Exploring Hierarchical Attention based Deep Neural Networks for Toxic Comments Classification
Introduction
Text classification is a task in NLP in which predefined categories are assigned to text documents. The two widely used approaches can be represented as follows:

One major difference in classical machine learning and deep learning approaches is that in the deep learning approach, feature extraction and classification is carried out together.
Proper feature representation is an important task in any Machine Learning task. In this case, we have text comments that are made of sentences and in return, sentences are made of words. A big challenge for NLP is to represent text in a proper format. We will be using Vector space models to represent the text corpus. The other inefficient method is the Standard Boolean method.
To represent the various features in the text corpus we use the GloVE Embedding vectors. GloVe is an unsupervised learning algorithm for obtaining vector representations for words. Training is performed on aggregated global word-word co-occurrence statistics from a corpus, and the resulting representations showcase interesting linear substructures of the word vector space.
We choose GloVE and not random embedding as in this embedding model, there are a few interesting properties:
-
Euclidean distance between expected similar words is minimized. This resembles the Nearest Neighbor method.
-
This nearest neighbor method to produce a single scalar quanitifying the relatedness of two words can be problematic as there may be other intricate relationships that exist across words. For example, man may be regarded as similar to woman in that both words describe human beings; on the other hand, the two words are often considered opposites since they highlight a primary axis along which humans differ from one another. A natural and simple candidate for an enlarged set of discriminative numbers is the vector difference between the two word vectors. GloVe is designed in order that such vector differences capture as much as possible the meaning specified by the juxtaposition of two words.
1. Data Visualization and Feature Analysis
Before we explore the Deep Learning models, we ensure that the dataset is understood well and that it is suitable for applying Deep Learning based methods. Tasks accomplished in this notebook:
- Visualizing categorization of data
- Visualizing categorization within toxic corpus
- Analysing the overlap across the various categories of toxicity
- Feature analysis
- Understanding the importance of certain features in different classes of toxicity
- Adversarial Validation to ensure we can use Cross validation on our classification model.
2. Baseline LSTM Model with Data Augmentation
Recurrent Neural Networks and its derivatives is a well-researched topic in NLP. RNNs use internal memory to process input sequences. Humans understand each word based on our understanding of a set of previous words because our thoughts are persistence. Traditional Neural networks cant handle this issue, but RNNs allow loops in them, allowing information to exist. The following chain like structure enables RNNs to initimately understand sequences and lists.

Long Term Dependencies: Sometimes, we need to look and understand only the very recent information to perform the present task, e.g. in doing the task of predicting the enxt word in a sentence, we might need a very limited context. However, there may be cases in which we need to have more context. As the gap between the most recent sequence entity and the context grows wider, RNNs are unable to learn to connect the information.

In order to handle such long term dependencies, we turn to LSTMs
LSTM
The key structural change in LSTMs is that they have 4 neural structures in the repeating unit rather than just the one in RNNs. The LSTM enables a cell state to run across the entire network. With the use of Gates, information is optimally let in and is enabled to affect the cell state.

- Forget Gate: What information from the cell state is to be thrown away based on the previous layer activation and current input
- Input Gate: Decides which values might be updated using a candidate vector
- Output Gate: Decides what parts of the cell state we can output
Modifications to this LSTM structure can include:
- Peephole connections to introduce cell state in all gating operations
- Gated Recurrent Units: Combines forget and input gates as one and also merges cell state and hidden state.
To ensure that the model doesn't overfit too soon, we have used the technique of Data Augmentation wherein I enabled the TextBLOB translation for the ENglish dataset to be used as an augmentation to the data. In the notebook, we use Baseline LSTM Model and GloVE embeddings which lead us to the following results:
-
Augmented Dataset:
- Validation accuracy: 98.92%
- Training accuracy: 99.19%
-
Basic Dataset
- Validation accuracy: 98.22%
- Training accuracy: 98.62%

3. Hierarchical Attention Network Model
Straight Neural Network methods are effective but better representation can be achieved by including knowledge of document structure in the model architecture. This can be understood as:
- Not all parts of the document is relevant for understanding the content
- Finding relevant sections in a document involves modeling the interactions of the words and not just the presence in isolation
THe hierarchical attention that can be used here is:
- Words from sentences
- Sentences from comments.
In the following example we can see that the third sentence delivers a strong meaning and the words amazing and superb provide the most defining sentiment of the sentence.

The Hierarchical Attention Network is made of several parts:
- A word sequence encoder : Get annotations of the words by summarising information from both directions
- A word-level attention layer: Not all words contribute equally to a sentence's meaning and this layer extracts such words that are important to the meaning of the sentence and aggregate the representation of those informative words
- A sentence encoder: Bidirectional LSTM to encode sentences
- A sentence-level attention layer: Rewards sentences that are clues to correctly classify a document

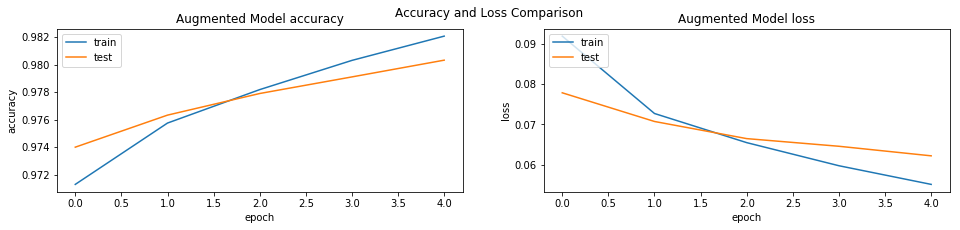
We use the augmented dataset and achieve the following results:
- Augmented Dataset:
- Validation accuracy: 98.03%
- Training accuracy: 98.21%
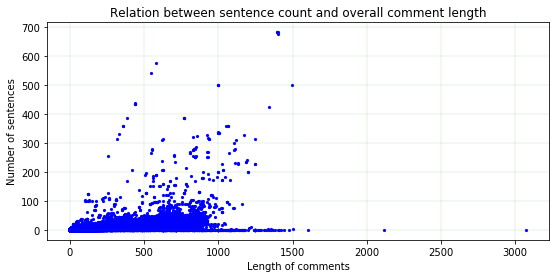
As one can see, the accuracy of the HAN based method is slightly worse than the traditional baseline LSTM model. This can be explained from the following figure. One can notice that obviously, not a lot of comments have a large number of sentences, but even if the comments have a large number of sentences, the length of these comments is just not large enough to derive proper weightings from the attention layer. My understanding is that due to such a limitation in the dataset, one gets such a result from the HAN model.