This is no longer being maintained
Please see Azure Databricks for the latest instructions on using Apache Spark with Power BI
spark-power-bi
A library for pushing data from Spark, SparkSQL, or Spark Streaming to Power BI.
Requirements
This library is supported on Apache Spark 1.4 and 1.5. The versions of the library match to the Spark version. So v1.4.0_0.0.7 is for Apache Spark 1.4 and v1.5.0_0.0.7 is for Apache Spark 1.5.
Power BI API
Additional details regarding the Power BI API are available in the developer center. Authentication is handled via OAuth2 with your Azure AD credentials specified via Spark properties. More details on registering an app and authenticating are available in the Power BI dev center. When pushing rows to Power BI the library will create the target dataset with table if necessary. The current Power BI service is limited to 10,000 rows per call so the library handles batching internally. The service also limits to no more than 5 concurrent calls at a time when adding rows. This is handled by the library using coalesce and can be tuned by with the spark.powerbi.max_partitions property.
Scaladoc
Scaladoc is available here
Configuration
A few of the key properties are related to OAuth2. These depend on your application's registration in Azure AD.
spark.powerbi.username
spark.powerbi.password
spark.powerbi.clientidRather than using your personal AD credentials for publishing data, you may want to create a service account instead. Then you can logon to Power BI using that account and share the data sets and dashboards with other users in your organization. Unfortunately, there's currently no other way of authenticating to Power BI. Hopefully in the future there'll be an organization-level API token that can publish shared data sets, without having to use an actual AD account. You can also use a Power BI group when publishing data.
Setting Up Azure Active Directory
You'll need to create an application within your Azure AD in order to have a client id to publish data sets.
- Using the Azure management portal, open up your directory and add a new Application (under the Apps tab)
- Select "Add an application my organization is developing"
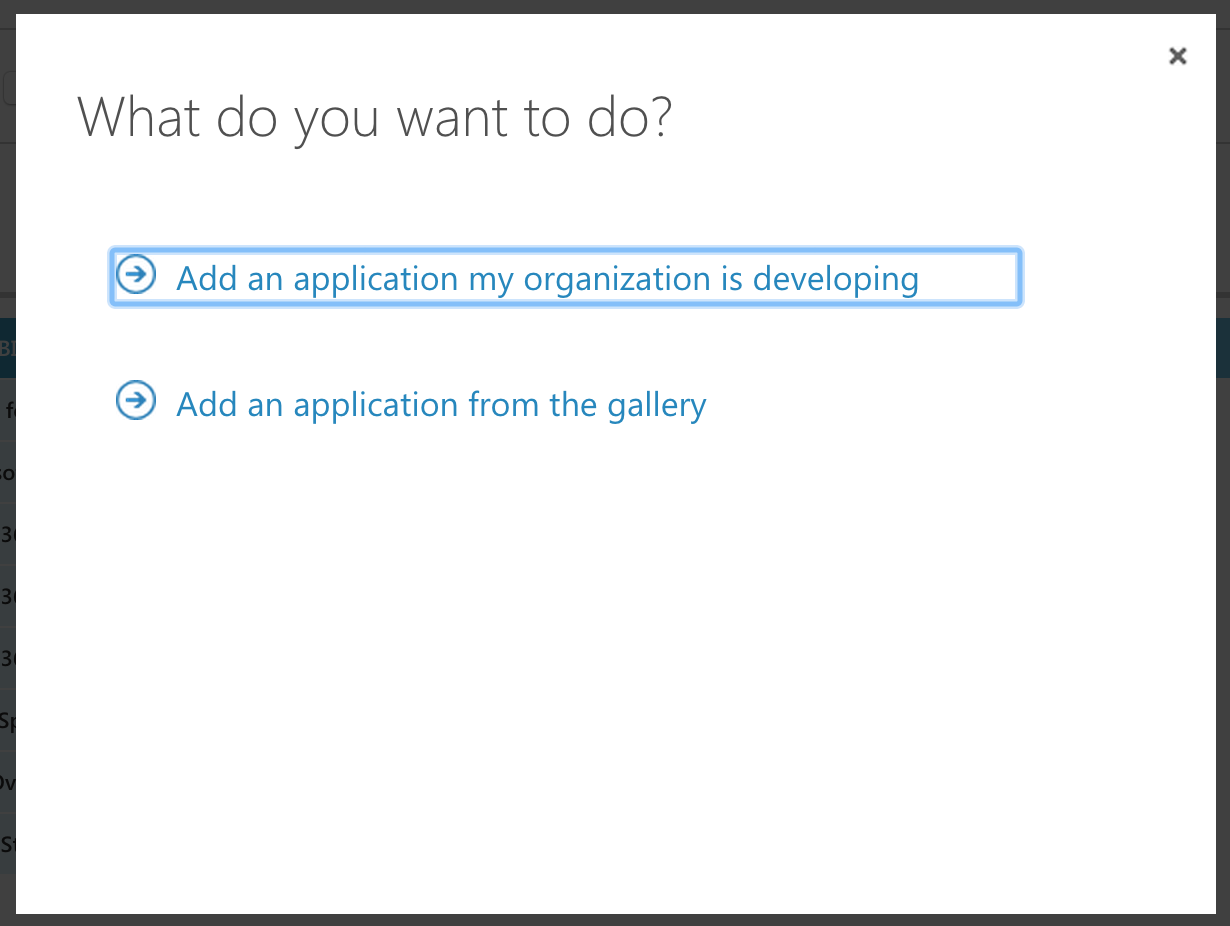
- Enter any name you want and select "Native Client Application"
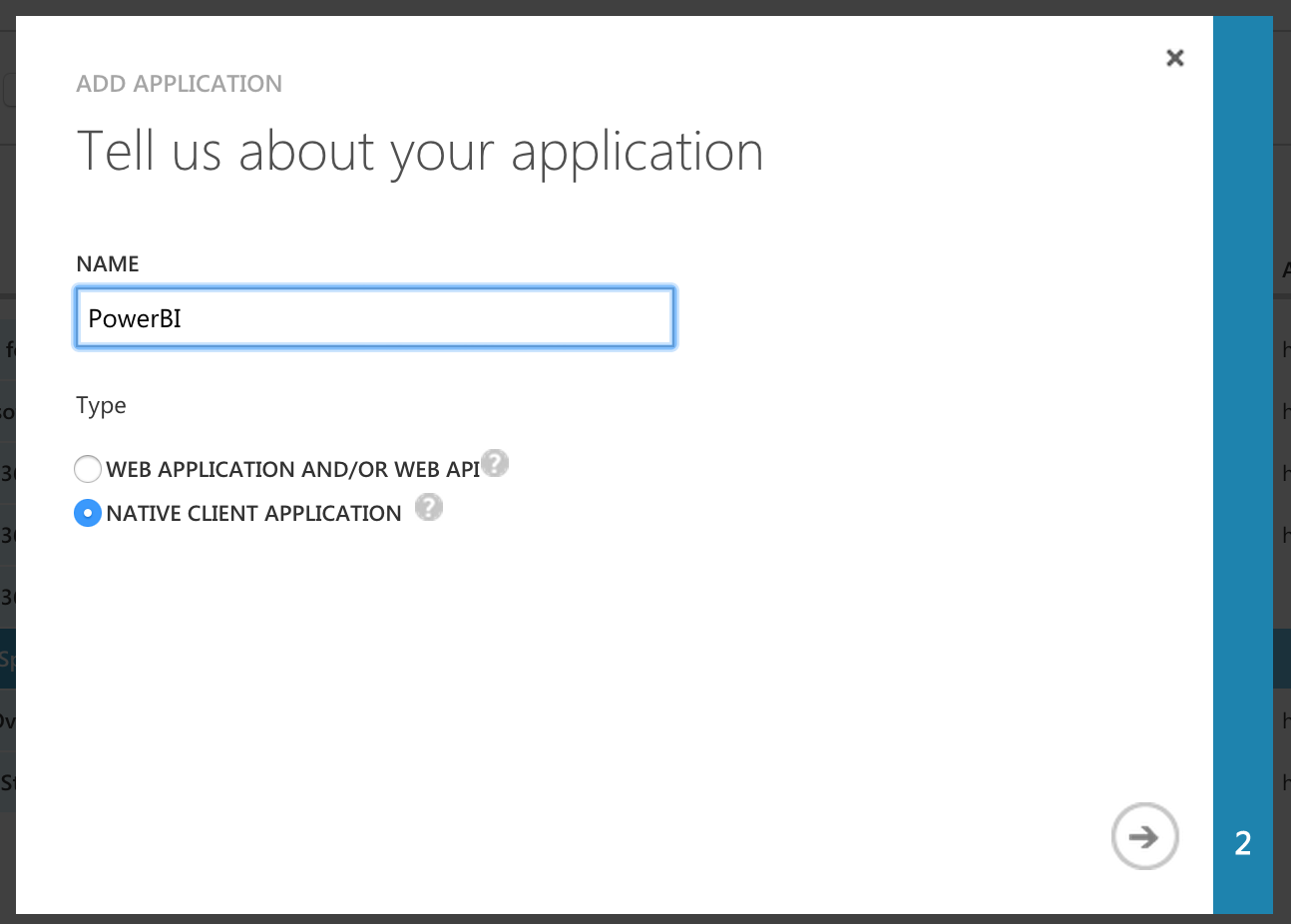
- Enter a redirect URI, this can be anything since it won't be used
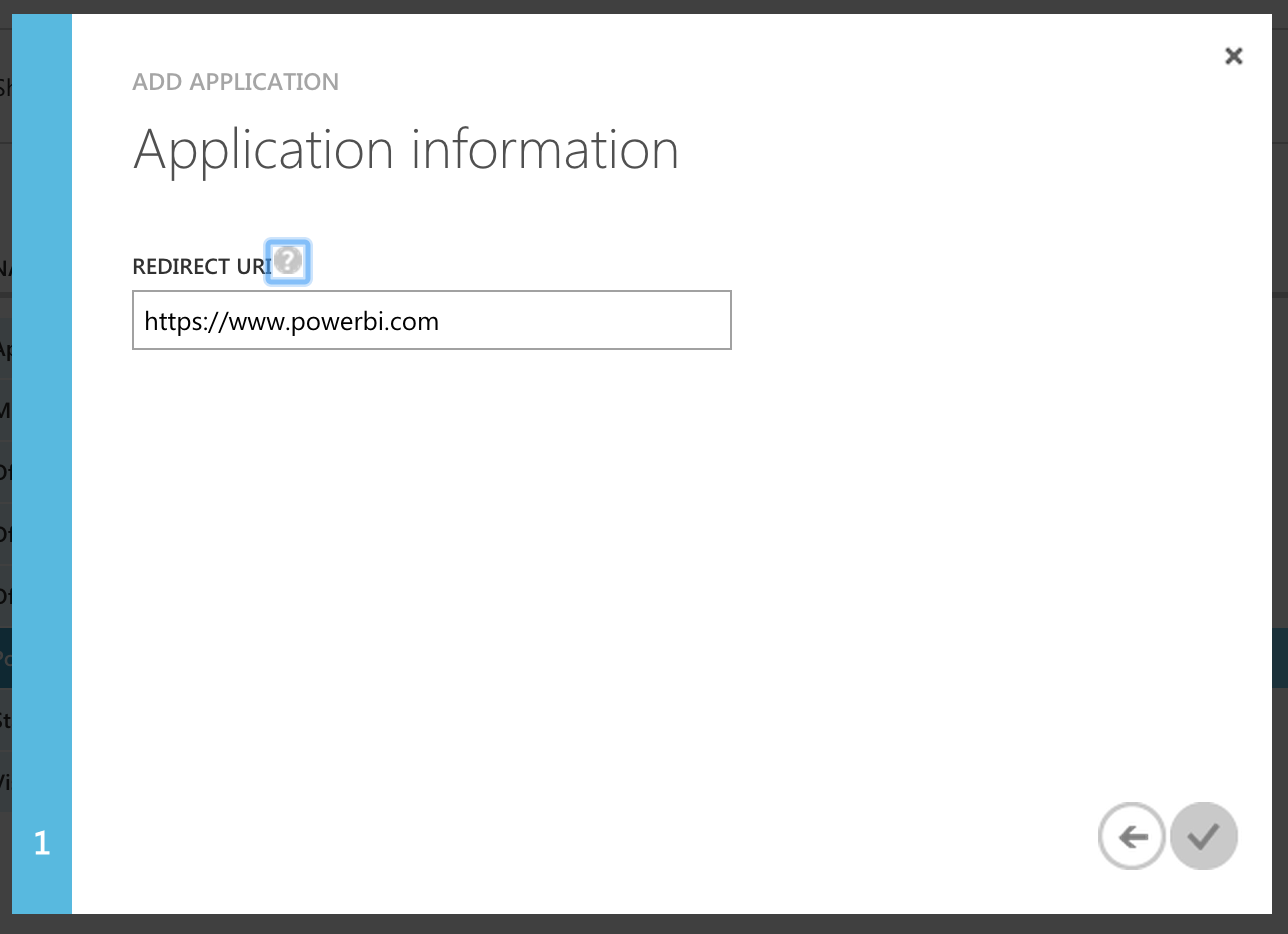
- Once the app has been added you need to grant permissions, click "Add application"
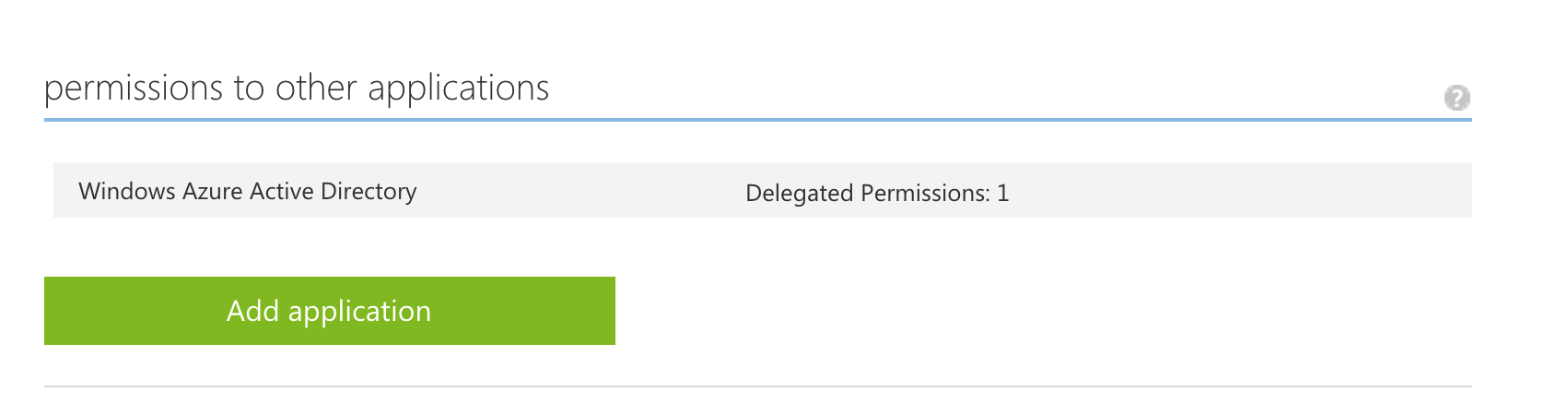
- Select the "Power BI Service"

- Add all 3 of the delegated permissions
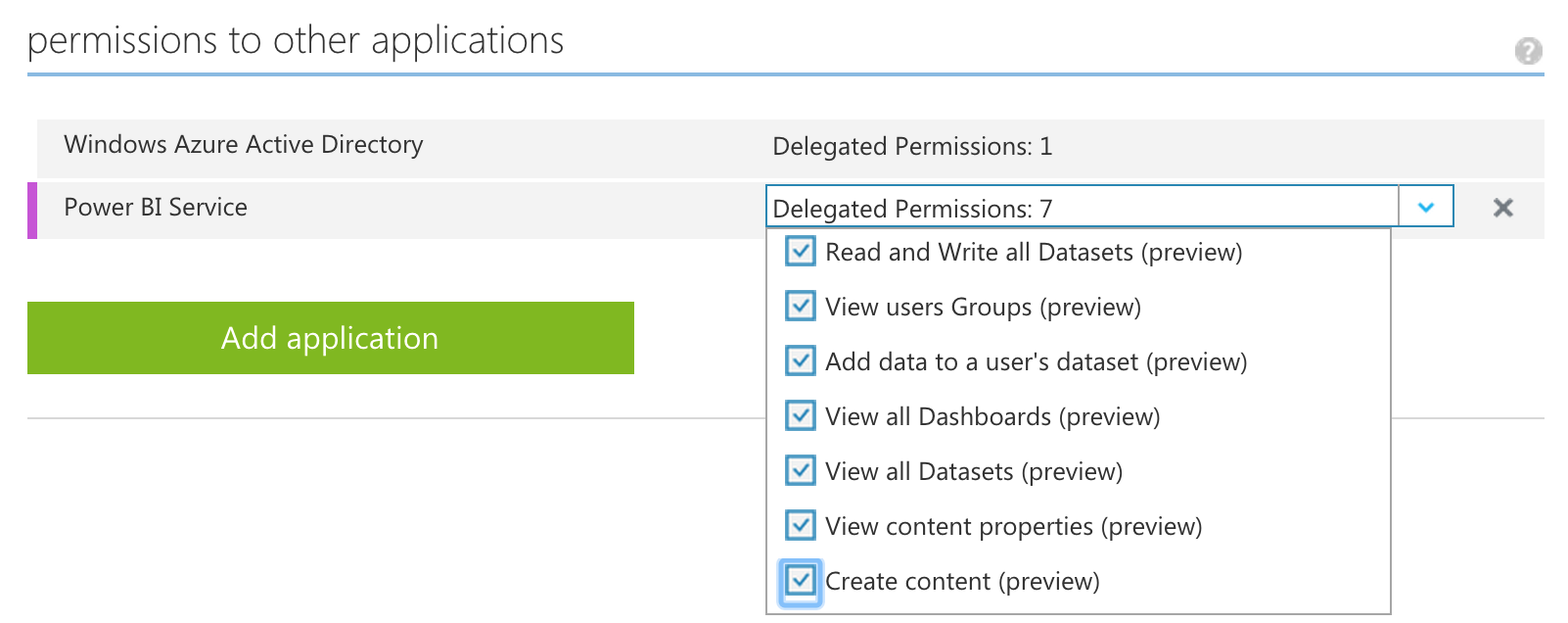
- Save your changes and use the newly assigned client id for the
spark.powerbi.clientidproperty
Spark Core
import com.granturing.spark.powerbi._
case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
val input = sc.textFile("examples/src/main/resources/people.txt")
val people = input.map(_.split(",")).map(l => Person(l(0), l(1).trim.toInt))
people.saveToPowerBI("Test", "People")SparkSQL
import com.granturing.spark.powerbi._
import org.apache.spark.sql._
val sqlCtx = new SQLContext(sc)
val people = sqlCtx.jsonFile("examples/src/main/resources/people.json")
people.write.format("com.granturing.spark.powerbi").options(Map("dataset" -> "Test", "table" -> "People")).saveSpark Streaming
val sc = new SparkContext(new SparkConf())
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc, Seconds(5))
val filters = args
val input = TwitterUtils.createStream(ssc, None, filters)
val tweets = input.map(t => Tweet(t.getId, t.getCreatedAt, t.getText, t.getUser.getScreenName))
val hashTags = input.flatMap(t => t.getHashtagEntities.map(h => HashTag(t.getId, h.getText, t.getUser.getScreenName)))
tweets.saveToPowerBI(dataset, "Tweets")
hashTags.saveToPowerBI(dataset, "HashTags")
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()Referencing As A Dependency
You can also easily reference dependencies using the --packages argument:
spark-shell --package com.granturing:spark-power-bi_2.10:1.5.0_0.0.7Building From Source
The library uses SBT and can be built by running sbt package.