VidChapters-7M: Video Chapters at Scale
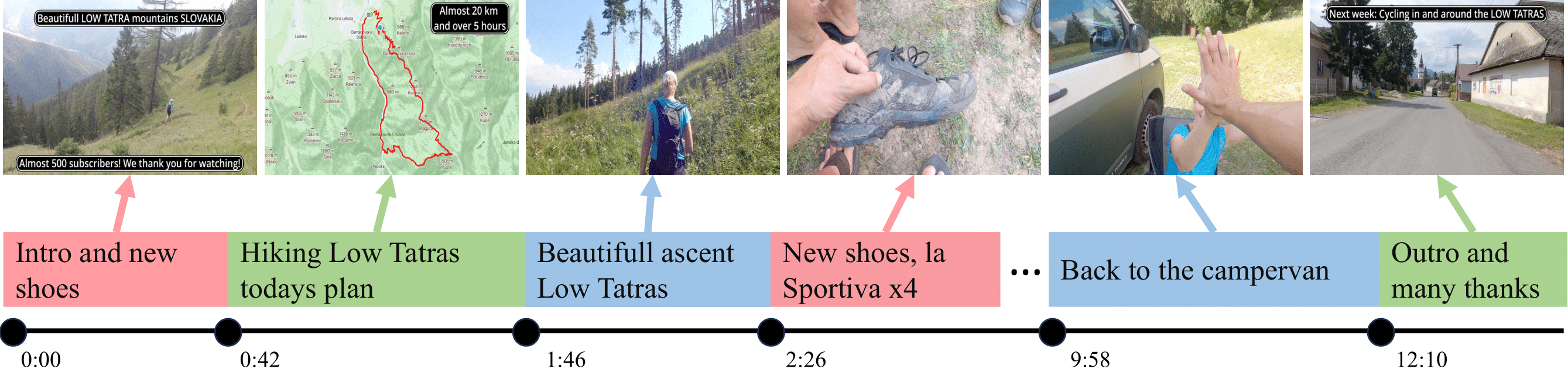
In this work, we present VidChapters-7M, a large-scale dataset of user-chaptered videos. We study three tasks on top of this dataset and show that video chapter generation models trained on VidChapters-7M transfer well to dense video captioning.
This repository provides the code for our paper, including:
- Environment setup
- Data collection pipeline for VidChapters-7M (in case you want to collect your own set of chaptered videos)
- Data downloading instructions and processed data files
- Data processing and analysis scripts (in case you want to reproduce the preprocessing)
- Training and evaluation scripts for the tasks of video chapter generation without or with ground-truth boundaries and video chapter grounding on VidChapters-7M, and dense video captioning on YouCook2 and ViTT
- Pretrained model checkpoints
- A demo to chapter or densely caption the video of your choice with a pretrained Vid2Seq model
This codebase also includes a PyTorch implementation of Vid2Seq (notably in model/vid2seq.py).
There are a few differences with the original Jax implementation, including:
- Usage of t5-base instead of t5-v1_1-base, which also results in a few architectural differences (
is_gated_act=Falseinstead of True) - Addition of a normalization of the weights related to time tokens at every optimization step
- No random temporal cropping during training
- Whisper ASR instead of Google ASR
Paths and Requirements
Fill the empty paths in the file args.py (and if you wish to use PDVC / Moment-DETR, in the scripts in PDVC/cfgs / moment_detr/moment_detr/scripts/).
To use the evaluation scripts with the METEOR captioning metric, you also need Java.
To install requirements (originally done in Python 3.7), run:
pip install -r requirements.txtNotes:
- The Whisper ASR extraction is done with a separate conda environment created as specified in WhisperX, with Python 3.10 and PyTorch 2.0.
- The PDVC experiments are run with a separate conda environment as suggested by PDVC , so to compile the deformable attention layer.
Data collection pipeline
To start, you should get a bunch of YouTube video IDs (that do not necessarily contain video chapters)
and use yt-dlp to download descriptions from YouTube,
e.g., yt-dlp https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=<VIDEO_ID> --write-description --skip-download.
Then, assuming the descriptions are downloaded as .txt files in SSD_DIR/chapters_descriptions,
you can run python collection/desc2chapters.py to extract chapters from descriptions.
The output file maps video IDs of user-chaptered videos to the chapter titles and timestamps.
You can then download the YouTube video content of videos with chapters with yt-dlp,
e.g., yt-dlp https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=<VIDEO_ID>.
Data downloading
VidChapters-7M: We provide the dataset annotations and ASR at this link.
You should download the annotations in DATA_DIR/AllChapters.
We also provide processed annotations here.
HowTo100M: We use a sentencified version of the dataset.
You should download it in DATA_DIR/howto100m.
ViTT: Download it from the data providers.
You will also need to download the mapping between 4-character IDs from YouTube-8M to YouTube video IDs.
You should download these in DATA_DIR/ViTT.
We also provide processed annotations, ASR and visual features here.
YouCook2: Download it from the data providers.
You should download these in YouCook2.
We also provide processed annotations, ASR and visual features here.
Data processing
Visual Feature Extraction
We follow FrozenBiLM to extract CLIP ViT-L/14 @ 224 pixels features at 1 FPS for all videos.
We store them in SSD_DIR/chapters_clipvitl14_features/SSD_DIR/howto100m_clip_features, one file per video, for VidChapters-7M/HowTo100M, and gather them in a single .pth file for all videos in YouCook2/ViTT.
ASR Extraction
To extract ASR, given a csv file prepared like for the visual feature extraction and an output_path where to store the extracted ASR, we run on a single GPU:
conda activate whisperX_env
python asr_extract/whisper_inference.py --csv=<csv> --output_path=<output_path> --fasterYou may parallelize this over many jobs.
Note that this requires having downloaded the Whisper Large-V2 model weights in <MODEL_DIR>.
We then gather the extracted ASR into a single file asr by running:
python asr_extract/merge_asr_whisper.py <output_path> DATA_DIR/AllChapters/whisper.pklTo extract word-level timestamps and segment the ASR into sentences, we run on a single GPU:
conda activate whisperX_env
python asr_extract/whisper_align.py --csv=<csv> --asr=DATA_DIR/AllChapters/whisper.pkl --output_path=<align_output_path>You may parallelize this over many jobs.
Note that this requires having downloaded the alignment model weights for all languages from WhisperX in <MODEL_DIR>.
Finally, we merge the aligned ASR into a single file by running:
python asr_extract/merge_asr_whisper_align.py <align_output_path> DATA_DIR/AllChapters/asr.pkl DATA_DIR/AllChapters/whisper.pklAnnotation files
To preprocess annotation files, use:
python preproc/chapters_to_dvc.py
python preproc/chapters_to_vmr.py
python preproc/vitt.py
python preproc/youcook.pyAnalysis
To detect languages from ASR or chapters, we run on single GPUs:
python analysis/language.py You may parallelize this over many jobs.
To obtain gender statistics, we run on a CPU:
python analysis/gender.py To detect videos with NSFW frames or toxic chapter titles or ASR, we run on single GPUs (for this, you will also need detoxify==0.5.1 that you can pip install):
python analysis/nsfw.py You may parallelize this over many jobs. Note that this requires having downloaded this NSFW classifier and the Detoxify language model.
You can also find the code for the paper plots in the notebook analysis/plots.ipynb, and the details of the manual assessment presented in the paper in analysis/manual_assessment.xlsx.
Model checkpoints
For HowTo100M pretraining, the full video chapter generation task, and dense video captioning tasks, we release the following Vid2Seq checkpoints and report their corresponding SODA performance.
| Training data | VidChapters-7M (test) | YouCook2 (val) | ViTT (test) | url | size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HowTo100M | Drive | 1.1GB | |||
| VidChapters-7M | 10.6 | Drive | 1.1GB | ||
| HowTo100M + VidChapters-7M | 11.4 | Drive | 1.1GB | ||
| HowTo100M + VidChapters-7M + YouCook2 | 10.3 | Drive | 1.1GB | ||
| HowTo100M + VidChapters-7M + ViTT | 15.0 | Drive | 1.1GB |
For the task of video chapter generation with ground-truth boundaries, we release the following Vid2Seq checkpoint and report its corresponding CIDEr performance.
| Training data | VidChapters-7M (test) | url | size |
|---|---|---|---|
| HowTo100M + VidChapters-7M | 120.5 | Drive | 1.1GB |
For the task of video chapter grounding, we release the following Moment-DETR checkpoint and report its corresponding R@10s performance.
| Training data | VidChapters-7M (test) | url | size |
|---|---|---|---|
| VidChapters-7M | 21.8 | Drive | 0.9GB |
Training and evaluation
Unless stated otherwise, to load a pretrained checkpoint with the following scripts, you can use --load=<CHECKPOINT>, and evaluation can be done with the same scripts as below but specifying --eval.
Note that most of our training runs were done using A100 GPUs with 80GB of memory. You may need to adapt the batch size if you are using lower memory GPUs.
Also, to use BLIP-2-based scripts, you need to download raw videos from the corresponding datasets and prepare a video_paths.json file that maps video IDs to the video path.
Vid2Seq Pretraining on HowTo100M
Run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env dvc.py --epochs=5 \
--fraction_warmup_steps=0.01 --lr=3e-4 --print_freq=1000 --save_dir=howto100m \
--combine_datasets htm --batch_size=8 --clip_max_norm=0.1Video Chapter Generation
For Vid2Seq, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env dvc.py --epochs=10 \
--lr=3e-4 --save_dir=chapters --combine_datasets chapters --combine_datasets_val chapters \
--batch_size=8 --batch_size_val=8 --clip_max_norm=0.1 --schedule="cosine_with_warmup"Multiple baselines reported in the paper can also be found in args.py, e.g. using only visual or speech input with --no_speech or --no_video, or training only using ASR with --gen_asr.
For PDVC, run:
cd PDVC
conda activate PDVC_env
python train.py --cfg_path cfgs/chapters_clip_pdvc.yml --gpu_id=0 --epoch=5 --no_self_iou --lr=1e-4Test inference with PDVC can be done by setting the evaluation paths to the test data in the config, using the same script, and setting the parameters --load=<CHECKPOINT> and --epoch=0.
For the text tiling + LLaMA zero-shot baseline, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env zs_speechvcg.py --combine_datasets=chapters \
--combine_datasets_val=chapters --save_dir=chapters_texttilingllama --model_name <MODEL_DIR>/7BHFPass --random to the previous command to run the random baseline.
For the shot detection + BLIP-2 zero-shot baseline, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env zs_visualvcg.py --combine_datasets=chapters \
--combine_datasets_val=chapters --save_dir=chapters_shotdetectblip2 --model_name Salesforce/blip2-flan-t5-xlVideo Chapter Generation with Ground-Truth Boundaries
For Vid2Seq, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env vc.py --epochs=20 --lr=3e-4 \
--save_dir=chapters_vcggt --combine_datasets chapters --combine_datasets_val chapters --batch_size=64 \
--batch_size_val=1 --schedule="cosine_with_warmup" --max_input_tokens=256 --max_output_tokens=32For the LLaMA zero-shot baseline, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env vc.py --model_name=<MODEL_DIR>/7BHF \
--save_dir=chapters_vcggt_zeroshotllama --combine_datasets chapters --combine_datasets_val chapters \
--batch_size_val=1 --max_input_tokens=256 --max_output_tokens=32 --evalPass --random to the previous command to run the random baseline.
For the BLIP-2 zero-shot baseline, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env vc.py --model_name=Salesforce/blip2-flan-t5-xl \
--save_dir=chapters_vcggt_zeroshotblip2 --combine_datasets chapters --combine_datasets_val chapters \
--batch_size_val=1 --max_input_tokens=256 --max_output_tokens=32 --evalVideo Chapter Generation Grounding
For Moment-DETR, run:
cd moment_detr
bash moment_detr/scripts/chapters.sh --max_v_l=1200 --downsample --clip_length=3 --lr=3e-4 \
--n_epoch=50 --max_es_cnt=50 --exp_id=chapters --bsz=256 --eval_bsz=256 --num_workers=16Inference with Moment-DETR can be run with the script moment_detr/scripts/chapters_inference.sh, the same parameters, and a parameter --resume=<CHECKPOINT>.
For the CLIP zero-shot baseline, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env zs_vcgr.py --save_dir=chapters_vcgr_clip \
--combine_datasets chapters --combine_datasets_val chaptersFor the BERT zero-shot baseline, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env zs_vcgr.py --save_dir=chapters_vcgr_bert \
--combine_datasets chapters --combine_datasets_val chapters --no_videoFor the random zero-shot baseline, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env zs_vcgr.py --save_dir=chapters_vcgr_random \
--combine_datasets chapters --combine_datasets_val chapters --randomDense Video Captioning
For Vid2Seq on YouCook2/ViTT, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env dvc.py --epochs=40 \
--lr=3e-4 --save_dir=youcook --combine_datasets youcook --combine_datasets_val youcook \
--batch_size=2 --batch_size_val=2 --schedule="cosine_with_warmup"
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 8 --use_env dvc.py --epochs=20 \
--lr=3e-4 --save_dir=vitt --combine_datasets vitt --combine_datasets_val vitt \
--batch_size=2 --batch_size_val=2 --schedule="cosine_with_warmup"The zero-shot evaluation can be simply done by loading a checkpoint pretrained on VidChapters-7M for evaluation using the arguments --load=<CHECKPOINT> --eval.
For PDVC on YouCook2/ViTT, run:
cd PDVC
conda activate PDVC_env
python train.py --cfg_path=cfgs/yc2_clip_pdvc.yml --gpu_id=0
python train.py --cfg_path=cfgs/vitt_clip_pdvc.yml --gpu_id=0 To load a pretrained PDVC checkpoint, set the parameters --load=<CHECKPOINT> and --load_vocab data/vocabulary_allchapters.json.
Test inference with PDVC can be done by setting the evaluation paths to the test data in the config, using the same script, and setting the parameters --load=<CHECKPOINT> and --epoch=0.
Demo
To run a pretrained Vid2Seq model (for video chapter generation or dense video captioning) on the video of your choice, you first need to extract ASR with the following command:
conda activate whisperX_env
python demo_asr.py --video_example=<VIDEO_PATH> --asr_example <OUTPUT_ASR_PATH> --combine_datasets chaptersThen you can run the model inference:
python demo_vid2seq.py --load=<CHECKPOINT> --video_example=<VIDEO_PATH> --asr_example <OUTPUT_ASR_PATH> --combine_datasets chaptersLicenses
This code is released under the MIT License. The licenses for datasets used in the paper are available at the following links: VidChapters-7M, HowTo100M, YouCook2, and ViTT.
Citation
If you found this work useful, consider giving this repository a star and citing our paper as followed:
@inproceedings{yang2023vidchapters,
title={VidChapters-7M: Video Chapters at Scale},
author={Antoine Yang and Arsha Nagrani and Ivan Laptev and Josef Sivic and Cordelia Schmid},
booktitle={NeurIPS},
year={2023}}





