gout
gout 是go写的http 客户端,为提高工作效率而开发
构架

feature
- 支持设置 GET/PUT/DELETE/PATH/HEAD/OPTIONS
- 支持设置请求 http header(可传 struct,map,array,slice 等类型)
- 支持设置 URL query(可传 struct,map,array,slice,string 等类型)
- 支持设置 json 编码到请求 body 里面(可传struct, map, string, []byte 等类型)
- 支持设置 xml 编码到请求 body 里面(可传struct, string, []byte 等类型)
- 支持设置 yaml 编码到请求 body 里面(可传struct, map, string, []byte 等类型)
- 支持设置 protobuf 编码到请求 body里面(可传struct)
- 支持设置 form-data(可传 struct, map, array, slice 等类型)
- 支持设置 x-www-form-urlencoded(可传 struct,map,array,slice 等类型)
- 支持设置 io.Reader,uint/uint8/uint16...int/int8...string...[]byte...float32,float64 至请求 body 里面
- 支持解析响应body里面的json,xml,yaml至结构体里(BindJSON/BindXML/BindYAML)
- 支持解析响应body的内容至io.Writer, uint/uint8...int/int8...string...[]byte...float32,float64
- 支持解析响应header至结构体里
- 支持接口性能benchmark,可控制压测一定次数还是时间,可控制压测频率
- 支持retry-backoff,可以指定重试条件
- 支持发送裸http数据包
- 支持导出curl命令
- 传入自定义*http.Client
- 支持请求中间件(https://github.com/antlabs/gout-middleware)
- 支持响应中间件ResponseUse
- 支持设置chunked数据格式发送
- 支持body, header的数据校验
- 支持通过build tag自由选择不同的json序列化方式(可选jsoniter,go_json,sonic等)
- 等等更多
演示
内容
-
- GET POST PUT DELETE PATH HEAD OPTIONS
- GET POST PUT DELETE PATH HEAD OPTIONS template
- Query Parameters
- http header *Do not convert http headers
- Set request header *Parsing the response header
- get all header
- data valid
- responseUse
- http body
- body
- json
- yaml
- xml
- form-data
- x-www-form-urlencoded
- callback
- Set request timeout
- proxy
- socks5
- cookie
- basic auth
- context
- Cancel a sending request
- unix socket
- http2 doc
- debug mode
- Turn on debug mode
- Turn off color highlighting in debug mode
- benchmark
- retry backoff
- import
- export
- Incoming custom * http.Client
- Using chunked data format
- NewWithOpt
- NewWithOpt proxy
- Global configuration
Installation
go get github.com/guonaihong/goutexample
examples 目录下面的例子,都是可以直接跑的。如果觉得运行例子还是不明白用法,可以把你迷惑的地方写出来,然后提issue
运行命令如下
cd _example
# GOPROXY 是打开go module代理,可以更快下载模块
# 第一次运行需要加GOPROXY下载模块,模块已安装的直接 go run 01-color-json.go 即可
env GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn go run 01-color-json.gobuild tag
Gout默认使用语言内置的encoding/json包。但是如果你想使用其他的json包,可以通过build tag来修改。
go build -tags=jsoniter .go build -tags=go_json .go build -tags="sonic avx" .quick start
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"time"
)
// 用于解析 服务端 返回的http body
type RspBody struct {
ErrMsg string `json:"errmsg"`
ErrCode int `json:"errcode"`
Data string `json:"data"`
}
// 用于解析 服务端 返回的http header
type RspHeader struct {
Sid string `header:"sid"`
Time int `header:"time"`
}
func main() {
rsp := RspBody{}
header := RspHeader{}
//code := 0
err := gout.
// POST请求
POST("127.0.0.1:8080").
// 打开debug模式
Debug(true).
// 设置查询字符串
SetQuery(gout.H{"page": 10, "size": 10}).
// 设置http header
SetHeader(gout.H{"X-IP": "127.0.0.1", "sid": fmt.Sprintf("%x", time.Now().UnixNano())}).
// SetJSON设置http body为json
// 同类函数有SetBody, SetYAML, SetXML, SetForm, SetWWWForm
SetJSON(gout.H{"text": "gout"}).
// BindJSON解析返回的body内容
// 同类函数有BindBody, BindYAML, BindXML
BindJSON(&rsp).
// 解析返回的http header
BindHeader(&header).
// http code
// Code(&code).
// 结束函数
Do()
// 判断错误
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("send fail:%s\n", err)
}
}
/*
> POST /?page=10&size=10 HTTP/1.1
> Sid: 15d9b742ef32c130
> X-Ip: 127.0.0.1
> Content-Type: application/json
>
{
"text": "gout"
}
*/API examples
GET POST PUT DELETE PATH HEAD OPTIONS
package main
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
url := "https://github.com"
// 发送GET方法
gout.GET(url).Do()
// 发送POST方法
gout.POST(url).Do()
// 发送PUT方法
gout.PUT(url).Do()
// 发送DELETE方法
gout.DELETE(url).Do()
// 发送PATH方法
gout.PATCH(url).Do()
// 发送HEAD方法
gout.HEAD(url).Do()
// 发送OPTIONS
gout.OPTIONS(url).Do()
}
GET POST PUT DELETE PATH HEAD OPTIONS template
package main
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
type testURLTemplateCase struct {
Host string
}
func main() {
url := "https://{{.Host}}"
// 发送GET方法
gout.GET(url, testURLTemplateCase{Host:"www.qq.com"}).Do()
// 发送POST方法
gout.POST(url, testURLTemplateCase{Host:"www.github.com"}).Do()
// 发送PUT方法
gout.PUT(url, testURLTemplateCase{Host:"www.baidu.com"}).Do()
// 发送DELETE方法
gout.DELETE(url, testURLTemplateCase{Host:"www.google.com"}).Do()
// 发送PATH方法
gout.PATCH(url, testURLTemplateCase{Host:"www.google.com"}).Do()
// 发送HEAD方法
gout.HEAD(url, testURLTemplateCase{Host:"www.google.com"}).Do()
// 发送OPTIONS
gout.OPTIONS(url, testURLTemplateCase{Host:"www.google.com"}).Do()
}
Query Parameters
SetQuery
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"time"
)
func main() {
err := gout.
//设置GET请求和url,:8080/test.query是127.0.0.1:8080/test.query的简写
GET(":8080/test.query").
//打开debug模式
Debug(true).
//设置查询字符串
SetQuery(gout.H{
"q1": "v1",
"q2": 2,
"q3": float32(3.14),
"q4": 4.56,
"q5": time.Now().Unix(),
"q6": time.Now().UnixNano(),
"q7": time.Now().Format("2006-01-02")}).
//结束函数
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%s\n", err)
return
}
}
/*
> GET /test.query?q1=v1&q2=2&q3=3.14&q4=4.56&q5=1574081600&q6=1574081600258009213&q7=2019-11-18 HTTP/1.1
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Length: 0
*/
SetQuery支持的更多数据类型
package main
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
code := 0
err := gout.
//发送GET请求 :8080/testquery是127.0.0.1:8080/testquery简写
GET(":8080/testquery").
// 设置查询字符串
SetQuery( /*看下面支持的情况*/ ).
//解析http code,如不关心服务端返回状态吗,不设置该函数即可
Code(&code).
Do()
if err != nil {
}
}
/*
SetQuery支持的类型有
* string
* map[string]interface{},可以使用gout.H别名
* struct
* array, slice(长度必须是偶数)
*/
// 1.string
SetQuery("check_in=2019-06-18&check_out=2018-06-18")
// 2.gout.H 或者 map[string]interface{}
SetQuery(gout.H{
"check_in":"2019-06-18",
"check_out":"2019-06-18",
})
// 3.struct
type testQuery struct {
CheckIn string `query:checkin`
CheckOut string `query:checkout`
}
SetQuery(&testQuery{CheckIn:2019-06-18, CheckOut:2019-06-18})
// 4.array or slice
// ?active=enable&action=drop
SetQuery([]string{"active", "enable", "action", "drop"})`http header
Do not convert http headers
与SetHeader API唯一的区别就是不修改header名. 大部分情况用SetHeader,如果有不修改header的需求再使用SetHeaderRaw。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"time"
)
func main() {
err := gout.
//设置GET请求和url,:8080/test.header是127.0.0.1:8080/test.header的简写
GET(":8080/test.header").
//设置debug模式
Debug(true).
//设置请求http header
SetHeaderRaw(gout.H{
"h1": "v1",
"h2": 2,
"h3": float32(3.14),
"h4": 4.56,
"h5": time.Now().Unix(),
"h6": time.Now().UnixNano(),
"h7": time.Now().Format("2006-01-02")}).
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%s\n", err)
return
}
}
/*
> GET /test.header HTTP/1.1
> h2: 2
> h3: 3.14
> h4: 4.56
> h5: 1574081686
> h6: 1574081686471347098
> h7: 2019-11-18
> h1: v1
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Length: 0
*/Set request header
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"time"
)
func main() {
err := gout.
//设置GET请求和url,:8080/test.header是127.0.0.1:8080/test.header的简写
GET(":8080/test.header").
//设置debug模式
Debug(true).
//设置请求http header
SetHeader(gout.H{
"h1": "v1",
"h2": 2,
"h3": float32(3.14),
"h4": 4.56,
"h5": time.Now().Unix(),
"h6": time.Now().UnixNano(),
"h7": time.Now().Format("2006-01-02")}).
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%s\n", err)
return
}
}
/*
> GET /test.header HTTP/1.1
> H2: 2
> H3: 3.14
> H4: 4.56
> H5: 1574081686
> H6: 1574081686471347098
> H7: 2019-11-18
> H1: v1
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Length: 0
*/Parsing the response header
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"time"
)
// 和解析json类似,如要解析http header需设置header tag
type rspHeader struct {
Total int `header:"total"`
Sid string `header:"sid"`
Time time.Time `header:"time" time_format:"2006-01-02"`
}
func main() {
rsp := rspHeader{}
err := gout.
// :8080/test.header是 http://127.0.0.1:8080/test.header的简写
GET(":8080/test.header").
//打开debug模式
Debug(true).
//解析请求header至结构体中
BindHeader(&rsp).
//结束函数
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%s\n", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("rsp header:\n%#v \nTime:%s\n", rsp, rsp.Time)
}
/*
> GET /test.header HTTP/1.1
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Length: 0
< Sid: 1234
< Time: 2019-11-18
< Total: 2048
*/
SetHeader和BindHeader支持的更多类型
data valid
数据校验使用 https://github.com/go-playground/validator 完成功能, 更多语法可看该文档.
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
type testValid struct {
Val string `valid:"required"`
}
func main() {
tv := testValid{}
err := gout.
// 设置POST方法和url
POST(":8080/req/body").
//打开debug模式
Debug(true).
//解析json, 并且当需要的字段没有值时, 返回错误
BindJSON(&tv).
//结束函数
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%s\n", err)
return
}
}responseUse
response中间件,在Bind()之前执行。可以对response进行通用逻辑处理。
如果只需要闭包逻辑,则可以使用WithResponseMiddlerFunc,而不必创建一个结构体,下面的例子中对两种方法都进行了使用。
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"errors"
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout/middler"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"time"
)
// response拦截器修改示例
type demoResponseMiddler struct{}
func (d *demoResponseMiddler) ModifyResponse(response *http.Response) error {
// 修改responseBody。 因为返回值大概率会有 { code, data,msg} 等字段,希望进行统一处理
//这里想验证code. 如果不对就返回error。 对的话将 data中的内容写入body,这样后面BindJson的时候就可以直接处理业务了
all, err := ioutil.ReadAll(response.Body)
if err != nil {
return err
}
obj := make(map[string]interface{})
err = json.Unmarshal(all, &obj)
if err != nil {
return err
}
code := obj["code"]
msg := obj["msg"]
data := obj["data"]
// Go中json中的数字经过反序列化会成为float64类型
if float64(200) != code {
return errors.New(fmt.Sprintf("请求失败, code %d msg %s", code, msg))
} else {
byt, _ := json.Marshal(&data)
response.Body = ioutil.NopCloser(bytes.NewReader(byt))
return nil
}
}
func demoResponse() *demoResponseMiddler {
return &demoResponseMiddler{}
}
func main() {
go server() //等会起测试服务
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 500) //用时间做个等待同步
responseUseExample()
}
func responseUseExample() {
//成功请求
successRes := new(map[string]interface{})
err := gout.GET(":8080/success").ResponseUse(
demoResponse(),
// 注意这里使用了WithResponseMiddlerFunc
middler.WithResponseMiddlerFunc(func(response *http.Response) error {
// Do your magic
return nil
}),
).BindJSON(&successRes).Do()
log.Printf("success请求 --> 响应 %s \n err %s \n ", successRes, err)
//fail请求
failRes := new(map[string]interface{})
err = gout.GET(":8080/fail").ResponseUse(demoResponse()).BindJSON(&failRes).Do()
log.Printf("fail请求 --> 响应 %s \n err %s \n ", successRes, err)
}
type Result struct {
Code int `json:"code"`
Msg string `json:"msg"`
Data interface{} `json:"data"`
}
type Item struct {
Id string `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
}
func server() {
router := gin.New()
router.GET("/success", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, Result{200, "请求成功了", Item{"001", "张三"}})
})
router.GET("/fail", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, Result{500, "查询数据库出错了", nil})
})
router.Run()
}http body
body
Set the data to the http request body
// SetBody 设置string, []byte等类型数据到http body里面
// SetBody支持的更多数据类型可看下面
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
err := gout.
// 设置POST方法和url
POST(":8080/req/body").
//打开debug模式
Debug(true).
// 设置非结构化数据到http body里面
// 设置json需使用SetJSON
SetBody("send string").
//结束函数
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%s\n", err)
return
}
}
/*
> POST /req/body HTTP/1.1
>
send string
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
< Content-Length: 2
*/
get all header
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
header := make(http.Header)
err := gout.
// 设置POST方法和url
POST(":8080/req/body").
//打开debug模式
Debug(true).
// 获取所有的响应http header
BindHeader(&header).
//结束函数
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%s\n", err)
return
}
}Parse the response body into a variable
// BindBody bind body到string, []byte等类型变量里面
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
s := ""
err := gout.
// 设置GET 方法及url
GET("www.baidu.com").
// 绑定返回值
BindBody(&s).
// 结束函数
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%s\n", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("html size = %d\n", len(s))
}
支持的类型有
- io.Reader(SetBody 支持)
- io.Writer(BindBody 支持)
- int, int8, int16, int32, int64
- uint, uint8, uint16, uint32, uint64
- string
- []byte
- float32, float64
明确不支持的类型有
- struct
- array, slice
json
Serialize json to request body
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
err := gout.POST(":8080/colorjson").
//打开debug模式
Debug(true).
//设置json到请求body
SetJSON(
gout.H{
"str": "foo",
"num": 100,
"bool": false,
"null": nil,
"array": gout.A{"foo", "bar", "baz"},
"obj": gout.H{"a": 1, "b": 2},
},
).
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
}
/*
> POST /colorjson HTTP/1.1
> Content-Type: application/json
>
{
"array": [
"foo",
"bar",
"baz"
],
"bool": false,
"null": null,
"num": 100,
"obj": {
"a": 1,
"b": 2
},
"str": "foo"
}
*/
Parsed http response body in json format
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
type rsp struct {
ErrMsg string `json:"errmsg"`
ErrCode int `json:"errcode"`
}
func main() {
rsp := rsp{}
err := gout.
GET(":8080/colorjson").
//打开debug模式
Debug(true).
//绑定响应json数据到结构体
BindJSON(&rsp).
//结束函数
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
}
do not escape html characters
- SetJSONNotEscape 和SetJSON唯一的区别就是不转义HTML字符
err := gout.POST(ts.URL).
Debug(true).
SetJSONNotEscape(gout.H{"url": "http://www.com?a=b&c=d"}).
Do()
//> POST / HTTP/1.1
//> Content-Type: application/json
//>
//{
// "url": "http://www.com?a=b&c=d"
//}
//< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
//< Date: Sun, 18 Dec 2022 14:05:21 GMT
//< Content-Length: 0yaml
- SetYAML() 设置请求http body为yaml
- BindYAML() 解析响应http body里面的yaml到结构体里面
发送yaml到服务端,然后把服务端返回的yaml结果解析到结构体里面
type data struct {
Id int `yaml:"id"`
Data string `yaml:"data"`
}
var d1, d2 data
var httpCode int
err := gout.POST(":8080/test.yaml").SetYAML(&d1).BindYAML(&d2).Code(&httpCode).Do()
if err != nil || httpCode != 200{
fmt.Printf("send fail:%s\n", err)
}
xml
- SetXML() 设置请求http body为xml
- BindXML() 解析响应http body里面的xml到结构体里面
发送xml到服务端,然后把服务端返回的xml结果解析到结构体里面
type data struct {
Id int `xml:"id"`
Data string `xml:"data"`
}
var d1, d2 data
var httpCode int
err := gout.POST(":8080/test.xml").SetXML(&d1).BindXML(&d2).Code(&httpCode).Do()
if err != nil || httpCode != 200{
fmt.Printf("send fail:%s\n", err)
}
form-data
- SetForm() 设置http body 为multipart/form-data格式数据
客户端发送multipart/form-data到服务端,curl用法等同go代码
curl -F mode=A -F text="good" -F voice=@./test.pcm -f voice2=@./test2.pcm url- 使用gout.H
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
code := 0
err := gout.
POST(":8080/test").
// 打开debug模式
Debug(true).
SetForm(
gout.H{
"mode": "A",
"text": "good",
// 从文件里面打开
"voice": gout.FormFile("test.pcm"),
"voice2": gout.FormMem("pcm"),
},
).
//解析http code,如不关心可以不设置
Code(&code).
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%s\n", err)
}
if code != 200 {
}
}
/*
> POST /test HTTP/1.1
> Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=2b0685e5b98e540f80b247d5e7c1283807aa07e62b827543859a6db765a8
>
--2b0685e5b98e540f80b247d5e7c1283807aa07e62b827543859a6db765a8
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="mode"
A
--2b0685e5b98e540f80b247d5e7c1283807aa07e62b827543859a6db765a8
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="text"
good
--2b0685e5b98e540f80b247d5e7c1283807aa07e62b827543859a6db765a8
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="voice"; filename="voice"
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
pcm pcm pcm
--2b0685e5b98e540f80b247d5e7c1283807aa07e62b827543859a6db765a8
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="voice2"; filename="voice2"
Content-Type: application/octet-stream
pcm
--2b0685e5b98e540f80b247d5e7c1283807aa07e62b827543859a6db765a8--
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Server: gurl-server
< Content-Length: 0
*/
- 使用结构体
type testForm struct {
Mode string `form:"mode"`
Text string `form:"text"`
Voice string `form:"voice" form-file:"true"` //从文件中读取
Voice2 []byte `form:"voice2" form-file:"mem"` //从内存中构造
}
type rsp struct{
ErrMsg string `json:"errmsg"`
ErrCode int `json:"errcode"`
}
t := testForm{}
r := rsp{}
code := 0
err := gout.POST(url).SetForm(&t).ShoudBindJSON(&r).Code(&code).Do()
if err != nil {
}x-www-form-urlencoded
- 使用SetWWWForm函数实现发送x-www-form-urlencoded类型数据
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
code := 0
err := gout.
POST(":8080/post").
// 打开debug模式
Debug(true).
// 设置x-www-form-urlencoded数据
SetWWWForm(
gout.H{
"int": 3,
"float64": 3.14,
"string": "test-www-Form",
},
).
// 关心http code 返回值设置
Code(&code).
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%s\n", err)
return
}
if code != 200 {
}
}
/*
> POST /post HTTP/1.1
> Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
>
float64=3.14&int=3&string=test-www-Form
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Length: 0
< Server: gurl-server
*/
protobuf
SetProtoBuf支持,protobuf序列化后的[]byte,或者生成的protobuf结构体指针
package main
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
httpCode := 0
err := GET(":8080/echo").
SetProtoBuf( /* protobuf 生成的结构体,必须传指针类型*/ ).
Code(&httpCode).
Do()
}callback
callback主要用在,服务端会返回多种格式body的场景, 比如404返回的是html, 200返回json。 这时候要用Callback挂载多种处理函数,处理不同的数据结构
func main() {
r, str404 := Result{}, ""
code := 0
err := gout.GET(":8080").Callback(func(c *gout.Context) (err error) {
switch c.Code {
case 200: //http code为200时,服务端返回的是json 结构
c.BindJSON(&r)
case 404: //http code为404时,服务端返回是html 字符串
c.BindBody(&str404)
}
code = c.Code
return nil
}).Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %s\n", err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("http code = %d, str404(%s) or json result(%v)\n", code, str404, r)
}
get .Response
func main() {
resp, err := gout.GET(":8080").SetJSON(`{"test":"value"}`).Response()
if resp != nil {
defer resp.Body.Close()
}
}
multiple binding functions
支持绑定多个对象, BindXXX函数可以多次调用。例子里面是BindJSON和BindBody
var responseStruct struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Age int `json:"age"`
}
func main() {
var responseStr string
err := gout.GET("url").
SetQuery(gout.H{}).
BindJSON(&responseStruct).
BindBody(&responseStr).
Do()
if err != nil {
return
}
log.Println(responseStr)
}
Auto decode body
响应头里面指明压缩格式,使用AutoDecodeBody接口可以自动解压。
//Content-Encoding: gzip
//Content-Encoding: deflate
//Content-Encoding: br
//gzip由标准库原生支持,不需要使用AutoDecodeBody接口,后两种由gout支持.
func main() {
gout.GET(url).AutoDecodeBody().BindBody(&s).Do()
}Set request timeout
setimeout是request级别的超时方案。相比http.Client级别,更灵活。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"time"
)
func main() {
err := gout.GET(":8080").
SetTimeout(2 * time.Second).
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
}
proxy
- SetProxy 设置代理服务地址
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"log"
)
func main() {
c := &http.Client{}
s := ""
err := gout.
New(c).
GET("www.qq.com").
// 设置proxy服务地址
SetProxy("http://127.0.0.1:7000").
// 绑定返回数据到s里面
BindBody(&s).
Do()
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println(s)
}
socks5
- SetSOCKS5 设置socks5地址
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
c := &http.Client{}
s := ""
err := gout.
New(c).
GET("www.qq.com").
// 设置proxy服务地址
SetSOCKS5("127.0.0.1:7000").
// 绑定返回数据到s里面
BindBody(&s).
Do()
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println(s)
}cookie
- SetCookies设置cookie, 可以设置一个或者多个cookie
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
// === 发送多个cookie ====
err := gout.
// :8080/cookie是http://127.0.0.1:8080/cookie的简写
GET(":8080/cookie").
//设置debug模式
Debug(true).
SetCookies(
//设置cookie1
&http.Cookie{
Name: "test1",
Value: "test1",
},
//设置cookie2
&http.Cookie{
Name: "test2",
Value: "test2",
},
).
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// === 发送一个cookie ===
err = gout.
// :8080/cookie/one是http://127.0.0.1:8080/cookie/one的简写
GET(":8080/cookie/one").
//设置debug模式
Debug(true).
SetCookies(
//设置cookie1
&http.Cookie{
Name: "test3",
Value: "test3",
},
).
Do()
fmt.Println(err)
}
basic auth
使用SetBasicAuth接口
func main() {
err := gout.POST(":8080/colorjson").
SetBasicAuth("userName", "password").
SetJSON(gout.H{"str": "foo",
"num": 100,
"bool": false,
"null": nil,
"array": gout.A{"foo", "bar", "baz"},
"obj": gout.H{"a": 1, "b": 2},
}).Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
}context
- WithContext设置context,可以取消http请求
Cancel a sending request
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"time"
)
func main() {
// 声明一个context
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
//调用cancel可取消http请求
go func() {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
cancel()
}()
err := gout.
GET("127.0.0.1:8080/cancel"). //设置GET请求以及需要访问的url
WithContext(ctx). //设置context, 外层调用cancel函数就可取消这个http请求
Do()
if err != nil {
}
}
unix socket
- UnixSocket可以把http底层通信链路由tcp修改为unix domain socket
下面的例子,会通过domain socket发送http GET请求,http body的内容是hello world
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
c := http.Client{}
g := gout.
New(&c).
UnixSocket("/tmp/test.socket") //设置unixsocket文件位置
err := g.
GET("http://a/test"). //设置GET请求
SetBody("hello world"). //设置body内容
Do()
fmt.Println(err)
}http2 doc
go 使用https访问http2的服务会自动启用http2协议,这里不需要任何特殊处理
- https://http2.golang.org/ (bradfitz建的http2测试网址,里面大约有十来个测试地址,下面的例子选了一个)
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
s := ""
err := gout.
GET("https://http2.golang.org/reqinfo"). //设置GET请求和请求url
Debug(true). //打开debug模式,可以看到请求数据和响应数据
SetBody("hello, ###########"). //设置请求body的内容,如果你的请求内容是json格式,需要使用SetJSON函数
BindBody(&s). //解析响应body内容
Do() //结束函数
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("send fail:%s\n", err)
}
_ = s
}
debug mode
Turn on debug mode
该模式主要方便调试用的,默认开启颜色高亮(如果要关闭颜色高亮,请往下看)
func main() {
err := gout.POST(":8080/colorjson").
Debug(true). //打开debug模式
SetJSON(gout.H{"str": "foo",
"num": 100,
"bool": false,
"null": nil,
"array": gout.A{"foo", "bar", "baz"},
"obj": gout.H{"a": 1, "b": 2},
}).Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
}Turn off color highlighting in debug mode
使用debug.NoColor()传入Debug函数关闭颜色高亮
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout/debug"
)
func main() {
err := gout.POST(":8080/colorjson").
Debug(debug.NoColor()).
SetJSON(gout.H{"str": "foo",
"num": 100,
"bool": false,
"null": nil,
"array": gout.A{"foo", "bar", "baz"},
"obj": gout.H{"a": 1, "b": 2},
}).Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
}
Custom debug mode
debug 自定义模式,可传递函数。下面演示用环境变量开启debug模式(只有传递IOS_DEBUG环境变量才输出日志)
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout/debug"
"os"
)
func IOSDebug() debug.Apply {
return gout.DebugFunc(func(o *debug.Options) {
if len(os.Getenv("IOS_DEBUG")) > 0 {
o.Debug = true
}
})
}
func main() {
s := ""
err := gout.
GET("127.0.0.1:8080").
// Debug可以支持自定义方法
// 可以实现设置某个环境变量才输出debug信息
// 或者debug信息保存到文件里面,可以看下_example/15-debug-save-file.go
Debug(IOSDebug()).
SetBody("test hello").
BindBody(&s).
Do()
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
// env IOS_DEBUG=true go run customize.gotrace info
debug.Trace()可输出http各个阶段的耗时,比如dns lookup时间,tcp连接时间等等。可以很方便的做些性能调优。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout/debug"
)
func openDebugTrace() {
err := gout.POST(":8080/colorjson").
Debug(debug.Trace()).
SetJSON(gout.H{"str": "foo",
"num": 100,
"bool": false,
"null": nil,
"array": gout.A{"foo", "bar", "baz"},
"obj": gout.H{"a": 1, "b": 2},
}).Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
}
- output
=================== Trace Info(S): ===================
DnsDuration : 0s
ConnDuration : 868.623µs
TLSDuration : 0s
RequestDuration : 376.712µs
WaitResponeDuration : 717.008µs
ResponseDuration : 76.158µs
TotalDuration : 2.13921ms
=================== Trace Info(E): ===================save to writer
debug.ToWriter可以传递任何io.Writer对象,比如bytes.Buffer, 文件等。。。
package main
import (
"bytes"
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout/debug"
)
func main() {
var buf bytes.Buffer
err := gout.POST(":8080/colorjson").
Debug(debug.ToWriter(&buf, false)).
SetJSON(gout.H{"str": "foo",
"num": 100,
"bool": false,
"null": nil,
"array": gout.A{"foo", "bar", "baz"},
"obj": gout.H{"a": 1, "b": 2},
}).Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
fmt.Println(buf.String())
}
save to file
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout/debug"
)
func main() {
err := gout.POST(":8080/colorjson").
Debug(debug.ToFile("./req.txt", false)).
SetJSON(gout.H{"str": "foo",
"num": 100,
"bool": false,
"null": nil,
"array": gout.A{"foo", "bar", "baz"},
"obj": gout.H{"a": 1, "b": 2},
}).Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
}extracting trace information
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout/debug"
)
func main() {
var buf bytes.Buffer
err := gout.POST(":8080/colorjson").
Debug(debug.TraceJSONToWriter(&buf)).
SetJSON(gout.H{"str": "foo",
"num": 100,
"bool": false,
"null": nil,
"array": gout.A{"foo", "bar", "baz"},
"obj": gout.H{"a": 1, "b": 2},
}).Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
fmt.Printf("%s", buf.String())
}
benchmark
benchmarking a certain number of times
下面的例子,起了20并发。对:8080端口的服务,发送3000次请求进行压测,内容为json结构
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
const (
benchNumber = 30000
benchConcurrent = 20
)
func main() {
err := gout.
POST(":8080"). //压测本地8080端口
SetJSON(gout.H{"hello": "world"}). //设置请求body内容
Filter(). //打开过滤器
Bench(). //选择bench功能
Concurrent(benchConcurrent). //并发数
Number(benchNumber). //压测次数
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%v\n", err)
}
}
benchmark-duration
下面的例子,起了20并发。对:8080端口的服务,压测持续时间为10s,内容为json结构
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"time"
)
const (
benchTime = 10 * time.Second
benchConcurrent = 30
)
func main() {
err := gout.
POST(":8080"). //压测本机8080端口
SetJSON(gout.H{"hello": "world"}). //设置请求body内容
Filter(). //打开过滤器
Bench(). //选择bench功能
Concurrent(benchConcurrent). //并发数
Durations(benchTime). //压测时间
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%v\n", err)
}
}
benchmark-rate
下面的例子,起了20并发。对:8080端口的服务,压测总次数为3000次,其中每秒发送1000次。内容为json结构
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
const (
benchNumber = 3000
benchConcurrent = 20
)
func main() {
err := gout.
POST(":8080"). //压测本机8080端口
SetJSON(gout.H{"hello": "world"}). //设置请求body内容
Filter(). //打开过滤器
Bench(). //选择bench功能
Rate(1000). //每秒发1000请求
Concurrent(benchConcurrent). //并发数
Number(benchNumber). //压测次数
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("%v\n", err)
}
}
Custom benchmark functions
自定义压测函数,构造每次不一样的http request数据
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/google/uuid"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout/filter"
"sync/atomic"
)
func main() {
i := int32(0)
err := filter.NewBench().
Concurrent(30). //开30个go程
Number(30000). //压测30000次
Loop(func(c *gout.Context) error {
// 下面的代码,每次生成不一样的http body 用于压测
uid := uuid.New() //生成uuid
id := atomic.AddInt32(&i, 1) //生成id, 可以理解为++i,线程安全版本
c.POST(":1234").SetJSON(gout.H{"sid": uid.String(),
"appkey": fmt.Sprintf("ak:%d", id),
"text": fmt.Sprintf("test text :%d", id)})
return nil
}).Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
}
retry-backoff
retry 功能使用带抖动功能和指数回退的算法实现backoff
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"time"
)
func main() {
err := gout.HEAD("127.0.0.1:8080").
Debug(true). //打开debug模式
Filter(). //打开过滤器
Retry(). //打开重试模式
Attempt(5). //最多重试5次
WaitTime(500 * time.Millisecond). //基本等待时间
MaxWaitTime(3 * time.Second). //最长等待时间
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}
}
retry conditions httpcode
指定重试条件,这里面的例子是服务端返回的状态码是209进行重试 完整代码
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout/filter"
"time"
)
func useRetryFuncCode() {
s := ""
err := gout.GET(":8080/code").Debug(true).BindBody(&s).F().
Retry().Attempt(3).WaitTime(time.Millisecond * 10).MaxWaitTime(time.Millisecond * 50).
Func(func(c *gout.Context) error {
if c.Error != nil || c.Code == 209 {
return filter.ErrRetry
}
return nil
}).Do()
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}retry conditions backupurl
指定条件进行重试,这里的例子是默认url不能访问,使用backup url进行访问 完整代码
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout/core"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout/filter"
"time"
)
func useRetryFunc() {
// 获取一个没有服务绑定的端口
port := core.GetNoPortExists()
s := ""
err := gout.GET(":" + port).Debug(true).BindBody(&s).F().
Retry().Attempt(3).WaitTime(time.Millisecond * 10).MaxWaitTime(time.Millisecond * 50).
Func(func(c *gout.Context) error {
if c.Error != nil {
c.SetHost(":1234") //必须是存在的端口
return filter.ErrRetry
}
return nil
}).Do()
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n", err)
}import
send raw http request
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
s := `POST /colorjson HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:8080
User-Agent: Go-http-client/1.1
Content-Length: 97
Content-Type: application/json
Accept-Encoding: gzip
{"array":["foo","bar","baz"],"bool":false,"null":null,"num":100,"obj":{"a":1,"b":2},"str":"foo"}
`
err := gout.NewImport().RawText(s).Debug(true).SetHost(":1234").Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %s\n", err)
return
}
}
export
generate curl command
仅仅生成curl命令, 不会发送http请求
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
// 1.formdata
err := gout.GET(":1234").
SetForm(gout.A{"text", "good", "mode", "A", "voice", gout.FormFile("./t8.go")}).
Export().Curl().Do()
// output:
// curl -X GET -F "text=good" -F "mode=A" -F "voice=@./voice" "http://127.0.0.1:1234"
// 2.json body
err = gout.GET(":1234").
SetJSON(gout.H{"key1": "val1", "key2": "val2"}).
Export().Curl().Do()
// output:
// curl -X GET -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d "{\"key1\":\"val1\",\"key2\":\"val2\"}" "http://127.0.0.1:1234"
fmt.Printf("%v\n", err)
}
generate curl command and send HTTP request
生成curl命令, 同时执行http请求, 在Curl()命令之行跟上GenAndSend()接口
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
// 1.formdata
err := gout.GET(":1234").
SetForm(gout.A{"text", "good", "mode", "A", "voice", gout.FormFile("./t8.go")}).
Export().Curl().GenAndSend().Do()
// output:
// curl -X GET -F "text=good" -F "mode=A" -F "voice=@./voice" "http://127.0.0.1:1234"
// 2.json body
err = gout.GET(":1234").
SetJSON(gout.H{"key1": "val1", "key2": "val2"}).
Export().Curl().GenAndSend().Do()
// output:
// curl -X GET -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d "{\"key1\":\"val1\",\"key2\":\"val2\"}" "http://127.0.0.1:1234"
fmt.Printf("%v\n", err)
}Incoming custom *http.Client
使用New接口即可使用自己的http.Client对象
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
c := &http.Client{} //http.Client里面有fd连接池,如果对这块优化不是太了解,只使用一个实例就行
err := gout.New(c). // New接口可传入http.Client对象
GET("www.qq.com").
Debug(true).
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %s\n", err)
return
}
}
Using chunked data format
使用Chunked接口, 设置为"Transfer-Encoding: chunked"的数据编码方式
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
err := gout.POST(":8080").
Chunked().
SetBody("11111111111").
Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err :%v\n", err)
}
}
// 使用nc 起一个tcp服务, 使用上面的代码发起数据观察下结果
// nc -l 8080NewWithOpt
这里记录全局配置的方法, 后面所有的全局配置都推荐使用gout.NewWithOpt接口的实现
insecure skip verify
忽略ssl验证, 使用gout.WithInsecureSkipVerify()接口配置该功能, 传入gout.NewWithOpt接口即可生效.
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
// globalWithOpt里面包含连接池, 这是一个全局可复用的对象
globalWithOpt := gout.NewWithOpt(gout.WithInsecureSkipVerify())
err := globalWithOpt.GET("url").Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n" ,err)
return
}
}turn off 3xx status code automatic jump
golang client库默认遇到301的状态码会自动跳转重新发起新请求, 你希望关闭这种默认形为, 那就使用下面的功能
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
// globalWithOpt里面包含连接池, 这是一个全局可复用的对象, 一个进程里面可能只需创建1个
globalWithOpt := gout.NewWithOpt(gout.WithClose3xxJump())
err := globalWithOpt.GET("url").Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n" ,err)
return
}
}new with opt set timeout
gout.WithTimeout 为了让大家少用gout.SetTimeout而设计
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
// globalWithOpt里面包含连接池, 这是一个全局可复用的对象, 一个进程里面可能只需创建1个
globalWithOpt := gout.NewWithOpt(gout.WithTimeout())
err := globalWithOpt.GET("url").Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n" ,err)
return
}
}new with opt unix socket
gout.WithUnixSocket 为了让大家少用.UnixSocket而设计
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
// globalWithOpt里面包含连接池, 这是一个全局可复用的对象, 一个进程里面可能只需创建1个, 如果有多个不同的unixsocket,可以创建多个
globalWithOpt := gout.NewWithOpt(gout.WithUnixSocket("/tmp/test.socket"))
err := globalWithOpt.GET("url").Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n" ,err)
return
}
}new with opt proxy
gout.WithProxy 为了让大家少用.SetProxy而设计
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
// globalWithOpt里面包含连接池, 这是一个全局可复用的对象, 一个进程里面可能只需创建1个, 如果有多个不同的proxy,可以创建多个
globalWithOpt := gout.NewWithOpt(gout.WithProxy("http://127.0.0.1:7000"))
err := globalWithOpt.GET("url").Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n" ,err)
return
}
}new with opt socks5
gout.WithSocks5 为了让大家少用.SetSOCKS5而设计
import (
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
// globalWithOpt里面包含连接池, 这是一个全局可复用的对象, 一个进程里面可能只需创建1个, 如果有多个不同的socks5,可以创建多个
globalWithOpt := gout.NewWithOpt(gout.WithSocks5("127.0.0.1:7000"))
err := globalWithOpt.GET("url").Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err = %v\n" ,err)
return
}
}Global configuration
set timeout
设置全局超时时间。可以简化一些代码。在使用全局配置默认你已经了解它会带来的一些弊端.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
"time"
)
func main() {
gout.SetTimeout(time.Second * 1)
err := gout.GET("www.baidu.com").Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err is:%v\n")
}
}set debug
打开全局debug开关。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
func main() {
gout.SetDebug(true)
err := gout.GET(":8080/colorjson").Do()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("err is:%v\n")
}
}
Unique features
forward gin data
gout 设计之初就考虑到要和gin协同工作的可能性,下面展示如何方便地使用gout转发gin绑定的数据。
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/guonaihong/gout"
)
type testQuery struct {
Size int `query:"size" form:"size"` // query tag是gout设置查询字符串需要的
Page int `query:"page" form:"page"`
Ak string `query:"ak" form:"ak"`
}
//下一个服务节点
func nextSever() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/query", func(c *gin.Context) {
q := testQuery{}
err := c.ShouldBindQuery(&q)
if err != nil {
return
}
c.JSON(200, q)
})
r.Run(":1234")
}
func main() {
go nextSever()
r := gin.Default()
// 演示把gin绑定到的查询字符串转发到nextServer节点
r.GET("/query", func(c *gin.Context) {
q := testQuery{}
// 绑定查询字符串
err := c.ShouldBindQuery(&q)
if err != nil {
return
}
// 开发转发, 复用gin所用结构体变量q
code := 0 // http code
err := gout.
//发起GET请求
GET("127.0.0.1:1234/query").
//设置查询字符串
SetQuery(q).
//关心http server返回的状态码 设置该函数
Code(&code).
Do()
if err != nil || code != 200 { /* todo Need to handle errors here */
}
c.JSON(200, q)
})
r.Run()
}
// http client
// curl '127.0.0.1:8080/query?size=10&page=20&ak=test'FAQ
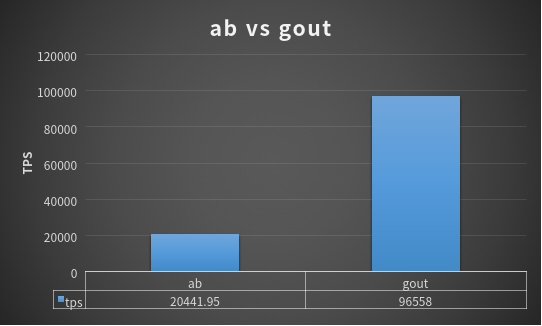
gout benchmark性能如何
下面是与apache ab的性能对比 _example/16d-benchmark-vs-ab.go