the system. This policy blocks the execution of executables and other potentially harmful file types in the Downloads folder, using the WDACConfig module.
This policy defends the system from malware that can launch itself automatically after being downloaded from the Internet. The user must ensure the file's safety and explicitly transfer it to a different folder before running it.
The WDAC policy employs a wildcard pattern to prevent any file from running in the Downloads folder. Additionally, it verifies that the system downloads folder in the user directory matches the downloads folder in the Edge browser's settings. If there is a discrepancy, a warning message is displayed on the console.
![]()
![]() Creates a custom WDAC policy that blocks the execution of the following executables:
Creates a custom WDAC policy that blocks the execution of the following executables:
- wscript.exe
- mshta.exe
- cscript.exe
They are insecure, unsandboxed script hosts that pose a security risk.
All of the policies can be easily removed using the Unprotect-WindowsSecurity or Remove-WDACConfig cmdlets.

Non-Admin Commands
You don't need Admin privileges to run this category, because no system-wide changes is made. Changes in this category only apply to the current user account that is running the PowerShell session.
 Shows known file extensions in File explorer
Shows known file extensions in File explorer
 Shows hidden files, folders and drives (toggles the control panel folder options item)
Shows hidden files, folders and drives (toggles the control panel folder options item)
 Disables websites accessing local language list - good for privacy
Disables websites accessing local language list - good for privacy
 Turns off safe search in Windows search, will enable +18 content to appear in searches; essentially toggles the button in: Windows settings > privacy and security > search permissions > safe search
Turns off safe search in Windows search, will enable +18 content to appear in searches; essentially toggles the button in: Windows settings > privacy and security > search permissions > safe search
 Enables Clipboard History
Enables Clipboard History
 Turns on text suggestions when typing on the physical keyboard
Turns on text suggestions when typing on the physical keyboard
 Turns on "Multilingual text suggestions" for the current user, toggles the option in Windows settings
Turns on "Multilingual text suggestions" for the current user, toggles the option in Windows settings
 Turns off sticky key shortcut of pressing shift key 5 times fast
Turns off sticky key shortcut of pressing shift key 5 times fast
 Disables Show reminders and incoming VoIP calls on the lock screen
Disables Show reminders and incoming VoIP calls on the lock screen

Related

![]() Azure DevOps Repository (mirror)
Azure DevOps Repository (mirror)
![]() Harden Windows Security website
Harden Windows Security website
![]() Official global IANA IP block for each country
Official global IANA IP block for each country
![]() Privacy, Anonymity and Compartmentalization
Privacy, Anonymity and Compartmentalization

Trust
How can you 100% trust this repository and know that nothing shady is going on?
This repository uses effective methods that make it easy to verify:
-
Change log history is present on GitHub. (Despite some of my awkward documentation typos)
-
Artifact attestations are used to establish provenance for builds. It guarantees that the package(s) you download from this repository are 100% created from the source code that exist in this repository.
-
SBOMs (Software Bill of Materials) are generated for the entire repository to comply with data protection standards and providing transparency. Together with attestation they provide SLSA L2 security level for the build process. In the future, the workflows will be upgraded to comply with SLSA L3 level.
-
You can open the files in Visual Studio Code / Visual Studio Code Web / GitHub CodeSpace, and view them in a nice and easy to read environment, they are well formatted, commented and indented.
-
Commits are verified either with my GPG key or SSH key and Vigilant mode is turned on in my GitHub account.
-
You can fork this repository, verify it until that point in time, then verify any subsequent changes/updates I push to this repository, at your own pace (using
Sync forkandCompareoptions on your fork), and if you are happy with the changes, allow it to be merged with your own copy/fork on your GitHub account. -
Explanations for some of the files used by the Harden Windows Security module, ask about any other file(s) if you have questions, they are all in clear text.
-
Registry.csv includes some of the security measures' registry data.
-
ProcessMitigations.csv includes the process mitigations data.
-
Default Security Policy.inf contains security policy data used during unprotect actions to restore defaults.
-
Registry resources.csv Includes the data used for compliance checking.
-
Harden-Windows-Security.ps1 is the boot-strapper for the Harden Windows Security module.
-
-
How Are Group Policies Used by the Harden Windows Security Module?
-
How are Group Policies for this module created and maintained?
-
How to verify Security-Baselines-X directory and 100% trust it?
[!TIP]\ All files in this repository are zipped and automatically submitted to VirusTotal for scanning. Any available packages in the last release is also directly uploaded for scanning. It is done through a GitHub Action that is triggered every time a release is made or a PR is merged. Find the history of the uploaded files in my Virus Total profile.

Support
![]() If you have any questions, requests, suggestions etc. about this GitHub repository and its content, please open a new discussion or Issue.
If you have any questions, requests, suggestions etc. about this GitHub repository and its content, please open a new discussion or Issue.
![]() Reporting a vulnerability on this GitHub repository.
Reporting a vulnerability on this GitHub repository.
 I can also be reached privately at: spynetgirl@outlook.com
I can also be reached privately at: spynetgirl@outlook.com

Security Recommendations
-
 Always download your operation system from official Microsoft websites. Right now, Windows 11 is the latest version of Windows, its ISO file can be downloaded from this official Microsoft server. One of the worst things you can do to your own security and privacy is downloading your OS, which is the root of all the active and passive security measures, from a 3rd party website claiming they have the official unmodified files. There are countless bad things that can happen as the result of it such as threat actors embedding malware or backdoors inside the customized OS, or pre-installing customized root CA certificates in your OS so that they can perform TLS termination and view all of your HTTPS and encrypted Internet data in plain clear text, even if you use VPN. Having a poisoned and compromised certificate store is the endgame for you, and that's just the tip of the iceberg.
Always download your operation system from official Microsoft websites. Right now, Windows 11 is the latest version of Windows, its ISO file can be downloaded from this official Microsoft server. One of the worst things you can do to your own security and privacy is downloading your OS, which is the root of all the active and passive security measures, from a 3rd party website claiming they have the official unmodified files. There are countless bad things that can happen as the result of it such as threat actors embedding malware or backdoors inside the customized OS, or pre-installing customized root CA certificates in your OS so that they can perform TLS termination and view all of your HTTPS and encrypted Internet data in plain clear text, even if you use VPN. Having a poisoned and compromised certificate store is the endgame for you, and that's just the tip of the iceberg.- Refer to Wiki to see how to create Bootable USB flash drive with no 3rd party tools
-
 Whenever you want to install a program or app, first use the Microsoft Store or Winget, if the program or app you are looking for isn't available in there, then download it from its official website. Somebody created a nice web interface for interacting with Winget CLI here. Using Winget or Microsoft store provides many benefits:
Whenever you want to install a program or app, first use the Microsoft Store or Winget, if the program or app you are looking for isn't available in there, then download it from its official website. Somebody created a nice web interface for interacting with Winget CLI here. Using Winget or Microsoft store provides many benefits:-
Microsoft store UWP apps are secure in nature, digitally signed, in MSIX format. That means, installing and uninstalling them is guaranteed and there won't be any leftovers after uninstalling.
-
Microsoft store has Win32 apps too, they are traditional
.exeinstallers that we are all familiar with. The store has a library feature that makes it easy to find the apps you previously installed. -
Both Microsoft and Winget check the hash of the files by default, if a program or file is tampered, they will warn you and block the installation, whereas when you manually download a program from a website, you will have to manually verify the file hash with the hash shown on the website, if any.
-
-
 Use Secure DNS; Windows 11 natively supports DNS over HTTPS and DNS over TLS.
Use Secure DNS; Windows 11 natively supports DNS over HTTPS and DNS over TLS.- Use my WinSecureDNSMgr module to easily configure DNS over HTTPS in Windows
 Only use Microsoft Edge for browser; It has the Highest-rated protection against phishing and malware, available by default on Windows OS, has tightly integrated valuable Security features such as Microsoft Defender Application Guard, Microsoft Defender SmartScreen, Hardware Enforced Stack Protection, Arbitrary Code Guard (ACG), Control Flow Guard (CFG), Tracking Prevention and Trusted built-in Secure Network feature from Cloudflare just to name a few.
Only use Microsoft Edge for browser; It has the Highest-rated protection against phishing and malware, available by default on Windows OS, has tightly integrated valuable Security features such as Microsoft Defender Application Guard, Microsoft Defender SmartScreen, Hardware Enforced Stack Protection, Arbitrary Code Guard (ACG), Control Flow Guard (CFG), Tracking Prevention and Trusted built-in Secure Network feature from Cloudflare just to name a few.
 Always enable Two-Factor/Multi-Factor Authentication on websites, apps and services that you use. Preferably, use Microsoft Authenticator app which has backup and restore feature, so you never lose access to your TOTPs (Time-Based One-Time Passwords) even if you lose your phone. Available for Android and IOS.
Always enable Two-Factor/Multi-Factor Authentication on websites, apps and services that you use. Preferably, use Microsoft Authenticator app which has backup and restore feature, so you never lose access to your TOTPs (Time-Based One-Time Passwords) even if you lose your phone. Available for Android and IOS.
 Make sure OneDrive backup for important folders (Desktop/Documents/Pictures) is enabled. It is fast, secure and works in any network condition and since it's x64 (64-bit), it can handle a Lot of small and large files simultaneously.
Make sure OneDrive backup for important folders (Desktop/Documents/Pictures) is enabled. It is fast, secure and works in any network condition and since it's x64 (64-bit), it can handle a Lot of small and large files simultaneously.
-
 When considering the use of a VPN, it is crucial to exercise discernment and only resort to it when absolutely necessary. A VPN can be a vital tool if you reside in a totalitarian, communist, or dictatorial regime, or in a nation where democratic principles are not upheld. However, if you live in a country that does not fall into these categories, it may be wise to reconsider the necessity of using a VPN. Your local ISP (Internet Service Provider) is likely more trustworthy than the ISP associated with a remote VPN server. By using a VPN, you are merely transferring the trust you place in your local ISP to an unknown entity—the ISP utilized by the VPN provider. It is important not to be swayed by the deceptive marketing tactics employed by VPN companies. The true identities, political affiliations, backgrounds, and loyalties of those behind these services often remain shrouded in mystery. In the permissive and open societies of the Western world, it is conceivable that a VPN service could be established by entities with questionable intentions, including state sponsors of terrorism or other hostile actors. Such services could be utilized to gather intelligence, conduct data mining, and track users, posing significant risks to your privacy and security.
When considering the use of a VPN, it is crucial to exercise discernment and only resort to it when absolutely necessary. A VPN can be a vital tool if you reside in a totalitarian, communist, or dictatorial regime, or in a nation where democratic principles are not upheld. However, if you live in a country that does not fall into these categories, it may be wise to reconsider the necessity of using a VPN. Your local ISP (Internet Service Provider) is likely more trustworthy than the ISP associated with a remote VPN server. By using a VPN, you are merely transferring the trust you place in your local ISP to an unknown entity—the ISP utilized by the VPN provider. It is important not to be swayed by the deceptive marketing tactics employed by VPN companies. The true identities, political affiliations, backgrounds, and loyalties of those behind these services often remain shrouded in mystery. In the permissive and open societies of the Western world, it is conceivable that a VPN service could be established by entities with questionable intentions, including state sponsors of terrorism or other hostile actors. Such services could be utilized to gather intelligence, conduct data mining, and track users, posing significant risks to your privacy and security.- There are situations where using VPN can provide security and privacy. For example, when using a public WiFi hotspot or basically any network that you don't have control over. In such cases, use Cloudflare WARP which uses WireGuard protocol, or as mentioned, use Secure Network in Edge browser that utilizes the same secure Cloudflare network. It's free, it's from an American company that has global radar and lots of insight about countries in the world in real-time, at least 19.7% of all websites use it (2022). Safe to say it's one of the backbones of the Internet.
 Go passwordless with your Microsoft account and use Windows Hello authentication. In your Microsoft account which has Outlook service, you can create up to 10 Email aliases in addition to the 1 Email address you get when you made your Microsoft account, that means without creating a new account, you can have 11 Email addresses all of which will use the same inbox and account. You can specify which one of those Email aliases can be used to sign into your account, in the sign in preferences of your Microsoft account settings. So for example, when going passwordless, if you need you can give one of your Email aliases to others for communication or add it to a public profile of yours, then block sign in using that Email alias so nobody can send you authenticator notifications by entering that Email alias in the sign in page, and use the other 10 aliases that are private to sign into your Microsoft account with peace of mind. You can create a rule in your Outlook so that all of the Emails sent to your public Email alias will be stored in a different folder, apart from your other inbox emails. All of this can be done using free Microsoft account and Outlook webapp.
Go passwordless with your Microsoft account and use Windows Hello authentication. In your Microsoft account which has Outlook service, you can create up to 10 Email aliases in addition to the 1 Email address you get when you made your Microsoft account, that means without creating a new account, you can have 11 Email addresses all of which will use the same inbox and account. You can specify which one of those Email aliases can be used to sign into your account, in the sign in preferences of your Microsoft account settings. So for example, when going passwordless, if you need you can give one of your Email aliases to others for communication or add it to a public profile of yours, then block sign in using that Email alias so nobody can send you authenticator notifications by entering that Email alias in the sign in page, and use the other 10 aliases that are private to sign into your Microsoft account with peace of mind. You can create a rule in your Outlook so that all of the Emails sent to your public Email alias will be stored in a different folder, apart from your other inbox emails. All of this can be done using free Microsoft account and Outlook webapp.
 Set a strong password for the UEFI firmware of your device so that it will ask for password before allowing any changes to be made to firmware. You can also configure the password to be required on startup.
Set a strong password for the UEFI firmware of your device so that it will ask for password before allowing any changes to be made to firmware. You can also configure the password to be required on startup.
 Use NTFS (which is the default Filesystem in Windows) or ReFS (Resilient File System, newer). In addition to all their benefits, they support
Use NTFS (which is the default Filesystem in Windows) or ReFS (Resilient File System, newer). In addition to all their benefits, they support Mark Of The Web(MOTW) orzone.identifier. When a file is downloaded to a device running Windows, Mark of the Web is added to the file, identifying its source as being from the internet. You can read all the information about it in here. If your USB flash drive is formatted asFAT32, change it toNTFS, becauseFAT32does not keep theMOTWof the files. If the file you are downloading is compressed in.zipformat, make sure you open/extract it using Windows built-in support for.zipfiles because it keeps the MOTW of the files. If the compressed file you downloaded is in other formats such as.7zipor.rar, make sure you use an archive program that supports keeping the mark of the Web of files after extraction. One of those programs is NanaZip which is a fork of 7zip, available in Microsoft Store and GitHub, compared to 7zip, it has better and modern GUI, and the application is digitally signed. After installation, open it, navigate toToolsat the top then selectOptions, setPropagate zone.id streamtoYes. You can use this PowerShell command to find all the info about the Zone Identifier of the files you downloaded from the Internet.
Get-Content <Path-To-File> -stream zone.identifier When using Xbox, make sure you configure sign-in preference and set it to either
When using Xbox, make sure you configure sign-in preference and set it to either Ask for my PINorLock it down. The latter is the most secure one since it will require authentication using Microsoft Authenticator app.Ask for my PINis recommended for the most people because it will only require a PIN to be entered using controller.
-
 A few reminders about open source programs:
A few reminders about open source programs:-
Unless you are a skilled programmer who can understand and verify every line of code in the source, and spends time to personally build the software from the source, and repeats all the aforementioned tasks for each subsequent version, then seeing the source code won't have any effect on you because you aren't able to understand nor verify it.
-
Do not assume that the entire Open Source community audits and verifies every line of code just because the source code is available, as we've seen in the XZ utility's backdoor by state sponsored actors, they can have backdoors implanted in them in broad daylight and nobody might notice it for a long time.
-
The majority of open source programs are unsigned, meaning they don't have a digital signature, their developers haven't bought and used a code signing certificate to sign their program. Among other problems, this might pose a danger to the end-users by making it harder to create trust for those programs in security solutions such as Application Control or App Whitelisting, and makes it hard to authenticate them. Read Microsoft's Introduction to Code Signing. Use Azure Trusted Signing which is affordable.
-
 Use Microsoft account (MSA) or Microsoft Entra ID to sign into Windows. Never use local administrators. Real security is achieved when there is no local administrator and identities are managed using Entra ID. You will be able to enforce Multi-factor unlock, for example use PIN + Fingerprint or PIN + Facial recognition, to unlock your device.
Use Microsoft account (MSA) or Microsoft Entra ID to sign into Windows. Never use local administrators. Real security is achieved when there is no local administrator and identities are managed using Entra ID. You will be able to enforce Multi-factor unlock, for example use PIN + Fingerprint or PIN + Facial recognition, to unlock your device.
 Enable Random Hardware Addresses In Windows Settings -> Network & Internet -> WIFI. Currently, there is no Group Policy or associated registry key to automatically turn it on, that is why it is mentioned here in the security recommendations section. It has various security and privacy benefits such as your device cannot be uniquely identified by its hardware Mac address and the routers your connect to cannot uniquely identify you. You can set it to change daily in your WIFI network adapter's settings in Windows settings for even more benefits.
Enable Random Hardware Addresses In Windows Settings -> Network & Internet -> WIFI. Currently, there is no Group Policy or associated registry key to automatically turn it on, that is why it is mentioned here in the security recommendations section. It has various security and privacy benefits such as your device cannot be uniquely identified by its hardware Mac address and the routers your connect to cannot uniquely identify you. You can set it to change daily in your WIFI network adapter's settings in Windows settings for even more benefits.
 More Security Recommendations coming soon...
More Security Recommendations coming soon...

Resources

- Microsoft.com
- Microsoft Learn - Technical Documentation
- Germany Intelligence Agency - BND - Federal Office for Information Security
- Microsoft Tech Community - Official blogs and documentations
- Microsoft Security baselines - Security baselines from Microsoft
- Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC) YouTube channel
- BlueHat Seattle 2019 || Guarding Against Physical Attacks: The Xbox One Story
- Security Update Guide: The Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC) investigates all reports of security vulnerabilities affecting Microsoft products and services, and provides the information here as part of the ongoing effort to help you manage security risks and help keep your systems protected.
- Microsoft Security Response Center Blog
- Microsoft Security Blog
- Microsoft Podcasts
- Bug Bounty Program - With bounties worth up to
250,000$ - Microsoft Active Protections Program
- Security Update Guide FAQs
- Microsoft On the Issues - Assessments, Investigations and Reports of APTs (Advanced Persistent Threats¹) and nation-sponsored cyberattack operations globally
- A high level overview paper by Microsoft (in
PDF), framework for cybersecurity information sharing and risk reduction. - Microsoft Threat Modeling Tool - for software architects and developers
- Important events to monitor
- Windows Security portal
- Security auditing
- Microsoft SysInternals Sysmon for Windows Event Collection or SIEM
- Privileged Access Workstations
- Enhanced Security Administrative Environment (ESAE)
- New Zealand 2016 Demystifying the Windows Firewall – Learn how to irritate attackers without crippli
- Download Windows virtual machines ready for development
- UK National Cyber Security Centre Advice & guidance
- Global threat activity
- Microsoft Zero Trust
- Understanding malware & other threats, phrases
- Malware naming
- Microsoft Digital Defense Report
- Microsoft Defender for Individuals
- Submit a file for malware analysis
- Submit a driver for analysis
- Service health status
- Microsoft Defender Threat Intelligence
- Microsoft Virus Initiative
- Digital Detectives @Microsoft
- Australia's Essential Eight
- NIST 800-53
- DoD's CMMC (Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification)
- ISO 27001
- DoD Cyber Stigs (Security Technical Implementation Guides)
- NIST SP 800-171 Rev. 2 - Protecting Controlled Unclassified Information in Nonfederal Systems and Organizations
- Clean source principle
- Windows Message Center
- Deprecated features for Windows client
- Microsoft Cybersecurity Reference Architectures
- BlueHat IL 2023 - David Weston - Default Security
- Windows Security best practices for integrating and managing security tools
- Microsoft Exploitability Index
- The Microsoft Incident Response Ninja Hub

Roadmap
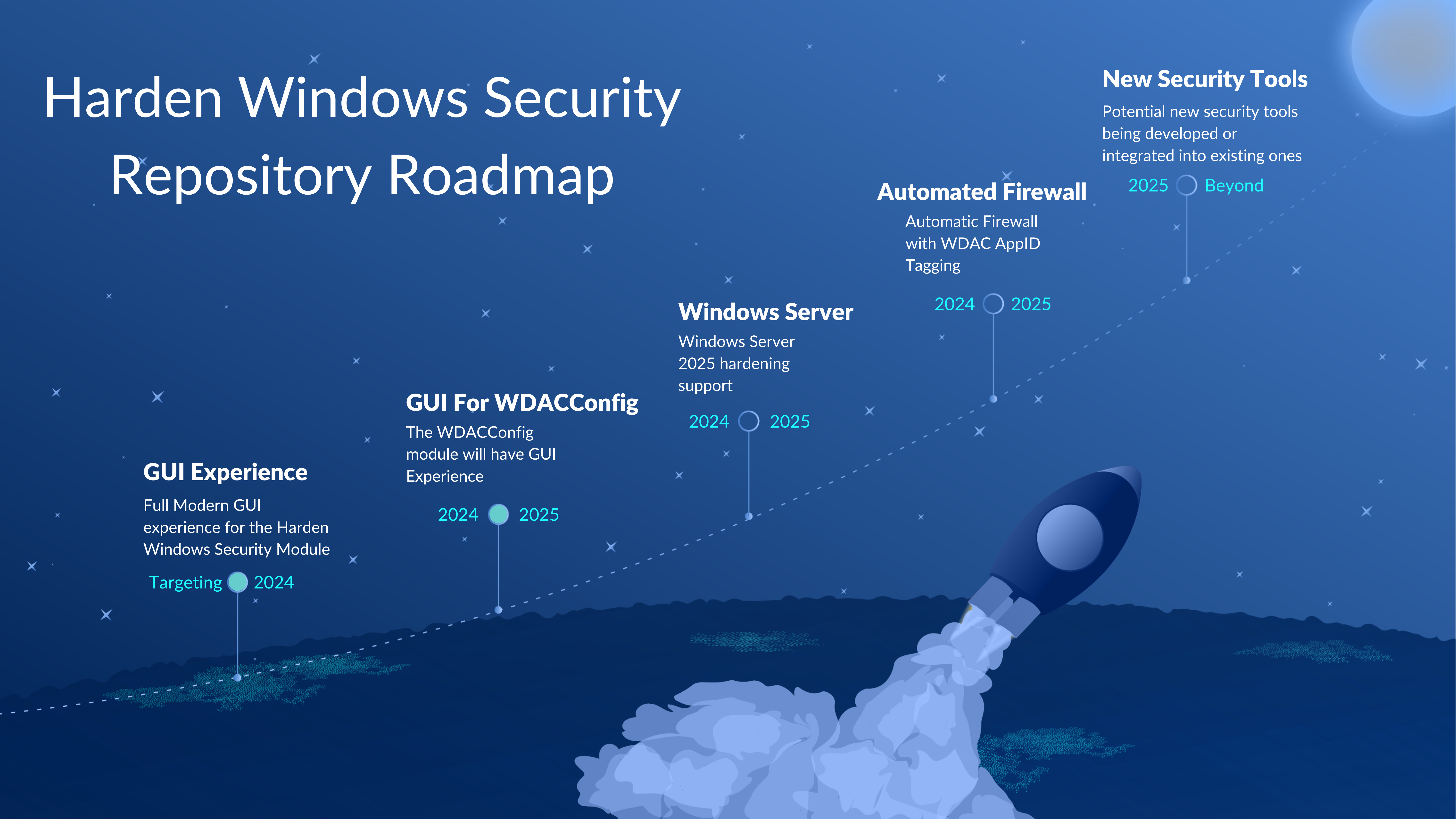

License
Using MIT License. Free information without any paywall or things of that nature. The only mission of this GitHub repository is to give all Windows users accurate, up to date and correct facts and information about how to stay secure and safe in dangerous environments, and to stay not one, but Many steps, ahead of threat actors.
Credits
- Some of the icons are from icons8
- Windows, Azure etc. are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation


&label=Harden%20Windows%20Security%20Module&labelColor=rgb(233%2C255%2C125)&color=rgb(246%2C%2082%2C%20160))
&label=WDACConfig%20Module&labelColor=rgb(233%2C255%2C125)&color=rgb(246%2C%2082%2C%20160))




















