SVGDigitizer — Extract (x,y) Data Points from SVG files
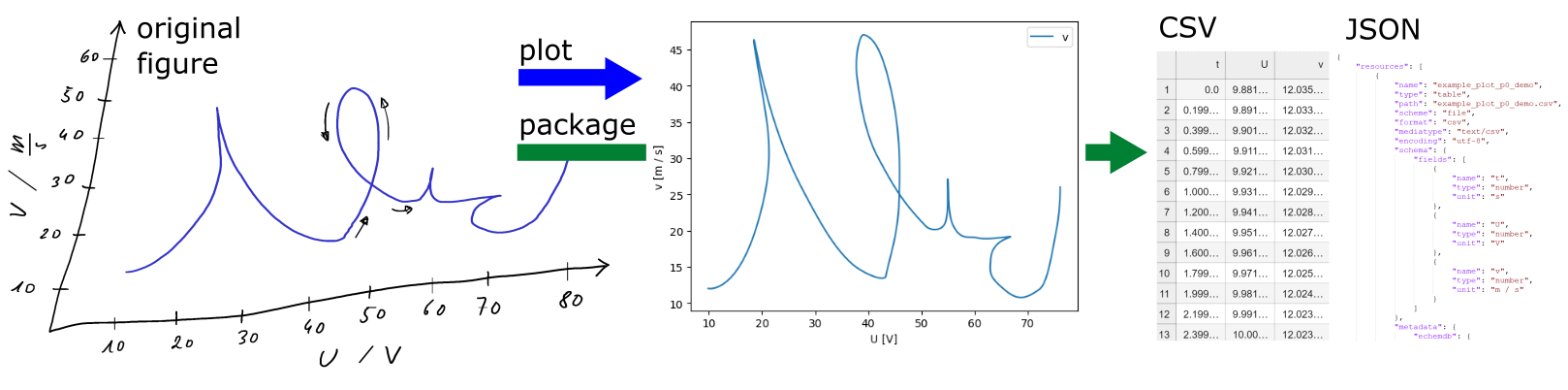
The svgdigitizer allows recovering data from a curve in a figure, plotted in a 2D coordinate system, which is usually found in scientific publications.
The data is accessible either with a command line interface or the API from a specifically prepared scaled vector graphics (SVG) file. The data can be stored as a frictionless datapackage (CSV and JSON) which can be used with unitpackage to access the plots metadata or create a database of such datapackages.
Features
The svgdigitizer has additional features compared to other plot digitizers, such as:
- supports multiple y (x) values per x (y) value
- usage of splines allows for very precise retracing of distinct features
- splines can be digitized with specific sampling intervals
- supports plots with distorted/skewed axis
- extracts units from axis labels
- reconstruct time series with a given scan rate
- supports scale bars
- supports scaling factors
- extracts metadata associated with the plot in the SVG
- saves data as frictionless datapackage (CSV + JSON) allowing for FAIR data usage
- inclusion of metadata in the datapackage
- Python API to interact with the retraced data
Refer to our documentation for more details.
Installation
This package is available on PiPY and can be installed with pip:
pip install svgdigitizerThe package is also available on conda-forge and can be installed with conda
conda install -c conda-forge svgdigitizeror mamba
mamba install -c conda-forge svgdigitizerPlease consult our documentation for more detailed installation instructions.
Command Line Interface
The CLI allows creating SVG files from PDFs and allows digitizing the processed SVG files. Certain plot types have specific commands to recover different kinds of metadata. Refer to the CLI documentation for more information.
$ svgdigitizer
Usage: svgdigitizer [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
The svgdigitizer suite.
Options:
--help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
cv Digitize a cylic voltammogram and create a frictionless datapackage.
digitize Digitize a 2D plot.
figure Digitize a figure with units on the axis and create a frictionless datapackage.
paginate Render PDF pages as individual SVG files with linked PNG images.
plot Display a plot of the data traced in an SVG.
$ svgdigitizer figure doc/files/others/looping_scan_rate.svg --sampling-interval 0.01API
You can also use the svgdigitizer package directly from Python, to access properties of the SVG or additional properties associated with the figure.
>>> from svgdigitizer.svg import SVG
>>> from svgdigitizer.svgplot import SVGPlot
>>> from svgdigitizer.svgfigure import SVGFigure
>>> figure = SVGFigure(SVGPlot(SVG(open('doc/files/others/looping.svg', 'rb')), sampling_interval=0.01))Examples:
figure.df provides a dataframe of the digitized curve.
figure.plot() shows a plot of the digitized curve.
figure.metadadata provides a dict with metadata of the original plot, such as original units of the axis.
The svgdigitizer can be enhanced with submodules, which are designed to digitize specific plot types, such as the submodule electrochemistry.cv.
This submodule allows digitizing cyclic voltammograms commonly found in the field of electrochemistry.
>>> from svgdigitizer.svg import SVG
>>> from svgdigitizer.svgplot import SVGPlot
>>> from svgdigitizer.electrochemistry.cv import CV
>>> cv_svg = 'doc/files/mustermann_2021_svgdigitizer_1/mustermann_2021_svgdigitizer_1_f2a_blue.svg'
>>> cv = CV(SVGPlot(SVG(open(cv_svg, 'rb')), sampling_interval=0.01))The resulting cv object has the same properties as the figure object above.