DBLOG.DatabaseLogAnalyzer can read the SQL Server transaction logs online, and return RedoSQL and UndoSQL for every transaction. It base on SQL Server fn_dblog() function and develop some extension.
below is a demo:
Connect to SQL Server, create a test table dbo.OrderDetail, and run some DML sql on this table.
-- create table
create table dbo.OrderDetail
(OrderID int not null,
ItemID int not null,
ItemNumber varchar(10),
QTY int,
Price decimal(8,2),
ADate date,
AUser char(20),
UDate datetime,
UUser varchar(20)
constraint pk_OrderDetail primary key(OrderID,ItemID)
)
-- transaction1: insert 3 rows
insert into dbo.OrderDetail(OrderID,ItemID,ItemNumber,QTY,Price,ADate,AUser,UDate,UUser)
select 1001,1,'D001',100,45.62,'2015-01-02','Xh6','2015-01-03 20:15:18','Lx4' union all
select 1001,2,'Z001_2',150,180,'2015-01-02','cx5','2015-01-08 02:45:32','Yx3' union all
select 1002,1,'Z001_2',300,182.07,'2015-12-12','CL1','2015-12-18 02:45:32','LY6'
-- transaction2: update 1 row
update dbo.OrderDetail set QTY=999 where OrderID=1001 and ItemID=1
-- transaction3: update 3 rows
update dbo.OrderDetail set ItemNumber='!@#$%'
-- transaction4: delete all rows
delete from dbo.OrderDetailAfter run, there is no records in test table.
-- query result
select * from dbo.OrderDetailRight now, we can use this tool to recover data online(no need to restore database and logs). Please download zip file in Releases, and extract files to a folder.
step1: Execute MSSQLLogAnalyzer.exe.
step2: Modify [ConnectionString], change it for your environment.
Modify [StartTime] and [EndTime] to what time range need to read logs.
Modify [TableName], It can be blank, when blank means read all table logs.
step3: Click [Readlog] button, wait for analysis results. below screenshot is the run result.
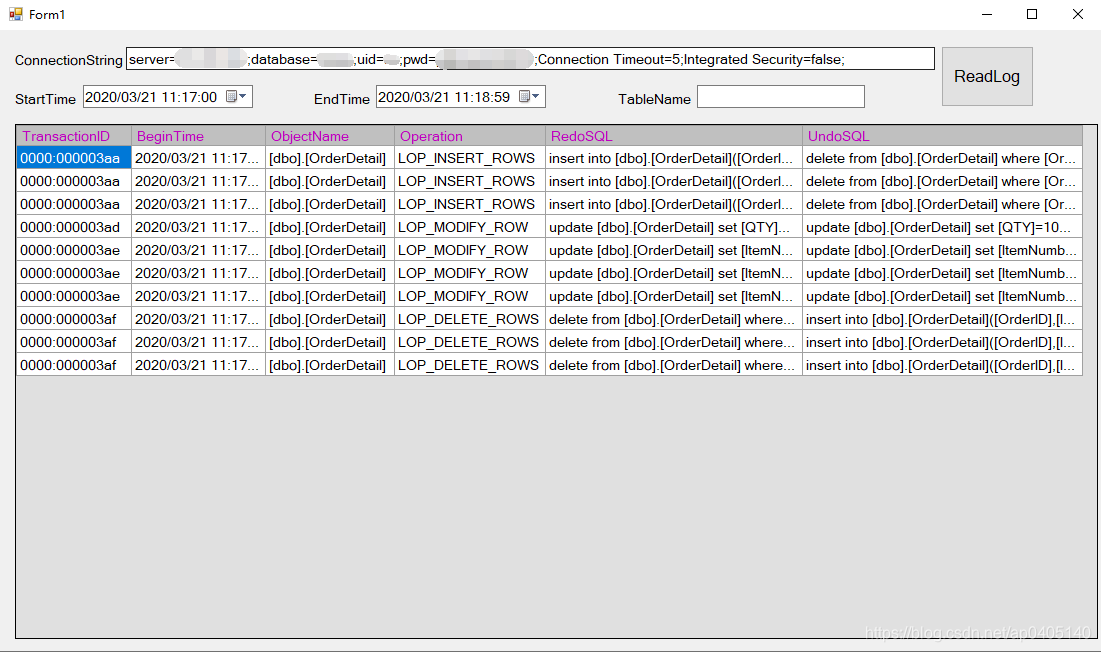 After run finished, It returned some RedoSQL and UndoSQL for every transaction, For recovery, we can use UndoSQL to recover all operations (execute from the back forward).
After run finished, It returned some RedoSQL and UndoSQL for every transaction, For recovery, we can use UndoSQL to recover all operations (execute from the back forward).
-- recover transaction4(delete all rows)
insert into dbo.OrderDetail([OrderID],[ItemID],[ItemNumber],[QTY],[Price],[ADate],[AUser],[UDate],[UUser]) values(1002, 1, '!@#$%', 300, 182.07, '2015-12-12', 'CL1', '2015-12-18 02:45:32.000', 'LY6');
insert into dbo.OrderDetail([OrderID],[ItemID],[ItemNumber],[QTY],[Price],[ADate],[AUser],[UDate],[UUser]) values(1001, 2, '!@#$%', 150, 180.00, '2015-01-02', 'cx5', '2015-01-08 02:45:32.000', 'Yx3');
insert into dbo.OrderDetail([OrderID],[ItemID],[ItemNumber],[QTY],[Price],[ADate],[AUser],[UDate],[UUser]) values(1001, 1, '!@#$%', 999, 45.62, '2015-01-02', 'Xh6', '2015-01-03 20:15:18.000', 'Lx4');
-- recover transaction3(update 3 rows)
update dbo.OrderDetail set [ItemNumber]='Z001_2' where [OrderID]=1002 and [ItemID]=1
update dbo.OrderDetail set [ItemNumber]='Z001_2' where [OrderID]=1001 and [ItemID]=2
update dbo.OrderDetail set [ItemNumber]='D001' where [OrderID]=1001 and [ItemID]=1
-- recover transaction2(update 1 row)
update dbo.OrderDetail set [QTY]=100 where [OrderID]=1001 and [ItemID]=1
-- query recovery result
select * from dbo.OrderDetail
Recovery finished!
Some Tips:
1. The SQL Server to be analyzed needs 2008 or later version.
2. Target Database Recovery model must be 'Full'.
3. This module only analyzes for DML transaction.
4. For develop, please install Visual Studio 2017 or later version and .NET Framework 4.8.
5. Please contact me when have any question: ap0405140@163.com
SQLCLR use example:
Deployment to SQLServer with SQLCLR, then we can use a SQL Function to readlog on SQL Server Management Studio.
use master
-- enable clr
exec sys.sp_configure 'clr enabled'
exec sys.sp_configure 'clr enabled',1
reconfigure
-- set trustworthy on
alter database [DatabaseName] set trustworthy on
use [DatabaseName]
-- function dbo.DBAReadLog
if exists(select 1 from sys.objects where name=N'DBAReadLog')
drop function dbo.DBAReadLog
if exists(select 1 from sys.assemblies where name=N'FCLR')
drop assembly FCLR
create assembly FCLR
from 'D:\MSSQLLogAnalyzer\FCLR\bin\Debug\FCLR.dll'
with permission_set=unsafe
alter assembly FCLR add file from 'D:\MSSQLLogAnalyzer\FCLR\bin\Debug\FCLR.pdb';
create function dbo.DBAReadLog(@connectionstring nvarchar(max),
@dt0 nvarchar(max),
@dt1 nvarchar(max),
@obj nvarchar(max))
returns table(LSN nvarchar(max),Type nvarchar(max),TransactionID nvarchar(max),BeginTime nvarchar(max),EndTime nvarchar(max),ObjectName nvarchar(max),Operation nvarchar(max),RedoSQL nvarchar(max),UndoSQL nvarchar(max),Message nvarchar(max))
as external name FCLR.UserDefinedFunctions.DBAReadLog
-- read log
select *
from dbo.DBAReadLog(N'server=[ServerName];database=[DatabaseName];uid=[LoginName];pwd=[Password];Connection Timeout=5;Integrated Security=false;', -- Database connection string
N'2020/11/23 10:00:00', --StartTime, example: 2020/11/23 10:00:00
N'2020/11/23 12:01:00', --EndTime, example: 2020/11/23 12:01:00
null) t --TableName, Need include schema name(like dbo.Table1), When blank or null means query all tables logs.
order by LSNDBLOG.dll use example:
step1: Start Visual Studio 2017, create a new project.
step2: Add reference DBLOG.dll to current project.
step3: At cs file header, add "using DBLOG;"
step4: Call DatabaseLogAnalyzer.ReadLog() for read logs.
string ConnectionString, StartTime, EndTime, TableName;
DatabaseLogAnalyzer dbla;
DatabaseLog[] logs;
//connection string: Please change below connection string for your environment.
ConnectionString = "server=[ServerName];database=[DatabaseName];uid=[LoginName];pwd=[Password];Connection Timeout=5;Integrated Security=false;";
//start time for analyze, format: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
StartTime = "2020-03-18 10:01:02";
//end time for analyze, format: yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
EndTime = "2020-03-18 10:02:02";
//table name: Need include schema name(like dbo.Table1), When blank means query all tables 's logs, you can change it for need.
TableName = "";
// Initializes a new instance of the DBLOG.DatabaseLogAnalyzer class.
dbla = new DatabaseLogAnalyzer(ConnectionString);
// read logs, return a DatabaseLog array, include below properties:LSN,TransactionID,BeginTime,EndTime,ObjectName,Operation,RedoSQL,UndoSQL.
logs = dbla.ReadLog(StartTime, EndTime, TableName); 