ez-Wheel SWD® ROS2 Controllers
Overview
This package has been tested on ROS2 Foxy, Galactic, Humble and Iron. It contains ROS2 nodes to control motors powered by the ez-Wheel Safety Wheel Drive (SWD®) technology.
 |
 |
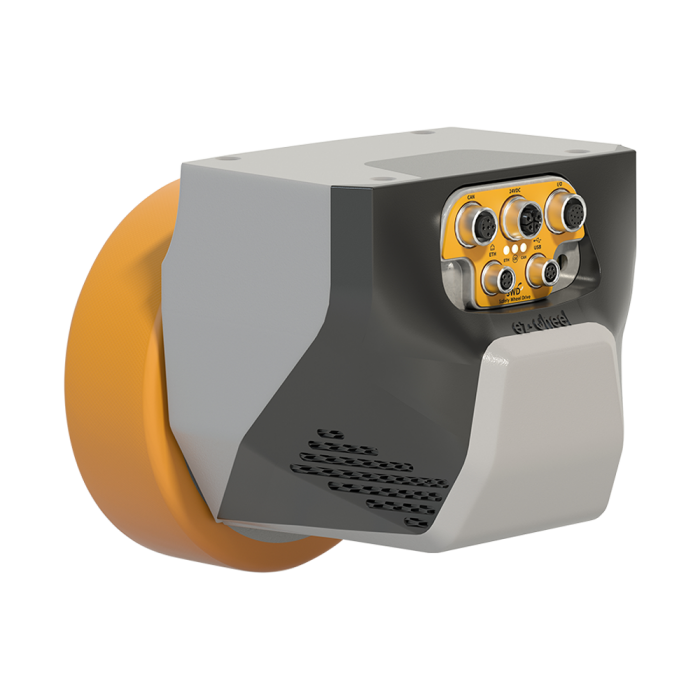 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
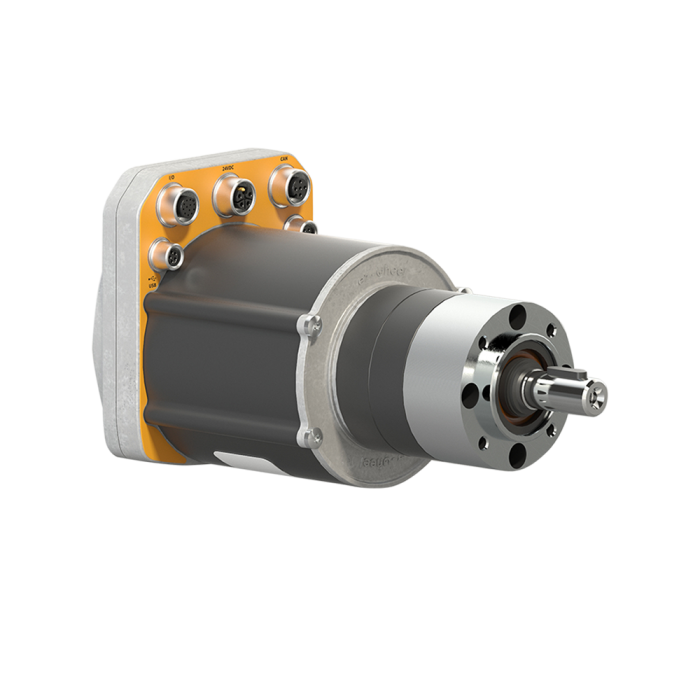
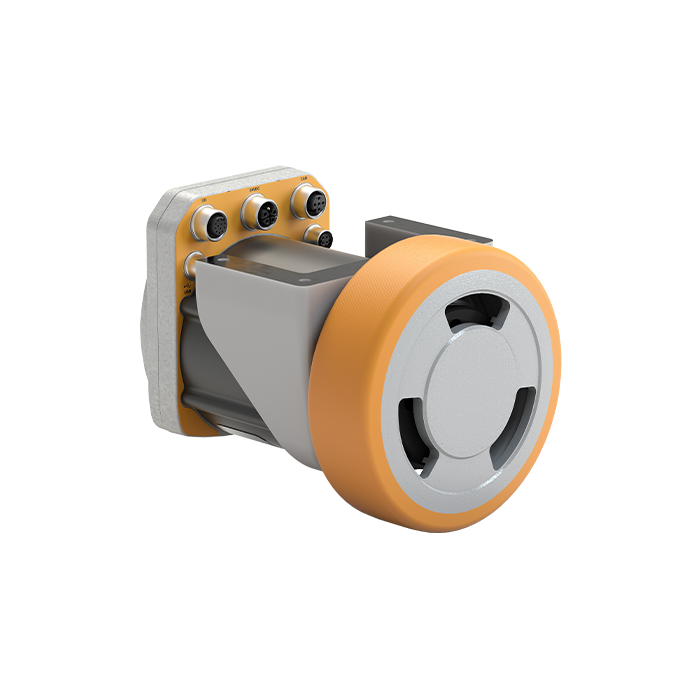
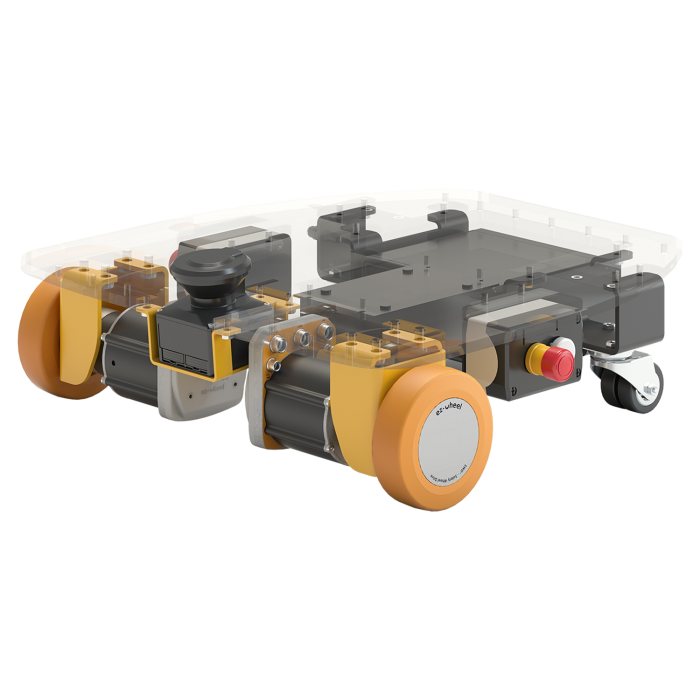
| SWD® Core | SWD® 125 | SWD® 150 | SWD® StarterKit |
| Safety gear motor | Medium duty Safety Wheel Drive | Heavy duty Safety Wheel Drive | Development kit for AGV and AMR |
Users should regularly inform themselves about updates of this driver (Activating GitHub notifications with "Watch", 'All activity' button on top of this page).
Prerequisites
- Two SWD® based wheels
SWD firmware(>= 1.0.1)- Ubuntu :
- 20.04 (Focal Fossa) and ROS2 (Foxy or Galactic)
- 22.04 (Jammy Jellyfish) and ROS2 (Humble or Iron)
swd-services(>= 2.0.0)
Pre-built debian package
It is available for the following platforms:
- ARM 64-bits, i.e. arm64 debian packages
- AMD 64-bits, i.e. amd64 debian packages, for x86 machines
Installation
METHOD 1: Ubuntu package manager
In order to install swd_ros2_controllers with apt, you need to add ez-Wheel repository to your Apt sources configuration file as sudo in: /etc/apt/sources.list. Type the following command:
echo "deb http://packages.ez-wheel.com:8081/ubuntu/ $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.listThen, download and add the GPG key. Type the following command:
sudo bash -c "wget -qO - http://packages.ez-wheel.com:8081/archive.key | gpg --dearmor > /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/ez-wheel-keyring.gpg"Now, you should be able to install ez-Wheel's packages using Advanced Packaging Tool (apt):
sudo apt update && sudo apt install swd-services ros-${ROS_DISTRO}-swd-ros2-controllersMETHOD 2: Compiling from source
To compile the package, make sure you added ez-Wheel repository to your Apt sources configuration file as sudo in: /etc/apt/sources.list, as specified above in METHOD 1.
So that you can install required swd-services, by typing:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt install swd-servicesIn the following instructions, replace <rosdistro> with the name of your ROS2 distro (e.g., galactic).
source /opt/ros/<rosdistro>/setup.bash
mkdir -p ~/ros2_ws/src/
cd ~/ros2_ws/src/
git clone https://github.com/ezWheelSAS/swd_ros2_controllers.git
cd ..
colcon build
source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bashUsage
A- On the SWD® Starter Kit
The package comes with a preconfigured launchfile which can be started using the ros2 launch command:
swd_diff_drive_controller_launch.py: is a launchfile for the SWD® Starter Kit which has a differential kinematic. To use it, run the following command:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/opt/ezw/usr/lib
ros2 launch swd_ros2_controllers swd_diff_drive_controller.launch.pyYou can always use the node with the ros2 run command, the minimum required parameters are:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/opt/ezw/usr/lib
ros2 run swd_ros2_controllers swd_diff_drive_controller --ros-args -p baseline_m:=0.485The corresponding D-Bus services have to be started in order to use the nodes.
Example with the SWD® Starter Kit:
- The service
ezw-dbus-user-session.serviceis equivalent to running:
dbus-launch > /tmp/SYSTEMCTL_dbus.id ## [OPTIONAL]- Prepare the environment
export $(cat /tmp/SYSTEMCTL_dbus.id) ## [OPTIONAL]
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/opt/ezw/usr/lib- The service
ezw-swd-left.serviceis equivalent to running:
/opt/ezw/usr/bin/ezw-smc-service /opt/ezw/usr/etc/ezw-smc-core/swd_left_config.ini- The service
ezw-swd-right.serviceis equivalent to running:
/opt/ezw/usr/bin/ezw-smc-service /opt/ezw/usr/etc/ezw-smc-core/swd_right_config.iniExample of configuration files for SWD® Starter Kit:
swd_left_config.ini
# SMC Drive service config file
contextId = 12
nodeId = 4
coreNodeId = 6
coreNodeIsMaster = true # Slave:false Master:true
canDevice = can0
dbusNamespace = swd_left
HWConfigurationEntry = SWD_CORE
HWConfigurationFile = /opt/ezw/data/configuration.json
CANOpenEDSFile = /opt/ezw/usr/etc/ezw-canopen-dico/swd_core.edsswd_right_config.ini
# SMC Drive service config file
contextId = 12
nodeId = 5
coreNodeId = 7
coreNodeIsMaster = true # Slave:false Master:true
canDevice = can0
dbusNamespace = swd_right
HWConfigurationEntry = SWD_CORE
HWConfigurationFile = /opt/ezw/data/configuration.json
CANOpenEDSFile = /opt/ezw/usr/etc/ezw-canopen-dico/swd_core.edsconfiguration.json
[
{
"name": "SWD_CORE",
"nbStepRevolutionElec": 6,
"nbPolePair": 5,
"reduction": 14.0,
"diameter": 125.0
}
]B- On your own IPC
As the minimal SWD® Starter Kit config files do not exist on your IPC, you can install them manually as specified above or install them via a third package.
In this case, make sure you added ez-Wheel repository to your Apt sources configuration file as sudo in: /etc/apt/sources.list, as specified above in METHOD 1.
First, create swd_sk user with sudo rights, with swd_sk as default password:
sudo addgroup swd_sk
sudo useradd -m -s /bin/bash -g swd_sk swd_sk
sudo bash -c 'echo swd_sk:swd_sk | chpasswd'
sudo usermod -aG sudo swd_skThen log in with user swd_sk:
su - swd_skThen install swd-system-config-2wheels using:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt install swd-system-config-2wheelsThis package will configure your system to start at boot up four new services (with user swd_sk account):
ezw-stack.service: initialize can0ezw-dbus-user-session: initialize D-Bus sessionezw-swd-left.service: start left D-Bus serviceezw-swd-right.service: start right D-Bus service
and add the following config files as specified above :
/opt/ezw/data/configuration.json/opt/ezw/usr/etc/ezw-smc-core/swd_left_config.ini/opt/ezw/usr/etc/ezw-smc-core/swd_right_config.ini
This packages comes also with the commissioning scripts used for each wheels :
/opt/ezw/commissioning/
You can modify them and apply the commissioning using:
cd /opt/ezw/commissioning/
./swd_left_4_commissioning.py
./swd_right_5_commissioning.pyThen refer to "Usage on a SWD® Starter Kit" for more information.
About ROS2 swd_diff_drive_controller node
This controller manages two ez-Wheel SWD® wheels as a differential kinetic robot.
Parameters
baseline_mof typedouble: The distance (in meters) between the 2 wheels (mandatory).left_swd_config_fileof typestring: Path to the.iniconfiguration file of the left motor (default /opt/ezw/usr/etc/ezw-smc-core/swd_left_config.ini) (read only).right_swd_config_fileof typestring: Path to the.iniconfiguration file of the right motor (default /opt/ezw/usr/etc/ezw-smc-core/swd_right_config.ini) (read only).pub_freq_hzof typeint: Frequency (in Hz) of published odometry and TFs (default20).watchdog_receive_msof typeint: The delay (in milliseconds) before stopping the wheels if no command is received (default500) (read only).base_frameof typestring: Frame ID for the moving platform, used in odometry and TFs (default'base_link') (see REP-150 for more info).odom_frameof typestring: Frame ID for theodomfixed frame used in odometry and TFs (default'odom') (see REP-150 for more info).publish_odomof typebool: Publish odometry messages (defaulttrue).publish_tfof typebool: Publish TF messages (defaulttrue).publish_safety_functionsof typebool: Publishswd_ros2_controllers::msg::SafetyFunctionsmessage (defaulttrue).motor_max_speed_rpmof typeint: Maximum allowed motor speed (in RPM), if a target speed of one of the motor is above this limit, the controller will limit the speed of the two motor without changing the robot's trajectory (default1050).motor_max_safety_limited_speed_1_rpmof typeint: Motor safety limited speed 1 (SLS_1) (in RPM), if an SLS_1 signal is detected (from a security LiDAR for example), the motor will be limited internally to the configured SLS_1 limit. The ROS2 controller uses this value to limit the target speed sent to the motor in the SLS_1 case (default560).motor_max_safety_limited_speed_2_rpmof typeint: Motor safety limited speed 2 (SLS_2) (in RPM), if an SLS_2 signal is detected (from a security LiDAR for example), the motor will be limited internally to the configured SLS_2 limit. The ROS2 controller uses this value to limit the target speed sent to the motor in the SLS_2 case (default680).have_backward_slsof typebool: Specifies if the robot have a backward SLS signal, coming for example from a back-facing security LiDAR. If an SLS signal is available for backward movements, set this totrueto take it into account. Otherwise, set the parameter tofalse, this will limit all backward movements to the selectedmotor_max_safety_limited_speed_1_rpm(defaultfalse).left_encoder_relative_errorof typedouble: Relative error for left wheel encoder, used to calculate variances and propagate them to calculate the uncertainties in the odometry message. Each encoder acquisitionDIFF_LEFT_ENCODERis modeled as: *`DIFF_LEFT_ENCODER +/- abs(left_encoder_relative_error DIFF_LEFT_ENCODER)** (default0.2` corresponding to 20% of error).right_encoder_relative_errorof typedouble: Relative error for right wheel encoder, used to calculate variances and propagate them to calculate the uncertainties in the odometry message. Each encoder acquisitionDIFF_RIGHT_ENCODERis modeled as: *`DIFF_RIGHT_ENCODER +/- abs(right_encoder_relative_error DIFF_RIGHT_ENCODER)** (default0.2` corresponding to 20% of error).
Subscribed Topics
/cmd_velof typegeometry_msgs/msg/Twist: Target linear and angular velocities./set_speedof typegeometry_msgs/msg/Point: Target speeds in rad/s for left (Point.x) and right (Point.y) wheels./soft_brakeof typestd_msgs/msg/Bool: Activate or release the soft brake, sendfalseto release the brake, ortrueto activate it.
Published Topics
/odomof typenav_msgs/msg/Odometry: Odometry message based on wheels encoders, containing the pose and velocity of the robot with their's associated uncertainties. Unless disabled by thepublish_tfparameter, TFs with the same information are also published./safetyof typeswd_ros2_controllers/msg/SafetyFunctions: Safety messages communicated by the wheels via CANOpen, the message includes information about Safe Torque Off (STO), Safety Limited Speed (SLS_1/SLS_2), Safe Direction Indication (forward/backward) (SDI+/-), and Safe Brake Control (SBC).
Custom message types
swd_ros2_controllers::msg::SafetyFunctions message
This message provides information about the state of the Safety functions.
The value is True if the safety function is enabled.
std_msgs/Header header
bool safe_torque_off # Safe Torque Off (STO)
bool safe_brake_control # Safe Brake Control (SBC)
bool safety_limited_speed_1 # Safety Limited Speed 1 (SLS_1)
bool safety_limited_speed_2 # Safety Limited Speed 2 (SLS_2)
bool safe_direction_indication_forward # Safe Direction Indication (positive)
bool safe_direction_indication_backward # Safe Direction Indication (negative)The main safe drive function is the STO whereby the immediately torque-off on the motor may be accompanied by an SBC command to close the brakes. The SLS functions cause the drive to decelerate (if required) and monitor whether the velocity is held within the defined limits. The functions SDIp and SDIn enable the motor movement only in the corresponding (positive or negative) direction.
Support
For any questions, open a GitHub issue.
About ez-Wheel®
ez-Wheel® is an innovative company founded in 2009 and located in Angoulême, France. ez-Wheel has developed the first industrial wheel drive, integrating motorisation, embedded electronics and batteries.
This revolutionary solution, which quickly turns any manually handled platform into an electrically assisted one. Our solutions have been adopted by hundreds of end-users to improve productivity and prevent work accidents caused by manual handling. Our products are used in a variety of applications, in fields of Automotive, Factory logistics, Warehouses, Food processing, Hospitals and Pharmaceutical industries.
SWD® products tackles industrial robotics applications, like Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs). It provides a unique solution for safety critical systems, with safety features related to the ISO 3691-4 standard.
ez-Wheel® has developed a unique know-how in embedded electronics, including safety critical systems, applied to battery powered electric traction.
Troubleshooting
Update swd-services
sudo apt update && sudo apt install swd-servicesCheck if other swd-packages can be upgraded:
sudo apt search swd-Error during commissioning
Before applying commissioning, stop swd_diff_drive_controller node.
Then, execute again python scripts in the commissionning directory:
./swd_"[...]"_commissioning.pyError with dbus session
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/ezw/usr/lib
export $(cat /tmp/SYS*.id)Then restart ezw-swd-left service and ezw-swd-right service.
Debug SWD with diagnostic tool
Use remote.py script installed with swd-services package in /opt/ezw/usr/sbin directory, with its dbusNamespace as argument, e.g.:
/opt/ezw/usr/sbin/remote.py smc_drive
/opt/ezw/usr/sbin/remote.py swd_left
/opt/ezw/usr/sbin/remote.py swd_rightCAN socket is not configured
sudo ip link set down can0
sudo ip link set can0 up type can bitrate 1000000 restart-ms 100
sudo ip link set can0 txqueuelen 1000