Language Modeling is Compression
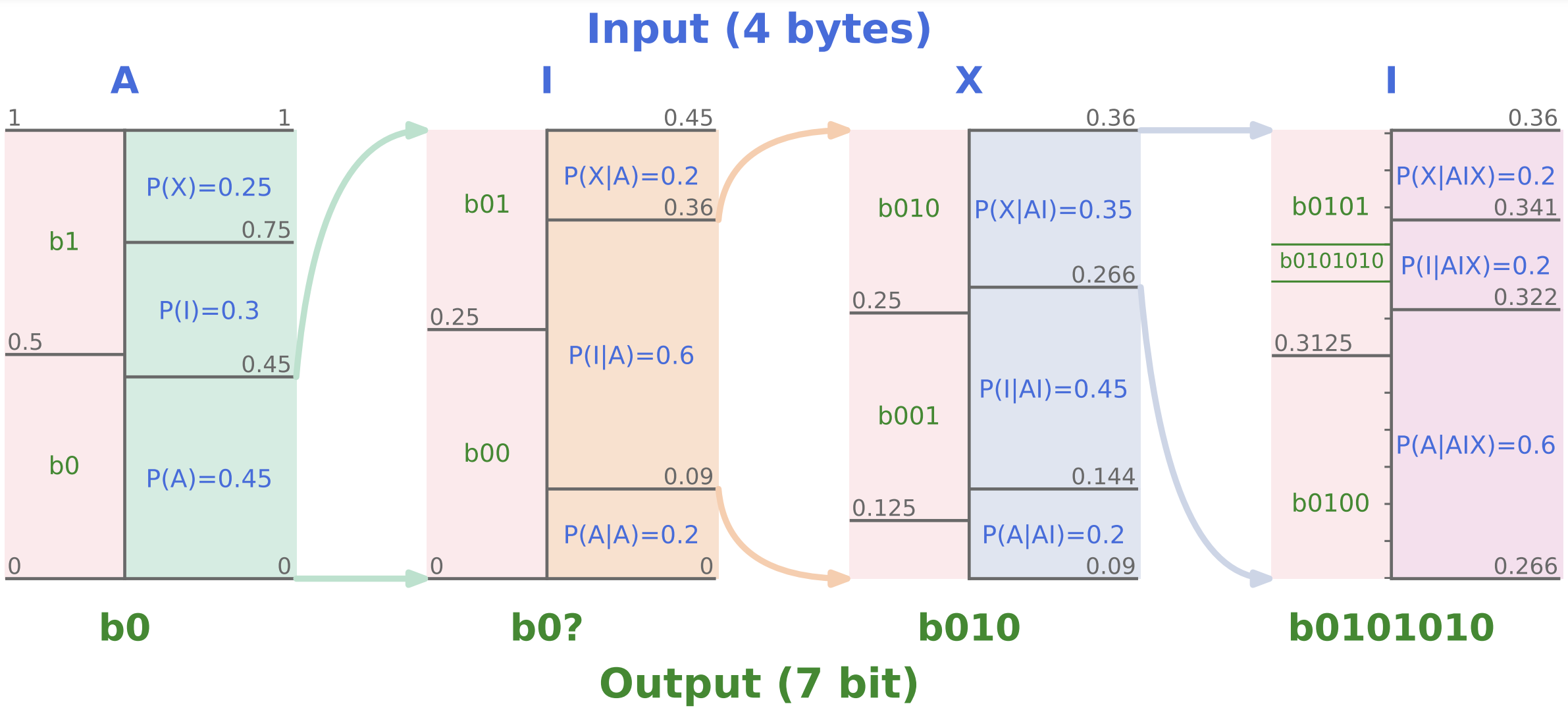
This repository provides an implementation of our ICLR 2024 paper Language Modeling is Compression.
It has long been established that predictive models can be transformed into lossless compressors and vice versa. Incidentally, in recent years, the machine learning community has focused on training increasingly large and powerful self-supervised (language) models. Since these large language models exhibit impressive predictive capabilities, they are well-positioned to be strong compressors. In this work, we advocate for viewing the prediction problem through the lens of compression and evaluate the compression capabilities of large (foundation) models. We show that large language models are powerful general-purpose predictors and that the compression viewpoint provides novel insights into scaling laws, tokenization, and in-context learning. For example, Chinchilla 70B, while trained primarily on text, compresses ImageNet patches to 43.4% and LibriSpeech samples to 16.4% of their raw size, beating domain-specific compressors like PNG (58.5%) or FLAC (30.3%), respectively. Finally, we show that the prediction-compression equivalence allows us to use any compressor (like gzip) to build a conditional generative model.
It contains all the code necessary to reproduce the experiments, including the training of small Transformer language models on enwik8 to retrieve the neural networks' weights. Chinchilla's weights are not provided.
Content
.
├── compressors
| ├── compressor.py - Defines a protocol for compressors.
| ├── flac.py - Lossless audio compressor FLAC (Coalson, 2008).
| ├── language_model.py - Interface for language models, and compression function using arithmetic coding.
| └── png.py - Lossless image compressor PNG (Boutell, 1997).
├── arithmetic_coder.py - Arithmetic Encoder and Decoder (Pasco, 1977).
├── compress.py - Script to compress data.
├── constants.py - Various constants like sequence length, alphabet size etc.
├── data_loaders.py - Defines all our datasets.
├── README.md
├── requirements.txt - Dependencies.
├── train.py - Script to train a language model on Enwik8.
├── transformer.py - Code for the Transformer model (Vaswani, 2017).
└── utils.py - Utilities like converting a sequence of bits to bytes.compressors contains all our compressors, either classical (like PNG or FLAC), or combining a predictor and an arithmetic coder (language models).
They all follow the protocol Compressor, defined in compressors/compressor.py.
Installation
pip install -r requirements.txt will install all required dependencies.
This is best done inside a conda environment.
To that end, install Anaconda.
Then, run the following commands:
# Clone the source code into a local directory:
git clone https://github.com/google-deepmind/language_modeling_is_compression.git
cd language_modeling_is_compression
# Create and activate the conda environment:
conda create --name lmic
conda activate lmic
# Install `pip` and use it to install all the dependencies:
conda install pip
pip install -r requirements.txtIf you have a GPU available (highly recommended for fast training), then you can install JAX with CUDA support.
pip install --upgrade "jax[cuda12_pip]" -f https://storage.googleapis.com/jax-releases/jax_cuda_releases.htmlNote that the jax version must correspond to the existing CUDA installation you wish to use (CUDA 12 in the example above). Please see the JAX documentation for more details.
Usage
Before running any code, make sure to activate the conda environment and set the PYTHONPATH:
conda activate lmic
export PYTHONPATH=$(pwd)/..If you want to compress with a language model, you need to train it first using:
python train.pyTo evaluate the compression rates, use:
python compress.pyCiting This Work
@inproceedings{deletang2024language,
author = {Gr{\'{e}}goire Del{\'{e}}tang and
Anian Ruoss and
Paul{-}Ambroise Duquenne and
Elliot Catt and
Tim Genewein and
Christopher Mattern and
Jordi Grau{-}Moya and
Li Kevin Wenliang and
Matthew Aitchison and
Laurent Orseau and
Marcus Hutter and
Joel Veness},
title = {Language Modeling Is Compression},
booktitle = {{ICLR}},
year = {2024}
}License and Disclaimer
Copyright 2023 DeepMind Technologies Limited
All software is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (Apache 2.0); you may not use this file except in compliance with the Apache 2.0 license. You may obtain a copy of the Apache 2.0 license at: https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
All other materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY). You may obtain a copy of the CC-BY license at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, all software and materials distributed here under the Apache 2.0 or CC-BY licenses are distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the licenses for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under those licenses.
This is not an official Google product.