pciSeq: Probabilistic Cell typing by In situ Sequencing
A Python package that implements the cell calling algorithm as described in Qian, X., et al. Nature Methods (2020)
Installation
python -m pip install pciSeqRequirement: Python >= 3.8
If you want to work with the source code you can download the repo and then replicate the python environment by
conda env create -n pciSeq -f /path/to/environment.ymlThat will create a conda environment with the name pciSeq containing all the necessary packages to run the algorithm. To activate it run
conda activate pciSeqor, if you open the project in your IDE, then in your project settings, switch your interpreter to the interpreter of the pciSeq env.
Usage
You need to create two pandas dataframes for the spots and the single cell data and a coo_matrix for the label image (which in
most cases will be the output of some image segmentation application). Then you pass them into the pciSeq.fit() method as follows:
import pciSeq
res = pciSeq.fit(spots=spots_df, coo=label_image, scRNAseq=scRNA_df)See the demo below for a more detailed explanation about the arguments of pciSeq.fit() and its return values.
There is also a fourth argument (optional) to override the default hyperparameter values which are initialised
by the config.py module. To pass user-defined hyperparameter values, create a dictionary with keys the
hyperparameter names and values their new values. For example, to exclude all Npy and Vip spots you can do:
import pciSeq
opts = { 'exclude_genes': ['Npy', 'Vip'] }
res = pciSeq.fit(spots=spots_df, coo=label_image, scRNAseq=scRNA_df, opts=opts)Demo
You can run a pciSeq demo in google colab:
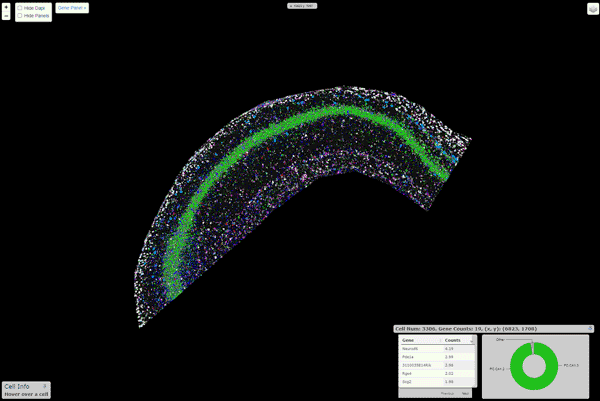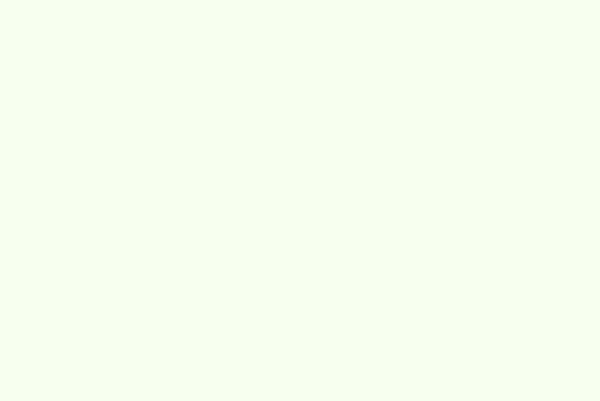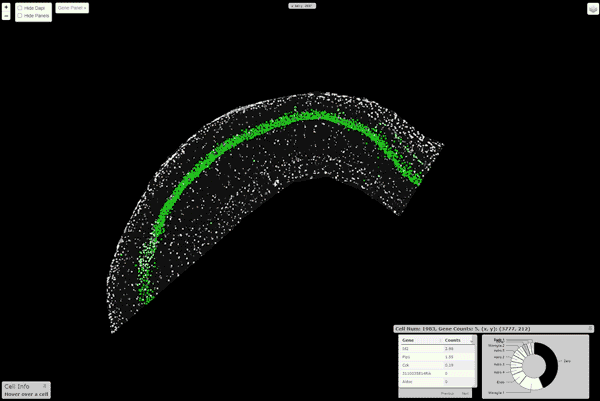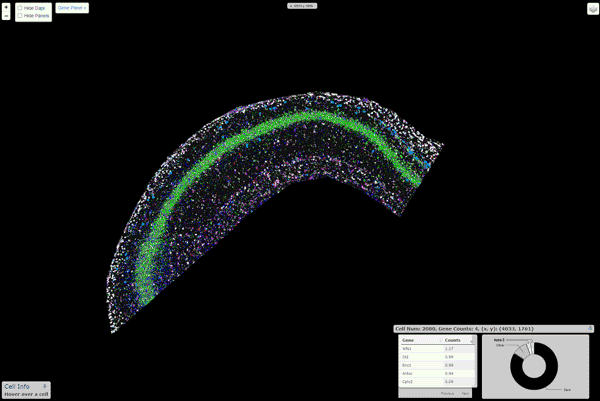
Viewer
An interactive viewer to explore the data runs on this url. Instructions about
building this viewer with your own data are here. \
If you have v 0.0.49 or greater you can also launch the viewer automatically by
setting opts = {'launch_viewer': True} and passing it to pciSeq.fit(), see
Diagnostics
Diagnostics will help you understand whether pciSeq has been misconfigured, the algorithm has taken the wrong path and will produce meaningless results when it finishes. You will need however to install redis (or Memurai if you are using Windows).
For linux do:
sudo apt-get install redis-server redis-tools
and then start the service:
sudo service redis-server start
You can get the free version of memurai from here. Once installed, the service should start automatically but you can manually do that by:
memurai.exe –service-start
If redis (or memurai) is missing from your system, the call to launch the diagnostics dashboard will be
ignored. If you are interested in this feature you may find this notebook
useful
Change Log
[0.0.59] - 2023-09-22
- Fixed a SIGSERV error under pandas '2.1.1'
[0.0.56] - 2023-07-03
-
Diagnostics dashboard
-
Baselayers on the viewer. You can have multiple background images and switch between them.
[0.0.50] - 2023-05-27
References
Qian, X., et al. (2020). Probabilistic cell typing enables fine mapping of closely related cell types in situ. Nat Methods 17, 101 - 106.





