skweak: Weak supervision for NLP

**Skweak is no longer actively maintained** (if you are interested to take over the project, give us a shout). Labelled data remains a scarce resource in many practical NLP scenarios. This is especially the case when working with resource-poor languages (or text domains), or when using task-specific labels without pre-existing datasets. The only available option is often to collect and annotate texts by hand, which is expensive and time-consuming. `skweak` (pronounced `/skwi:k/`) is a Python-based software toolkit that provides a concrete solution to this problem using weak supervision. `skweak` is built around a very simple idea: Instead of annotating texts by hand, we define a set of _labelling functions_ to automatically label our documents, and then _aggregate_ their results to obtain a labelled version of our corpus. The labelling functions may take various forms, such as domain-specific heuristics (like pattern-matching rules), gazetteers (based on large dictionaries), machine learning models, or even annotations from crowd-workers. The aggregation is done using a statistical model that automatically estimates the relative accuracy (and confusions) of each labelling function by comparing their predictions with one another. `skweak` can be applied to both sequence labelling and text classification, and comes with a complete API that makes it possible to create, apply and aggregate labelling functions with just a few lines of code. The toolkit is also tightly integrated with [SpaCy](http://www.spacy.io), which makes it easy to incorporate into existing NLP pipelines. Give it a try!
**Full Paper**:
Pierre Lison, Jeremy Barnes and Aliaksandr Hubin (2021), "[skweak: Weak Supervision Made Easy for NLP](https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-demo.40/)", *ACL 2021 (System demonstrations)*. **Documentation & API**: See the [Wiki](https://github.com/NorskRegnesentral/skweak/wiki) for details on how to use `skweak`.
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/11574012/114999146-e0995300-9ea1-11eb-8288-2bb54dc043e7.mp4
## Dependencies - `spacy` >= 3.0.0 - `hmmlearn` >= 0.3.0 - `pandas` >= 0.23 - `numpy` >= 1.18 You also need Python >= 3.6. ## Install The easiest way to install `skweak` is through `pip`: ```shell pip install skweak ``` or if you want to install from the repo: ```shell pip install --user git+https://github.com/NorskRegnesentral/skweak ``` The above installation only includes the core library (not the additional examples in `examples`). Note: some examples and tests may require trained spaCy pipelines. These can be downloaded automatically using the syntax (for the pipeline `en_core_web_sm`) ```shell python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm ``` ## Basic Overview
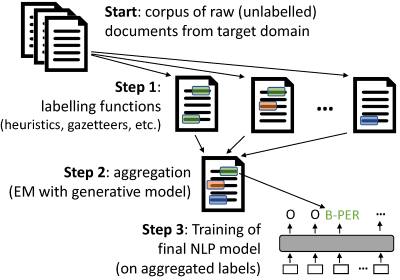
Weak supervision with `skweak` goes through the following steps: - **Start**: First, you need raw (unlabelled) data from your text domain. `skweak` is build on top of [SpaCy](http://www.spacy.io), and operates with Spacy `Doc` objects, so you first need to convert your documents to `Doc` objects using SpaCy. - **Step 1**: Then, we need to define a range of labelling functions that will take those documents and annotate spans with labels. Those labelling functions can comes from heuristics, gazetteers, machine learning models, etc. See the  for more details. - **Step 2**: Once the labelling functions have been applied to your corpus, you need to _aggregate_ their results in order to obtain a single annotation layer (instead of the multiple, possibly conflicting annotations from the labelling functions). This is done in `skweak` using a generative model that automatically estimates the relative accuracy and possible confusions of each labelling function. - **Step 3**: Finally, based on those aggregated labels, we can train our final model. Step 2 gives us a labelled corpus that (probabilistically) aggregates the outputs of all labelling functions, and you can use this labelled data to estimate any kind of machine learning model. You are free to use whichever model/framework you prefer. ## Quickstart Here is a minimal example with three labelling functions (LFs) applied on a single document: ```python import spacy, re from skweak import heuristics, gazetteers, generative, utils # LF 1: heuristic to detect occurrences of MONEY entities def money_detector(doc): for tok in doc[1:]: if tok.text[0].isdigit() and tok.nbor(-1).is_currency: yield tok.i-1, tok.i+1, "MONEY" lf1 = heuristics.FunctionAnnotator("money", money_detector) # LF 2: detection of years with a regex lf2= heuristics.TokenConstraintAnnotator("years", lambda tok: re.match("(19|20)\d{2}$", tok.text), "DATE") # LF 3: a gazetteer with a few names NAMES = [("Barack", "Obama"), ("Donald", "Trump"), ("Joe", "Biden")] trie = gazetteers.Trie(NAMES) lf3 = gazetteers.GazetteerAnnotator("presidents", {"PERSON":trie}) # We create a corpus (here with a single text) nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm") doc = nlp("Donald Trump paid $750 in federal income taxes in 2016") # apply the labelling functions doc = lf3(lf2(lf1(doc))) # create and fit the HMM aggregation model hmm = generative.HMM("hmm", ["PERSON", "DATE", "MONEY"]) hmm.fit([doc]*10) # once fitted, we simply apply the model to aggregate all functions doc = hmm(doc) # we can then visualise the final result (in Jupyter) utils.display_entities(doc, "hmm") ``` Obviously, to get the most out of `skweak`, you will need more than three labelling functions. And, most importantly, you will need a larger corpus including as many documents as possible from your domain, so that the model can derive good estimates of the relative accuracy of each labelling function. ## Documentation See the [Wiki](https://github.com/NorskRegnesentral/skweak/wiki). ## License `skweak` is released under an MIT License. The MIT License is a short and simple permissive license allowing both commercial and non-commercial use of the software. The only requirement is to preserve the copyright and license notices (see file [License](https://github.com/NorskRegnesentral/skweak/blob/main/LICENSE.txt)). Licensed works, modifications, and larger works may be distributed under different terms and without source code. ## Citation See our paper describing the framework: Pierre Lison, Jeremy Barnes and Aliaksandr Hubin (2021), "[skweak: Weak Supervision Made Easy for NLP](https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-demo.40/)", *ACL 2021 (System demonstrations)*. ```bibtex @inproceedings{lison-etal-2021-skweak, title = "skweak: Weak Supervision Made Easy for {NLP}", author = "Lison, Pierre and Barnes, Jeremy and Hubin, Aliaksandr", booktitle = "Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations", month = aug, year = "2021", address = "Online", publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics", url = "https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-demo.40", doi = "10.18653/v1/2021.acl-demo.40", pages = "337--346", } ```


