data.table 
data.table provides a high-performance version of base R's data.frame with syntax and feature enhancements for ease of use, convenience and programming speed.
Why data.table?
- concise syntax: fast to type, fast to read
- fast speed
- memory efficient
- careful API lifecycle management
- community
- feature rich
Features
- fast and friendly delimited file reader:
?fread, see also convenience features for small data - fast and feature rich delimited file writer:
?fwrite - low-level parallelism: many common operations are internally parallelized to use multiple CPU threads
- fast and scalable aggregations; e.g. 100GB in RAM (see benchmarks on up to two billion rows)
- fast and feature rich joins: ordered joins (e.g. rolling forwards, backwards, nearest and limited staleness), overlapping range joins (similar to
IRanges::findOverlaps), non-equi joins (i.e. joins using operators>, >=, <, <=), aggregate on join (by=.EACHI), update on join - fast add/update/delete columns by reference by group using no copies at all
- fast and feature rich reshaping data:
?dcast(pivot/wider/spread) and?melt(unpivot/longer/gather) - any R function from any R package can be used in queries not just the subset of functions made available by a database backend, also columns of type
listare supported - has no dependencies at all other than base R itself, for simpler production/maintenance
- the R dependency is as old as possible for as long as possible, dated April 2014, and we continuously test against that version; e.g. v1.11.0 released on 5 May 2018 bumped the dependency up from 5 year old R 3.0.0 to 4 year old R 3.1.0
Installation
install.packages("data.table")
# latest development version (only if newer available)
data.table::update_dev_pkg()
# latest development version (force install)
install.packages("data.table", repos="https://rdatatable.gitlab.io/data.table")See the Installation wiki for more details.
Usage
Use data.table subset [ operator the same way you would use data.frame one, but...
- no need to prefix each column with
DT$(likesubset()andwith()but built-in) - any R expression using any package is allowed in
jargument, not just list of columns - extra argument
byto computejexpression by group
library(data.table)
DT = as.data.table(iris)
# FROM[WHERE, SELECT, GROUP BY]
# DT [i, j, by]
DT[Petal.Width > 1.0, mean(Petal.Length), by = Species]
# Species V1
#1: versicolor 4.362791
#2: virginica 5.552000Getting started
- Introduction to data.table vignette
- Getting started wiki page
- Examples produced by
example(data.table)
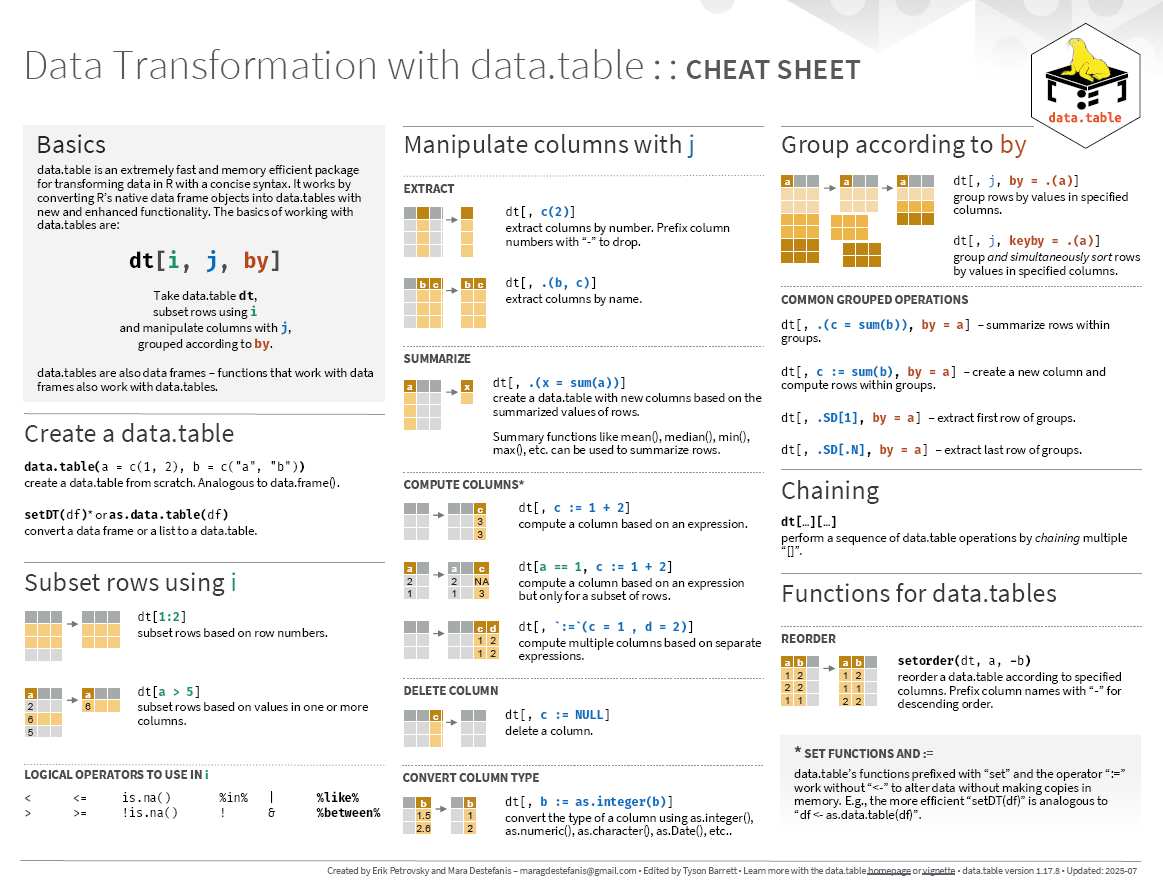
Cheatsheets
Community
data.table is widely used by the R community. It is being directly used by hundreds of CRAN and Bioconductor packages, and indirectly by thousands. It is one of the top most starred R packages on GitHub, and was highly rated by the Depsy project. If you need help, the data.table community is active on StackOverflow.
A list of packages that significantly support, extend, or make use of data.table can be found in the Seal of Approval document.
Stay up-to-date
- click the Watch button at the top and right of GitHub project page
- read NEWS file
- follow #rdatatable and the r_data_table account on X/Twitter
- follow #rdatatable and the r_data_table account on fosstodon
- follow the data.table community page on LinkedIn
- watch recent Presentations
- read recent Articles
- read posts on The Raft
Contributing
Guidelines for filing issues / pull requests: Contribution Guidelines.