****
THIS REPOSITORY HAS BEEN MOVED BEHIND OUR DEVELOPERS PORTAL
BUT PLEASE WATCH 👁️🗨️ ALL ACTIVITY IT AS WE REPORT THE README AND CHANGELOG HERE. YOU'LL BE NOTIFIED WITH:
- Bug fixes
- OS version update
- Support of new products
****
Flutter CaptureSDK 1.5.19
The repository has been relocated within the Socket Mobile Developer Portal to enhance camera scanning capabilities with the SocketCam C860.
It employs a high-performance decoder capable of swiftly reading damaged barcodes in various lighting conditions.
The new SocketCam C860 is provided to developers at no cost and requires no additional coding efforts if the application includes a UI trigger button.
Activation of the C860 is left to the application's end user, who can enable its use by purchasing a subscription.
It's important to note that the free version of our camera-based scanner, the SocketCam C820, remains accessible.
Both the C860 and C820 utilize the same APIs as our physical scanner products, ensuring a seamless transition between a camera-based scanner and a physical barcode scanner.
More documentation can be found here.
For more information and how to access, please visit our page about this new product.
On 1st of July 2024, there won't be any support for this repository and we will focus on the Flutter CaptureSDK hosted through our DEVELOPERS PORTAL.
Devices compatibility and CaptureSDK versions
| Devices | <= 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SocketCam C860 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| SocketCam C820 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| S720/D720/S820 | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| D600, S550, and all other barcode scanners | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| S370 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| DW930/XS930 and DW940/XS940 | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| S320 | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
Installation
Install the flutter package by adding the following to your pubspec.yaml file.
dependencies:
...
capturesdk_flutter:
git:
url: https://oauth2:<YOUR-AUTH-TOKEN-FROM-SOCKET-MOBILE-DEVELOPERS-PORTAL>@sdk.socketmobile.com/capture/flutter-capturesdk.git
version: ^1.5.19
...Then, in your application's main.dart, you can import the Flutter CaptureSDK by adding this line to the top of your file.
import 'package:capturesdk_flutter/capturesdk.dart';For the rest of the things to add in your project, go to iOS and Android.
Getting started
Create a Capture instance with the line Capture capture = Capture(logger);. logger is an optional argument that is passed to Capture and can be helpful with tracing values and requests throughout the app, particularly in Capture and HttpTransport where the bulk of the Capture logic and requests are handled.
Open the connection wth the Capture library by using the open method on the Capture instance. See below.
int? response = await capture.openClient(appInfo, _onCaptureEvent);
stat = 'handle: $response';
mess = 'capture open success';appInfo is an instance of the AppInfo class and consists of the same parameters found in other Capture SDKs. See an example of appInfo below.
final appInfo = AppInfo(
'android:com.example.example',
'MC4CFQDNCtjazxILEh8oyT6w/wlaVKqS1gIVAKTz2W6TB9EgmjS1buy0A+3j7nX4',
'ios:com.example.example',
'MC0CFA1nzK67TLNmSw/QKFUIiedulUUcAhUAzT6EOvRwiZT+h4qyjEZo9oc0ONM=',
'bb57d8e1-f911-47ba-b510-693be162686a');To generate app info, head to the docs and follow the prompts to register your app and generate your appInfo credentials. See the important section at the end of the README for more information specific to Flutter.
Next, _onCaptureEvent is the callback passed to open that can handle the event notifications from the Capture SDK. Below are three important events to consider, which are accessible in the CaptureEventIds class.
deviceArrival is the event that is triggered when the scanner connects to your device.
deviceRemoval is the event that is triggered when the scanner is disconnected from the device.
decodedData is the event that is triggered when you scan something with the connected scanner.
See an example of event handling below in _onCaptureEvent.
_onCaptureEvent(e, handle) {
if (e == null) {
return;
} else if (e.runtimeType == CaptureException) {
_updateVals("${e.code}", e.message, e.method, e.details);
return;
}
logger.log('onCaptureEvent from: ', '$handle');
switch (e.id) {
case CaptureEventIds.deviceArrival:
Capture deviceCapture = Capture(logger);
setState(() {
_deviceCapture = deviceCapture;
});
_openDeviceHelper(deviceCapture, e);
break;
case CaptureEventIds.deviceRemoval:
_closeDeviceHelper(e, handle);
break;
case CaptureEventIds.decodedData:
setState(() {
/// storing scanned data in state for future use
_currentScan = e;
});
_updateVals('Decoded Data', "Successful scan!");
break;
}
}The data the user will need to anticipate will be a CaptureEvent which might contain an instance of DecodedData, CaptureException, a client or device handle, etc. When you first connect to the service, the response will be a client handle (an integer) or a CaptureException instance will be thrown.
It's important to create another Capture instance when you have successfully connected the scanner to your device (see var newCapture = Capture(logger);). This capture instance is tied to your device and will allow the root capture instance to remain open, regardless of what happens with your device. The new instance allows you to create a capture connection to the device to handle various actions specific to the connected device, such as getProperty and setProperty.
getProperty enables you to retrieve specific values for the connected device, such as friendlyNameDevice which is the property corresponding to the scanners given name (as opposed to id/guid). Create a property instance with the provided values corresponding to the property id and type, as well an empty object. You can retrieve the friendly name of a device with the following request.
Future<void> _handleGetNameProperty() async {
CaptureProperty property = CaptureProperty(
CapturePropertyIds.friendlyNameDevice,
CapturePropertyTypes.none,
{});
try {
CaptureProperty propertyResponse =
await _deviceCapture!.getProperty(property);
print('Successfully Retrieved "name" property for device: ${propertyResponse.value}';);
//can incorporate UI logic to update device in device list
} on CaptureException catch (e) {
print(e.code);
}
}setProperty allows you to update the value of a specific property. The CaptureProperty instance you provide is similar to the one in getProperty but instead of an empty object for the value, you will send the value you want assigned to the property. You will also send the data type for the property as well instead of CapturePropertyTypes().none. In the case of friendlyNameDevice, you would send a string value with the type CapturePropertyTypes().string. See below.
Future<void> _handleSetNameProperty() async {
CaptureProperty property = CaptureProperty(
CapturePropertyIds.friendlyNameDevice,
CapturePropertyTypes.string,
_newName);
try {
CaptureProperty propertyResponse =
await _deviceCapture!.setProperty(property);
print('Successfully set "name" property to "$_newName".');
//can incorporate UI logic to update device in device list
} on CaptureException catch (e) {
print(e.code);
}
}The response in setProperty does not contain a value property. You can access the updated value by calling the getProperty request after a successful setProperty call or you can use the locally stored value that you're using for assignment.
Getting started iOS
You will need to change three things in your app in order for it to work with iOS. First will need to update the Podfile in the ios directory of your app in order to be compatible with the version used in our SDK and the source of our iOS CaptureSDK
source "https://oauth2:<YOUR-AUTH-TOKEN-FROM-SOCKET-MOBILE-DEVELOPERS-PORTAL>@sdk.socketmobile.com/capture/cocoapods-repo.git"
platform :ios, '13.0'
target 'MyProject' do
....
endSecond, go to ios/Runner/Info.plist and at the bottom, just above </dict>, include the below code.
<key>NSBluetoothAlwaysUsageDescription</key>
<string>Bluetooth is needed to connect to a Socket Mobile device</string>
<key>UISupportedExternalAccessoryProtocols</key>
<array>
<string>com.socketmobile.chs</string>
</array>
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Need to enable camera access for SocketCam</string>
<key>LSApplicationQueriesSchemes</key>
<array>
<string>sktcompanion</string>
</array>If you do not do this, you will encounter an error saying This app has crashed because it attempted to access privacy-sensitive data without a usage description. The app's Info.plist must contain an NSBluetoothAlwaysUsageDescription key with a string value explaining to the user how the app uses this data.. This is a bluetooth security measure, and to permit bluetooth access you will need to add the above entry in your Info.plist file. The other item related to NSCameraUsageDescription is to permit camera access in order to use SocketCam C820 and C860
For SocketCam C860 which is an enhanced version of SocketCam C820, you also need to add the following key to your Info.plist: LSApplicationQueriesSchemes (Queried URL Schemes) with a new item: sktcompanion (in lower case).
In order to use it you have to install Socket Mobile Companion on your device.
You can find more details about SocketCam C860 on our website.
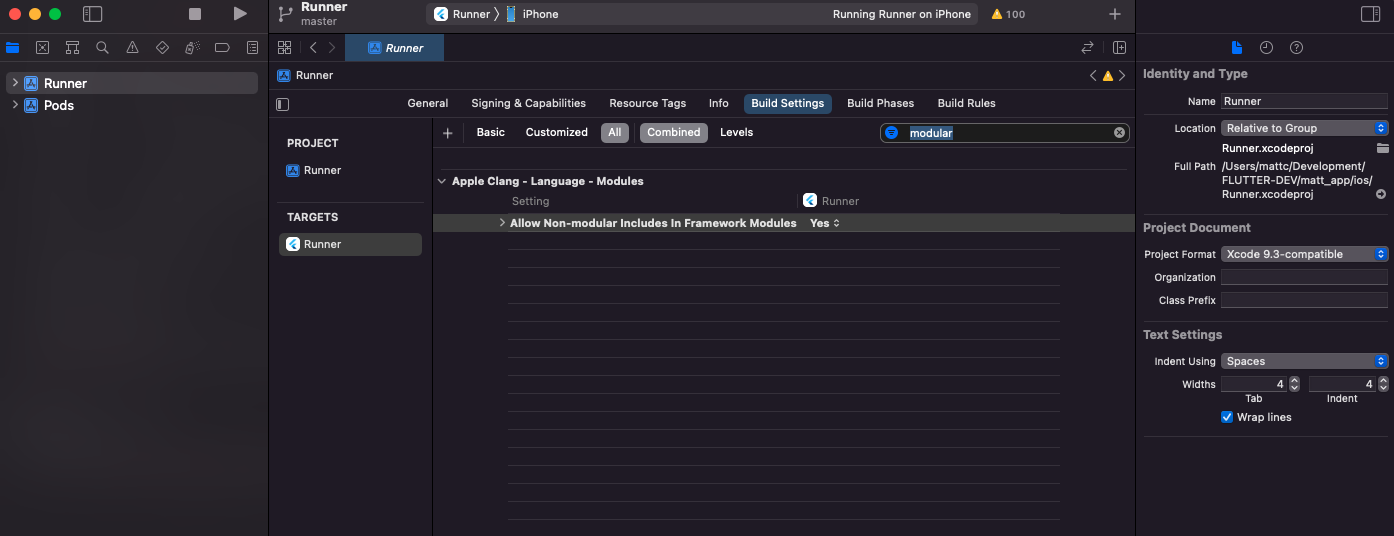
Third, open the project's iOS directory in xcode. Once you've done that, select the Runner and navigate to the build settings. In the search bar, type in 'module' and then look for the portion that says "Allow Non-modular includes in Framework Modules". Once that property is location, select "Yes". See the image below for what it should look like.
Getting started Android
You will need to update the network configuration to enable the Android Capture client. You can find out more about network configuration here.
In order to pass the internet permissions, you need to have the below line in your Android manifest.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />In order to use SocketCam C820, you will need to add the below to your Android manifest.
<activity android:name="com.facebook.react.devsupport.DevSettingsActivity" />
<meta-data android:name="com.socketmobile.capture.APP_KEY" android:value="{YOUR_APP_KEY}"/>
<meta-data android:name="com.socketmobile.capture.DEVELOPER_ID" android:value="{YOUR_DEVELOPER_ID}"/>Where it says YOUR_APP_KEY, you need to include the android app key that you got for your app when you registered it. Where it says YOUR_DEVELOPER_ID is the developer ID you use for your socket mobile developer portal.
ALSO: The package name in AndroidManifest.xml, it needs to be both all lowercase and must match your Bundle ID that you have in your app's registration information in your dev portal.
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.yourpackagename">Enable Start Capture Service on Android
You might also have to add the file network_security_config.xml file to android/app/src/main/res/xml in order to avoid a clearText permissions error. See the code below for the file.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<network-security-config>
<base-config cleartextTrafficPermitted="false" />
<domain-config cleartextTrafficPermitted="true">
<domain includeSubdomains="false">localhost</domain>
<domain includeSubdomains="false">127.0.0.1</domain>
</domain-config>
</network-security-config>Then, in their app's AndroidManifest.xml file, the developer will need to add the below property into the <application> tag.
android:networkSecurityConfig="@xml/network_security_config"Finally, add the below line into just before the AndroidManifest.xml file's closing </manifest> tag.
<queries>
<package android:name="com.socketmobile.companion"/>
</queries>For more on the network security configuration for Android, please check out the cleartext section in the Android docs.
Important
To register your app for Flutter, you can select the Flutter language first, and then you can pick one of two platform options; Android and iOS. Below is an example of credentials generated during iOS registration.
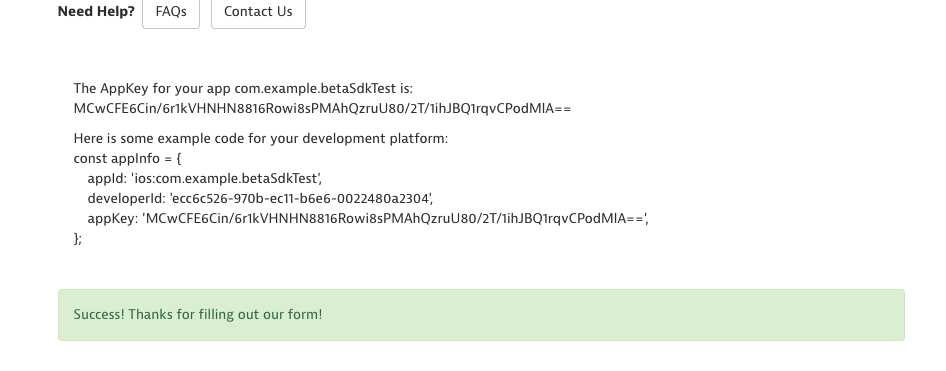
If you want to add support for both platforms you will need to generate an app key for one platform first and then the other separately. Once these two keys are generated, all you need to do is inlcude the iOS and Android appKey and appId, respectively, to the same AppInfo instance.
final appInfo = AppInfo(
'android:com.example.example',
'MC4CFQDNCtjazxILEh8oyT6w/wlaVKqS1gIVAKTz2W6TB9EgmjS1buy0A+3j7nX4',
'ios:com.example.example',
'MC0CFA1nzK67TLNmSw/QKFUIiedulUUcAhUAzT6EOvRwiZT+h4qyjEZo9oc0ONM=',
'bb57d8e1-f911-47ba-b510-693be162686a');In order for it to work, you will need to add five argments to AppInfo in the following order:
- Android appId
- AppKey after Android registration
- iOS appId
- AppKey after iOS registration
- Developer ID
For more information about the Flutter CaptureSDK, please visit the documentation.
For a full demonstration, check out this video.
Environment Information
Run flutter doctor -v to see your environment tools. Here's what you need:
Visual Studio Code with Flutter extension
Flutter SDK v3.0.0 and Dart v3.0.0 minimum
DevTools v2.31.1 with Chrome as optional
Xcode 15
Android Studio
To make sure everything is installed, you can also run flutter upgrade. This will upgrade the Flutter SDK and the tools for Android and iOS if needed.
Build & Run Instructions
cd example- Run
flutter pub get
Then you can run the app through Android Studio and Xcode or through Visual Studio Code directly with the debugger module. See this page for more details: https://docs.flutter.dev/tools/vs-code#running-and-debugging.
Android
cd android- Run
flutter runor open the project in Android Studio to run on connected iOS device.
iOS
cd ios- Run
pod install --repo-update - Run
flutter runor open the project in Xcode to run on connected iOS device.