Eru
Eru
The open JavaFX SCADA
| Development | Master | Chat | License |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Resume
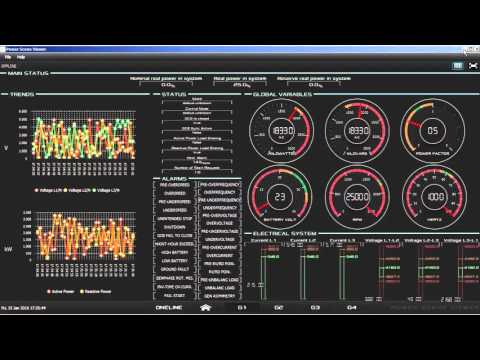
Eru allows easy monitoring of a process or machine operation by displaying a pictorial graphic that shows the operation of the process. It allows an operator to manipulate the process and system components in an easy intuitive manner.
There are 4 main components in Eru:
- Connections.
- Devices.
- Tags.
-
Displays.
Basically, in the normal workflow, you: 1) Create a "connection" to communicate with remote devices (Like PLC, Solar Panels, Engine controllers, Residence automation (Doors, Lights, Windows, etc) etc). 2) Create a "device" that uses that connection and organize addresses to read (E.g. in the windows device we want to read the current height of the window so we have to add an Address called height in the window device). 3) Create a "tag" to represent the actual value of the Address of the device. (Using the same example, we adjust the value obtained from the window to "meters" adding a factor and scale). 4) Create a "displayName" to see the current height of the window (tag) graphically.
Key Features
- Tag based
- Tags to read devices. You can scale the value using offset or factors, masks, and custom scripts.
- JavaFX based
- Use State of Art gauge creation techniques.
- Remote clients using http tunnels.
- Open source.
- Dark/Light using CSS.
- Embedded Modbus (Serial or TCP). You do not need to get additional Modbus handler... It is embedded in Eru.
- Save the historic preview as PDF.
- Full screen mode
- Cross platform
- Windows, Mac and Linux ready.
How To Use
To clone and run this application, you'll need Git and Java SE Development Kit 8 (which comes with JavaFX) installed on your computer. From your command line:
# Go to your workspace
cd ~/Workspace
# Create a folder called "eru" (Recommended)
mkdir eru
# Go there
cd eru/
# Clone this repository
git clone https://github.com/assemblits/eru.gitYou can use IntelliJ IDE to have the same experience of the developers:
1) Launch IJ. 2) Click import project. 3) Select the Gradle Build file in the eru workspace. 4) Let IJ do the magic.
Credits
This software uses code from several open source packages like:
- Java
- Groovy
- Spring
- Gradle
- Loombok
- Log4J
- Open Dolphin
- Medusa Project
- Jamod
- RXTX for Java. Courtesy of Mfizz, Inc.
Skills from:
Contributions from:
- Comelecinca Power Systems. Specially from Octavio Casado