Jackline - a minimalistic secure XMPP client
This is unreleased software... feedback welcome!
You can read more about jackline (January 2017).
Jackline uses several clean-slate libraries (OCaml-TLS, OCaml-OTR) and only has a minimal few features: no support for HTML markup, avatars, which music you're playing, timezone you're living in, ...
Supported features:
- single XMPP account
- OTR (built-in and enabled by default)
- strict TLS certificate verification
- plain text (no HTML!)
- XEP-0184 (Message Delivery Receipts)
- no import of OTR keys or configuration
- no plaintext connections to XMPP server
I (so far successfully) try to preserve three core properties:
- any data written on disk (using lots of silly parens) by jackline will stay being readable by every future jackline version
- once the initial configuration file (and private key and maybe password) is created, it will never be written to by jackline
- jackline will never transmit any data or open a network connection unless initiated by you (this means no "autoconnect on startup", or "user is typing" indication sent). There is an automated reconnect to the same server if the connection terminated.
NB: jackline and
torsocks are
friends: torify jackline works.
Security and trusted code base
The configuration file has to include the trust anchor for the server certificate (or the SHA256 fingerprint of the certificate) - otherwise there is no way how to ensure talking to the correct XMPP server. There won't be any 'ignore ssl warnings' option.
The trusted code base contains at the moment:
- OCaml-OTR
- OCaml-TLS
- XMPP
- XML
- OCaml compiler (and its runtime)
- underlying UNIX system
Transitive dependencies are only partially listed. For a complete
list, use opam list --required-by=jackline --recursive.
Why should you trust this? Well, first of all whom do you trust? And why? Did you read through your kernel, libc and malloc implementation? What about OpenSSL? libotr? libpurple, loudmouth (or whatever XMPP implementation you use)? Programming language runtime?
OCaml is a game changer compared to C: automatic memory management; I try to stick to a purely functional (using immutable data and declarative) coding style (this code here is not there yet).
OPAM is the OCaml package manager, and not directly needed, but very convenient for installation and updating. It lacks package signing, but I've some work-in-progress.
Installing jackline
Be aware that this is unreleased software. Bug reports are welcome (pull requests as well).
Get OCaml (>= 4.08.0), get opam (>= 2.0.0),
gmp is required as well.
If you have an older OCaml compiler, run opam switch 4.08.1 and follow instructions.
Run the following commands:
- `opam repo add xmpp-opam git+https://github.com/hannesm/xmpp-opam.git
opam updateopam install jackline
A cryptographically signed package (using conex) is available, you have to follow the steps in the README.
Now you should have a ~/.opam/system/bin/jackline (or
~/.opam/4.08.1/bin/jackline), which should be in your PATH (if you
executed eval `opam config env`).
To update, simply run opam update followed by opam upgrade. This
will get you the latest version (git master).
Compiling using a git checkout
If you clone this repository, and install the required dependencies (see above), you can compile jackline by running
dune buildThis will produce _build/default/bin/jackline.exe.
Configuration
Read the jackline --help output:
-f configuration directory (defaults to ~/.config/ocaml-xmpp-client/)
-d debug log (either filename or out.txt)
-a ASCII only output
--fd-gui File descriptor to receive GUI focus updates on.
--fd-nfy File descriptor to send notification updates on.When you start jackline for the first time (or with an empty configuration directory), it starts an interactive configuration dialog asking about account details. There is no need to provide optional information. Hostname and which common name should appear in the certificate is derived from the jabber id.
The configuration file is stored as config.sexp in your configuration
directory. Next to it, there is a file containing your password (unless you
decided to enter it on every start of jackline), otr_dsa.sexp containing your
OTR key, a users directory with a file for each contact (OTR fingerprints,
custom OTR policies, ...), and a histories directory if you enable logging for
a specific contact (/log on).
Using jackline
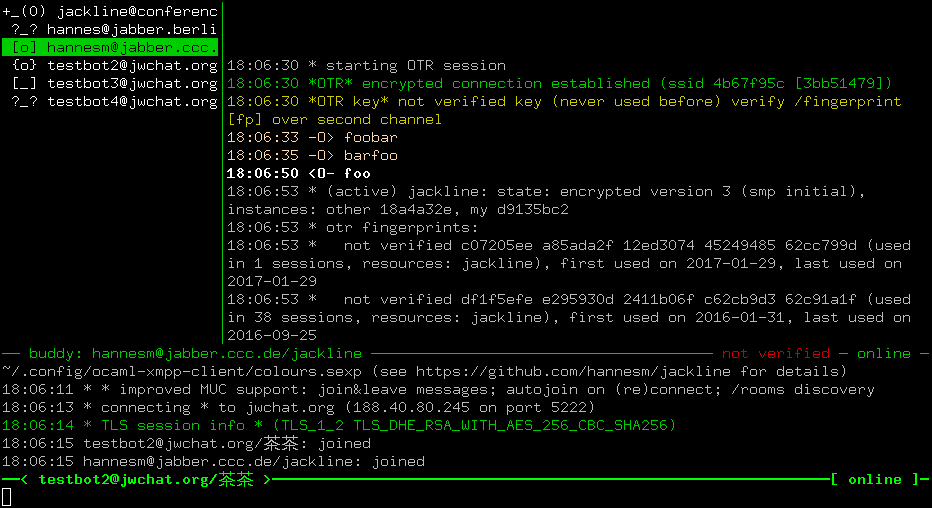
Left is the contact list, in the middle the chat window, below the log
buffer. F10 and F11 (and Shift + F10, Shift + F11) modify
their sizes. The bottom line is read-line prompt with tab-completion.
In the contact list, mutual presence subscription information is
indicated by [ and ] (F if contact is only subscribed to your
presence updates, T if you are subscribed to the presence updates of
the contact), ? for no presence subscription). The own contact uses
curly braces { and }, and certain operations are not available.
The presence is indicated by a single character (o = online, f = free,
a = away, d = do not disturb, x = extended away, _ = offline).
A single contact is active, which can be modified by PgUp/PdDown.
The active contact is shown in reversed foreground and background
colour. Its chat content is displayed in the chat window. Certain
commands and operations (such as sending a message) require an active
contact.
XMPP allows a contact to be logged in several times. By default, the
resource with the highest priority (and most online status) is used
for communication. If a contact is logged in multiple times, a +
occurs to its left side, and pressing return will expand the
contact, displaying all its sessions. Communicating with the
expanded base contact will deliver the message to the bare contact, if
a specific resource is active, messages will be sent there. The chat
log is filtered by messages to the specific resource, and merged in
the base contact. An unexpanded contact equals to the resource with
highest priority.
When a new message is received, this is indicated by blinking of the contact, a
prepended * (or ☀ in case of collapsed contact), a yellow ## in the bottom
left corner, execution of notification_callback, and a message to a file
descriptor (if --fd-nfy is used).
The most basic callback would be a script that emits a BEL and a terminal that
translates a bell to urgency (in your .Xdefaults, have the line
Xterm*vt100.bellsUrgent: true);
bell.sh:
if [ $3 != "connect" ]; then
printf '\a'
fiA message is sent to the active contact by typing it followed by
return.
In the chat window, each message is prefixed with 3 characters:
*- local<--- incoming unencrypted<O-- incoming OTR encrypted-->- outgoing unencrypted, delivered (XEP 184)?->- outgoing unencrypted, waiting for receipt (XEP 184)-O>- outgoing OTR encrypted, delivered (XEP 184)?O>- outgoing OTR encrypted, waiting for receipt (XEP 184)
Keybindings
PgUp,PgDownnavigates through the contact listUp,Downrotate through per-contact input historyLeft,Right,Home,Endnavigate in input lineCtrl-qjumps to next notificationCtrl-xjumps to last active userCtrl-ccycle to next crypto userF5toggles display of offline contactsF12toggles between display of contact list, full screen chat, and raw (only received messages)F11andShift-F11(orCtrl-F11) increases and decreases width of contact list (/buddywidth)F10andShift-F10(orCtrl-F10) increases and decreases height of log window (/logheight)Ctrl-PgUp(orCtrl-p),Ctrl-PgDown(orCtrl-n) scrolls chat window<tab>tab completion (largest prefix, suggestions are displayed in grey while typingx)Ctrl-a(jump to beginning of line),Ctrl-e(jump to end of line),Ctrl-k(kill text to the right of cursor),Ctrl-u(kill text to the left of cursor),Ctrl-left(jump word backwards),Ctrl-right(jump word forwards),Ctrl-f(forward one character),Ctrl-b(backward one character)Ctrl-space(mark, indicated by underline)Ctrl-w(cut),Ctrl-y(yank)Ctrl-_undo
/help prints the available commands, /help command more detailed help of the given command.
Colours
Colours are mainly used to indicate security properties: enabled end-to-end encryption (of the active contact) let's the frame turn green, disabled end-to-end encryption makes the frame red. Green is also used to indicate verified public keys, red for unverified ones.
A contact in the contact list is green if there is an active end-to-end encrypted session, red if not and the contact is online, black if the contact is offline or a groupchat. Inverse highlights the active contact, and if the buddy name in the status bar is inverted, logging is turned on.
Default colours are:
- Chat "empty"
- GroupChat "empty"
- Transit "gray 18"
- Presence "gray 12"
- Info "gray 18"
- Warning "yellow"
- Error "red"
- Success "green"
To draw all presence messages in cyan instead of gray, create a
colours.sexp in your config folder with the contents:
((Presence "cyan"))Available colours (notty documentation):
- empty,
- black, red, green, yellow, blue, magenta, cyan, white,
- lightblack, lightred, lightgreen, lightyellow, lightblue, lightmagenta, lightcyan, lightwhite,
- gray n (where
n >= 0 && n <= 23, - rgb r g b (where
r >= 0 && r <= 5 && g >= 0 && g <= 5 && b >= 0 && b <= 5)
FAQ
- How do I update the fingerprint of the server certificate (getting authentication failure messages)? -- Currently you have to edit
config.sexp: find the(Fingerprint XXX)data, and replace XXX with the new fingerprint (openssl s_client -connect SERVER:5222 -starttls xmpp | openssl x509 -fingerprint -sha256 -nooutmight be useful (or tlsclient usingtlsclient --starttls xmpp -z SERVER:5222). - How do I prevent jackline from doing DNS lookups? -- Interactive configuration or specify
(hostname ("146.255.57.229"))inconfig.sexp. - The server certificate does not match the server name, how do I fix this? -- Interactive configuration or specify
(cert_hostname ("blabla.com"))inconfig.sexp. - I hate the default colours. -- they're now customisable
- Keys do not work on MacOSX -- This might be useful.
- I want to receive notifications. -- A hook script can be defined during interactive configuration or
(notification_callback (/my/favorite/script.sh))inconfig.sexp. It is executed with three (or four) arguments: the local user's jabber id, a summary of the state of jackline, the event type that caused this execution, and perhaps other things; seecli/cli_state.mlsearch formodule Notifyfor details. - I want a systray icon. -- there are several projects, posiputt/jackification, cfcs/misc, jackline-gtk
- I want to have notifications on MacOSX. - Andrej wrote a script using terminal notifier; otherwise this guide might help.
- Support? -- join us at jackline@conference.jabber.ccc.de
- The interface is inspired by mcabber
- The installation failed on OpenBSD - try with a larger stack size:
ulimit -s 8192should be good - How do I increase the multi-user chat history? - insert
(muc_max_stanzas (500))in yourconfig.sexp(where 500 is the amount of messages to request from the server)