HitchStory
Type-safe StrictYAML python integration testing framework. With this framework, your tests can:
Rewrite themselves from program output (command line test example)
Autogenerate documentation (website test example)
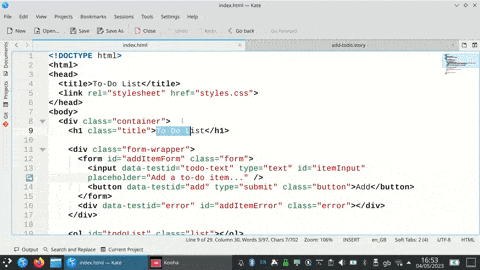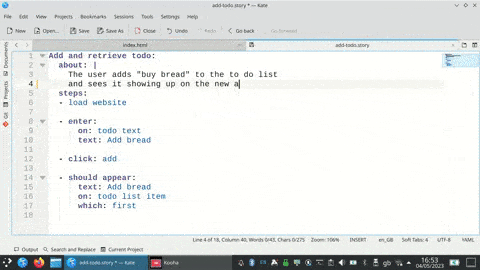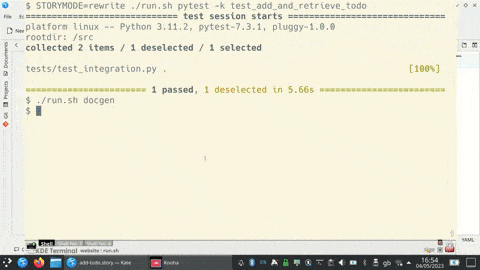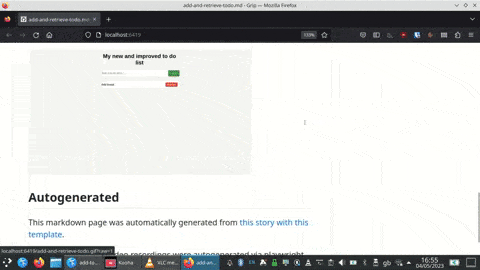
The tests can be run on their own or as pytest tests.
Demo projects with demo tests
| Project | Storytests | Python code | Doc template | Autogenerated docs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Website | add todo, correct spelling | engine.py | docstory.yml | Add todo, Correct my spelling |
| REST API | add todo, correct spelling | engine.py | docstory.yml | Add todo, Correct my spelling |
| Interactive command line app | add todo, correct spelling | test_integration.py | docstory.yml | Add todo, Correct my spelling |
| A Python API | add todo, correct spelling | test_integration.py | docstory.yml | Add todo, Correct my spelling |
Code Example
example.story:
Logged in:
given:
website: /login # preconditions
steps:
- Form filled:
username: AzureDiamond
password: hunter2
- Clicked: login
Email sent:
about: |
The most basic email with no subject, cc or bcc
set.
based on: logged in # inherits from and continues from test above
following steps:
- Clicked: new email
- Form filled:
to: Cthon98@aol.com
contents: | # long form text
Hey guys,
I think I got hacked!
- Clicked: send email
- Email was sentengine.py:
from hitchstory import BaseEngine, GivenDefinition, GivenProperty
from hitchstory import Failure, strings_match
from strictyaml import Str
class Engine(BaseEngine):
given_definition = GivenDefinition(
website=GivenProperty(Str()),
)
def __init__(self, rewrite=False):
self._rewrite = rewrite
def set_up(self):
print(f"Load web page at {self.given['website']}")
def form_filled(self, **textboxes):
for name, contents in sorted(textboxes.items()):
print(f"Put {contents} in name")
def clicked(self, name):
print(f"Click on {name}")
def failing_step(self):
raise Failure("This was not supposed to happen")
def error_message_displayed(self, expected_message):
"""Demonstrates steps that can rewrite themselves."""
actual_message = "error message!"
try:
strings_match(expected_message, actual_message)
except Failure:
if self._rewrite:
self.current_step.rewrite("expected_message").to(actual_message)
else:
raise
def email_was_sent(self):
print("Check email was sent!")>>> from hitchstory import StoryCollection
>>> from pathlib import Path
>>> from engine import Engine
>>>
>>> StoryCollection(Path(".").glob("*.story"), Engine()).named("Email sent").play()
RUNNING Email sent in /path/to/working/example.story ... Load web page at /login
Put hunter2 in name
Put AzureDiamond in name
Click on login
Click on new email
Put Hey guys,
I think I got hacked!
in name
Put Cthon98@aol.com in name
Click on send email
Check email was sent!
SUCCESS in 0.1 seconds.Install
$ pip install hitchstoryCommunity
Help is available if you ask questions in these places: Github discussions | Github issues (not just for bugs) | Slack channel
Using HitchStory
Every feature of this library is documented and listed below. It is tested and documented with itself.
Using HitchStory: With Pytest
If you already have pytest set up, you can quickly and easily write a test using hitchstory that runs alongside your other pytest tests:
Using HitchStory: Engine
How to use the different features of the story engine:
- Hiding stacktraces for expected exceptions
- Given preconditions
- Gradual typing of story steps
- Match two JSON snippets
- Match two strings and show diff on failure
- Extra story metadata - e.g. adding JIRA ticket numbers to stories
- Story with parameters
- Story that rewrites given preconditions
- Story that rewrites itself
- Story that rewrites the sub key of an argument
- Raising a Failure exception to conceal the stacktrace
- Arguments to steps
- Strong typing
Using HitchStory: Documentation Generation
How to autogenerate documentation from your tests:
Using HitchStory: Inheritance
Inheriting stories from each other:
- Inherit one story from another simply
- Story inheritance - given mapping preconditions overridden
- Story inheritance - override given scalar preconditions
- Story inheritance - parameters
- Story inheritance - steps
- Variations
Using HitchStory: Runner
Running the stories in different ways:
- Continue on failure when playing multiple stories
- Flaky story detection
- Play multiple stories in sequence
- Run one story in collection
- Shortcut lookup for story names
Approach to using HitchStory
Best practices, how the tool was meant to be used, etc.
- Is HitchStory a BDD tool? How do I do BDD with hitchstory?
- Complementary tools
- Domain Appropriate Scenario Language (DASL)
- Executable specifications
- Flaky Tests
- The Hermetic End to End Testing Pattern
- ANTIPATTERN - Analysts writing stories for the developer
- Separation of Test Concerns
- Snapshot Test Driven Development (STDD)
- Test Artefact Environment Isolation
- Test concern leakage
- Tests as an investment
- What is the difference betweeen a test and a story?
- The importance of test realism
- Testing non-deterministic code
- Specification Documentation Test Triality
Design decisions and principles
Design decisions are justified here:
- Declarative User Stories
- Why does hitchstory mandate the use of given but not when and then?
- Why is inheritance a feature of hitchstory stories?
- Why does hitchstory not have an opinion on what counts as interesting to "the business"?
- Why does hitchstory not have a command line interface?
- Principles
- Why does HitchStory have no CLI runner - only a pure python API?
- Why Rewritable Test Driven Development (RTDD)?
- Why does HitchStory use StrictYAML?
Why not X instead?
HitchStory is not the only integration testing framework. This is how it compares with the others:
- Why use Hitchstory instead of Behave, Lettuce or Cucumber (Gherkin)?
- Why not use the Robot Framework?
- Why use hitchstory instead of a unit testing framework?
Using HitchStory: Setup on its own
If you want to use HitchStory without pytest:
Using HitchStory: Behavior
Miscellaneous docs about behavior of the framework: