spring-rest-invoker
Spring invoker that binds remote JSON REST services to java interfaces similarily to how HttpInvokerProxyFactoryBean works. Invoking methods on those interfaces will make an HTTP request to the remote service and (de)serialize any objects to/from JSON. The concrete mapping between an interface and a remote service can be done programmatically or by annotating interfaces with Spring or JAX-RS annotations.
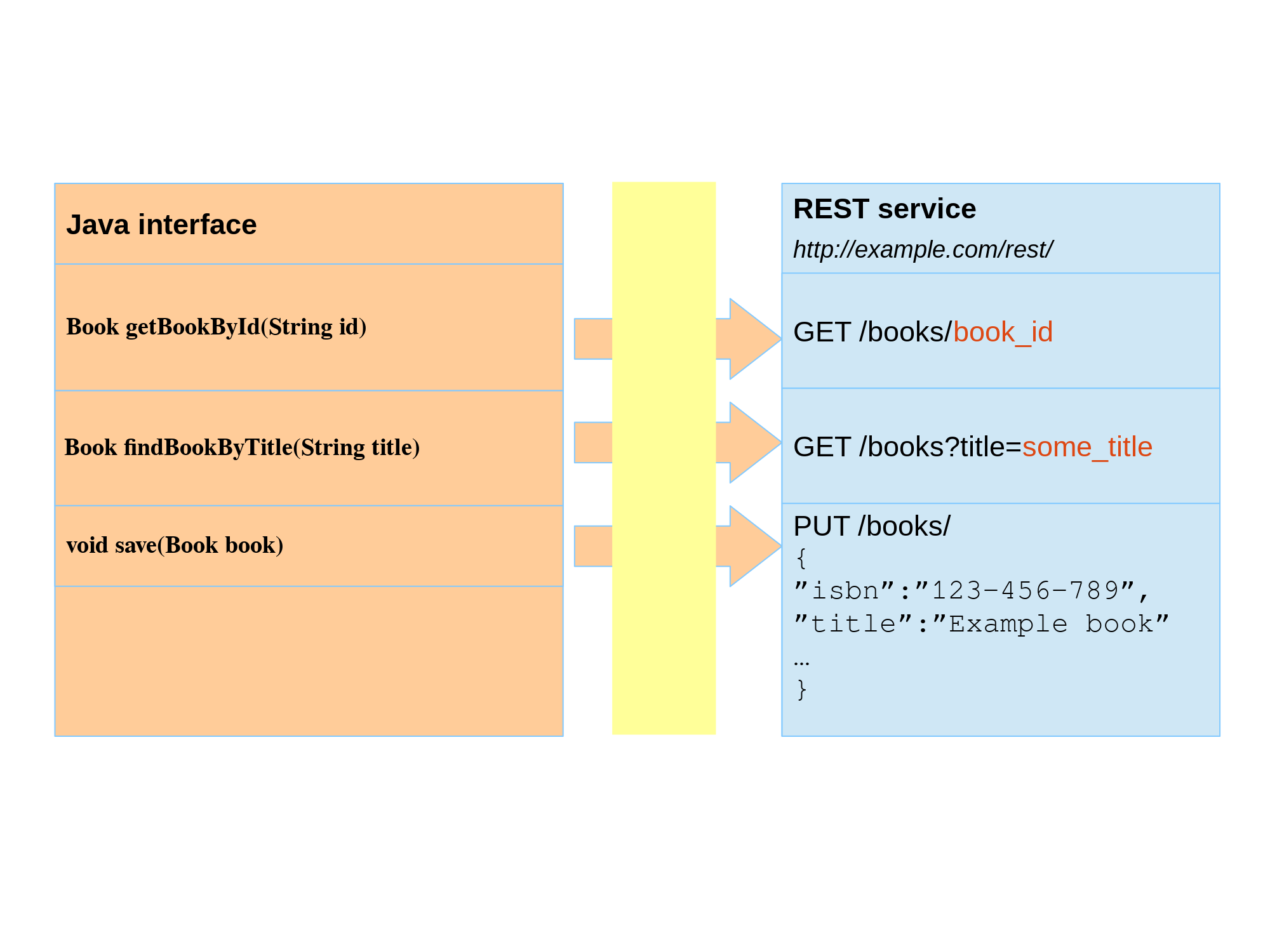
Features:
- Consume REST JSON services
- Declare a service interface and bind it to remote URLs with annotations (spring or jax-rs)
- Convert JSON to Java POJOs and vice versa
- Convert method arguments to GET parameters
- POST one or more objects
News
2021-06-10: Released 1.8 to maven central. Corrections in documentation, example for annotation-based configuration, supporting more Spring annotations (thanks Arturo Volpe), added MT test for opaque proxy factory (thanks Arturo Volpe), upgraded jackson dependencies, supporting Spring mapping path computation (thanks Serhii Teroshyn)
2018-06-22: Released 1.7 to maven central
2017-09-27: Released 1.6. #26 CglibProxyFactory now really creating opaque proxies; refactored ProxyFactory API.
2017-09-20: Released 1.5. #20 Backported to Java 6, #21 Separate integration tests, #22 HTTP method headers for JaxRs
2017-08-04: Released 1.4. Handling parametrised return types (credits to Valentin Ozanne)
2017-06-04: Released 1.3. Updated dependencies
2016-01-07: Released 1.2. Fixed order of parameters and attributes in JSON, updated Spring, Jackson
2014-08-17: edited 1.0.RC-SNAPSHOT to fix broken unit tests and rename proxy factories
2014-08-12: version 1.0.RC-SNAPSHOT adds support for opaque (cglib) proxies
2014-08-11: version 0.0.9-SNAPSHOT adds support for bean expressions in RequestMapping and Path annotations
2014-07-25: version 0.0.7-SNAPSHOT adds support for logging HTTP traffic
2014-07-12: version 0.0.6-SNAPSHOT is out with support for jax-rs annotations, arguments as HTTP headers, arguments as cookies
2014-05-25: version 0.0.5-SNAPSHOT is out with support for multipart form encoding
2014-04-04: version 0.0.3-SNAPSHOT is out with support for more HTTP methods such as PUT, DELETE etc.
Using
0. Getting
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ggeorgovassilis</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-rest-invoker</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>Building
git clone https://github.com/ggeorgovassilis/spring-rest-invoker
mvn clean install jxr:jxr pmd:pmd pmd:cpd surefire-report:report site
jax-rs support requires a further dependency with the annotations, ie.:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jboss.resteasy</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxrs-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.8.Final</version>
</dependency>1. Declare an interface, eg:
@RequestMapping("volumes")
public interface BookService {
@GetMapping
QueryResult findBooksByTitle(@RequestParam("q") String q);
@GetMapping("{id}")
Item findBookById(@PathVariable("id") String id);
@PostMapping
Long createBook(@RequestBody NewItem newItem);
}Note that the annotations are from spring's web package.
Or, with jax-rs annotations:
public interface BookServiceJaxRs extends BookService{
@Override
@GET
@Path("/volumes")
QueryResult findBooksByTitle(@QueryParam("q") String q);
@Override
@GET
@Path("/volumes/{id}")
Item findBookById(@PathParam("id") String id);
}2. Then map it to the remote REST URL you want to consume:
<bean id="BookService"
class="com.github.ggeorgovassilis.springjsonmapper.spring.SpringRestInvokerProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="baseUrl" value="https://www.googleapis.com/books/v1" />
<property name="remoteServiceInterfaceClass" value="com.github.ggeorgovassilis.springjsonmapper.services.spring.BookServiceSpring"/>
</bean>with jax-rs
<bean id="BookService"
class="com.github.ggeorgovassilis.springjsonmapper.jaxrs.JaxRsInvokerProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="baseUrl" value="https://www.googleapis.com/books/v1" />
<property name="remoteServiceInterfaceClass" value="com.github.ggeorgovassilis.springjsonmapper.services.jaxrs.BookServiceJaxRs"/>
</bean>3. Use it
...
@Autowired
RemoteBookService bookService;
...
QueryResult results = bookService.findBooksByTitle("Alice in Wonderland");
4. Examples
POSTing an object:
public interface BankService {
@PostMapping(value = "verify")
Boolean checkAccount(@RequestBody Account account);
}or the jax-rs way:
public interface BankService {
@POST
@Path("/verify")
Boolean checkAccount(@BeanParam Account account);
}POSTing multiple objects (object names are passed through parameters @RequestParam):
public interface BankService {
@PostMapping(value="transfer")
Account transfer(
@RequestBody @RequestParam("fromAccount") Account fromAccount,
@RequestBody @RequestParam("actor") Customer actor,
@RequestBody @RequestParam("toAccount") Account toAccount,
@RequestBody @RequestParam("amount") int amount,
@RequestParam("sendConfirmationSms") boolean sendConfirmationSms);
}Or the respective jax-rs declaration:
public interface BankService {
@POST
@Path("/transfer")
Account transfer(@BeanParam @QueryParam("fromAccount") Account fromAccount, @BeanParam @QueryParam("actor") Customer actor,
@BeanParam @QueryParam("toAccount") Account toAccount, @BeanParam @QueryParam("amount") int amount,
@QueryParam("sendConfirmationSms") boolean sendConfirmationSms);
}which will POST a JSON object similar to:
{
"fromAccount": {
"accountNumber": 1234,
"balance": 99,
"customer":{
"name":"joe doe"
}
},
"actor":{
"name":"joe doe"
},
"toAccount": {
"accountNumber": 7890,
"balance": 0,
"customer": {
"name":"jane doe"
}
},
"amount": 123
}Alternatively, if you prefer annotation-based configuration over XML:
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration{
@Bean
SpringRestInvokerProxyFactoryBean BankService() {
SpringRestInvokerProxyFactoryBean proxyFactory = new SpringRestInvokerProxyFactoryBean();
proxyFactory.setBaseUrl("http://localhost/bankservice");
proxyFactory.setRemoteServiceInterfaceClass(BankServiceSpring.class);
return proxyFactory;
}Supported Annotations
Spring
@RequestMapping // Specify the URL to bind to. Variable parts are written as {varname} and are replaced with the values of @PathParam. Property placeholders like ${property_name} can also be used which will be looked up in the application context.
@GetMapping // same as @RequestMapping(method = GET)
@PutMapping // same as @RequestMapping(method = PUT)
@PostMapping // same as @RequestMapping(method = POST)
@DeleteMapping // same as @RequestMapping(method = DELETE)
@PatchMapping // same as @RequestMapping(method = PATCH)@PathVariable // Replace parts of the @Path with the (string) value of this argument
@PathVariable // Replace parts of the @Path with the (string) value of this argument
@RequestParam // Pass argument value as URL parameter (or JSON field, see below)
@Header // Pass argument (string) value as HTTP header
@RequestBody // Pass argument as JSON in the request body. If a @QueryParam has been specified, then encode it with that JSON field name
@RequestPart // Pass argument as multipart form request
@CookieValue // Pass argument as cookieJAX-RS
@Path // Specify the URL to bind to. Variable parts are written as {varname} and are replaced with the values of @PathParam. Property placeholders like ${property_name} can also be used which will be looked up in the application context.
@GET, @POST etc // Specify the HTTP request method to use
@Produces // Value of the Accept HTTP header
@Consumes // Value of the Content-Type HTTP header
@PathParam // Replace parts of the @Path with the (string) value of this argument
@QueryParam // Pass argument value as URL parameter (or JSON field, see below)
@HeaderParam // Pass argument (string) value as HTTP header
@BeanParam // Pass argument as JSON in the request body. If a @QueryParam has been specified, then encode it with that JSON field name
@FormParam // Pass argument as multipart form request. Mandatory argument can be blank
@Headers // Non-standard annotation which adds HTTP headers to requestF.A.Q.
What does @RequestParam do?
Method arguments annotated with @RequestParam are, unless otherwise specified, taken as strings and passed as HTTP parameters, e.g.
public interface BookService {
@GetMapping(value="books")
Book findBook(@RequestParam("isbn") String isbn);
}
...
bookService.findBook("123");an invocation of findBook will result in an HTTP GET request to this url: /books?isbn=123
When there is also a @RequestBody, then the handling is different - look further down the F.A.Q.
What does @RequestBody do?
Used when sending JSON to a REST service via an HTTP POST request. Method arguments annotated with @RequestBody are serialized into JSON and sent to the remote service. If there is only a single method argument annotated with @RequestBody, then that argument is serialized and sent over. If multiple arguments are annotated, then each @RequestBody needs to be accompanied by a @RequestParam which specifies the field name of the object.
In an ideal world we wouldn't need @RequestParam because the invoker would, supposedly, be able to read method argument names and pick URL parameter names accordingly; in Java that's suprisingly hard to do since the reflection API does not expose method argument names.
For example:
public interface BookService {
@PostMapping(value = "books")
void saveBook(@RequestBody Book book);
}
...
bookService.saveBook(book);will result in this JSON being posted to /books:
{
"name":"Some Book Title",
"author":"John Doe",
"genres":["technology","educational"],
"availability":{
"available":true,
"itemsInStock":4
}
} Using multiple arguments:
public interface BookService {
@PostMapping(value="books")
void saveBook(@RequestBody @RequestParam("book") Book book, @RequestBody @RequestParam("availability") availability);
}
...
bookService.saveBook(book, availability);will result in this JSON being posted to /books:
{
"book":{
"name":"Some Book Title",
"author":"John Doe",
"genres":["technology","educational"]
},
"availability":{
"available":true,
"itemsInStock":4
}
} What does @PathVariable do?
Some REST services incorporate parameters in the URL path rather than URL parameters, i.e.: example.com/service/findBooks/isbn/1234 as opposed to ```example.com/service/findBooks?isbn=1234````
@PathVariable is specified together with a @RequestParam and indicates the the method argument is not to be sent as a URL parameter. Note that you need to specify a matching placeholder with @RequestMapping:
public interface BookService {
@GetMapping("volumes/{id}")
Item findBookById(@PathVariable("id") String id);
}or jax-rs:
public interface BookService {
@Path("/volumes/{id}")
Item findBookById(@PathParam("id") String id);
}The {id} notation in @RequestMapping must match the one specified in @PathVariable
How do I post a JSON object to a remote service?
See the section earlier in this document about posting. In short: if you want to post just a single object, then a JSON object is posted to the remote service where fields have the name of member variables (this applies recursively for objects within objects).
public interface BankService {
@PostMapping(value = "verify")
Boolean checkAccount(@RequestBody Account account);
}or jax-rs:
public interface BookService {
@POST
@Path("/verify")
Boolean checkAccount(@BeanParam Account account);
}Multiple objects can be posted through multiple method arguments, also including a @RequestParam mapping so that the invoker knows under which field names to place the generated JSON objects:
public interface BankService {
@PostMapping(value = "transfer")
Account transfer(@RequestBody @RequestParam("fromAccount") Account fromAccount, @RequestBody @RequestParam("actor") Customer actor,
@RequestBody @RequestParam("toAccount") Account toAccount, @RequestBody @RequestParam("amount") int amount,
@RequestParam("sendConfirmationSms") boolean sendConfirmationSms);
}or jax-rs:
public interface BankService {
@POST
@Path("/transfer")
Account transfer(@BeanParam @QueryParam("fromAccount") Account fromAccount, @BeanParam @QueryParam("actor") Customer actor,
@BeanParam @QueryParam("toAccount") Account toAccount, @BeanParam @QueryParam("amount") int amount,
@QueryParam("sendConfirmationSms") boolean sendConfirmationSms);
}The remote service requires messages to be submitted as multipart form posts...
... for example Twitter https://dev.twitter.com/docs/api/1.1/post/statuses/update_with_media
Use @RequestPart instead of @RequestBody :
@PostMapping(value = "join-accounts")
Account joinAccounts(@RequestPart @RequestParam("account1") Account account1, @RequestPart @RequestParam("account2") Account account2);or the jax-rs way:
@POST
@Path("/join-accounts")
Account joinAccounts(@FormParam("") @QueryParam("account1") Account account1, @FormParam("") @QueryParam("account2") Account account2);Dependencies?
The maven pom will pull in dependencies required for the spring mapper's basic features to work. pom.xml declares more dependencies for advanced features as optional which can be pulled into the project by re-declaring them in the project's pom.xml.
JAX-RS support:
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.ws.rs</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.ws.rs-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
</dependency>If you use the logging interceptor then you'll also need some logging implementation for commons logging, ie. log4j:
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>Opaque proxies require cglib:
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
</dependency>Is the spring-rest-invoker a JAX-RS implementation?
Yes, since 0.0.6-SNAPSHOT. See the introduction.
How do I log the entire HTTP communication with the remote service?
You need to provide your own RestTemplate, have a look at this http://stackoverflow.com/a/22620168/3194801 which enables logging. If you want to use the logging interceptor that comes with this library, then have a look at the configuration example in the unit tests: https://github.com/ggeorgovassilis/spring-rest-invoker/blob/master/spring-rest-invoker/src/test/resources/test-context-googlebooks-spring.xml
Also enable logging in your log4j configuration:
log4j.logger.com.github.ggeorgovassilis.springjsonmapper.Request=DEBUG
log4j.logger.com.github.ggeorgovassilis.springjsonmapper.Response=DEBUGI need to modify the outgoing HTTP request / I need to supply a client certificate / I need to validate a server certificate
Again the solution is to provide your own RestTemplate, see the previous section.
I need to parametrise the mapping URL depending on the execution environment
Just use property place holders in the URL, i.e.:
@PostMapping(value = "${serverIp}/join-accounts")
Account joinAccounts(@RequestPart @RequestParam("account1") Account account1, @RequestPart @RequestParam("account2") Account account2);Whenever the joinAccounts method is invoked, the serverIp property will be looked up in the application context and replaced by its current value. Note that this mechanism works only for values of the @RequestMapping and @Path annotations.
Where can I find more examples?
Have a look at mapping declarations for the unit test: https://github.com/ggeorgovassilis/spring-rest-invoker/tree/master/src/test/java/com/github/ggeorgovassilis/springjsonmapper/services
I need proxies to extend a specific class
Since 1.0.RC it's possible to generate opaque proxies with cglib instead of the default dynamic proxies. Opaque proxies extend a concrete class and implement the REST mapping interface. In order to do so, specify a ProxyFactory instance, e.g.:
<bean id="BookService_OpaqueProxy" class="com.github.ggeorgovassilis.springjsonmapper.spring.SpringRestInvokerProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="baseUrl" value="https://www.googleapis.com/books/v1" />
<property name="remoteServiceInterfaceClass"
value="com.github.ggeorgovassilis.springjsonmapper.services.spring.BookServiceSpring" />
<property name="proxyFactory">
<bean
class="com.github.ggeorgovassilis.springjsonmapper.utils.CglibProxyFactory">
<property name="proxyTargetClass"
value="com.github.ggeorgovassilis.springjsonmapper.support.BaseProxyClass" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>I specified some (other) annotations on the mapping interface but they are missing on the service proxy
Symptoms: you specified more annotations on the mapping interface like @Transactional or @Valid but they don't seem to work on the remote service proxies. The code that is looking for annotations doesn't know how to deal with dynamic proxies properly. Either fix that or use opaque proxies; see "I need proxies to extend a specific class".
Are there any alternatives?
Have a look at RESTEasy http://resteasy.jboss.org/
How do I build from source code?
git clone https://github.com/ggeorgovassilis/spring-rest-invoker
mvn clean install jxr:jxr pmd:pmd pmd:cpd surefire-report:report site
or without the fancies:
mvn clean install -DskipTests=true